File
advertisement

WORLD GEOGRAPHYCHAPTER 5 NOTES
Climatic regions of an area are set apart from other climatic regions by a set
of characteristics:
temperature range
precipitation levels
patterns of sunniness or cloudiness
wind conditions
length of each season
the way its seasons vary
If you were given the characteristics of these regions would you be able to
place yourself in a particular region.
For Example, similar climatic features place Newfoundland and Central Russia
in the same climatic region.
Other areas with similar climates
Western California and New Zealand
Southern Florida and Vietnam
Brazil and Nigeria
Bolivia and Madagascar
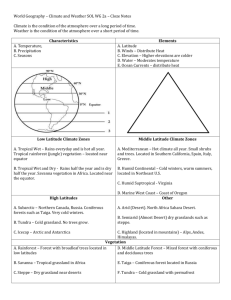
Climatologists have recognized six general climatic regions of the Earth.
Each region may be divided into two or three subregions. See fig. 5.2/page 75.
Tropical Climates
Dry Climates
Temperate Mild Winter Climates
Temperate Cold Winter Climates
Polar Climates
Highlands Climate (Mountains)
Climograph:
Temperature is plotted as a line graph joining the twelve months of the year
Precipitation is shown as a series of bars, one for each month.
Reading a Climograph See Fig. 5.2/page 76
Temperature for these Climographs vary from region to region.
Temperature can range widely from high to low for the same area.
Precipitation can vary from region to region.
It can be constant for all year (high, low, moderate)
It can range widely between dry and wet conditions for a year. (Monsoons)
See Fig. 5.3/page 76: Some general terms used to describe climate
Term
Description
Tropical
Monthly temperatures always above 18 degrees Celsius
Seasonal
There is a wide range between summer and winter temperatures.
Monsoonal
There are two yearly seasons: extremely dry and extremely wet.
Dry
Total precipitations is less than 500 mm
Cold Winter
Temperature in coldest month is below - 3 degrees Celsius.
Mild Winter
Temperature in coldest month is above -3 degrees Celsius.
Hot Summer
Temperature in warmest month is above 22 degrees Celsius.
Mild Summer
Temperature in warmest month is below 22 degrees Celsius.
Moderate
Precipitation
Amount of precipitation each month falls in a narrow range
above 60 mm.
Earth’s Climatic Regions
Tropical Climates
Temperature:
Several areas of the world experiences warm to hot temperatures of over 18
degrees Celsius every day of the year
These areas exist near the equator or between the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of
Capricorn
High temperatures of high latitude tropical areas are maintained by warm ocean
currents and trade winds
These factors affect east coast areas as opposed to west coast areas
{“Think Northeast Trade Winds”}
Precipitation:
Two patterns of precipitation : Tropical Wet; Tropical Wet and Dry
Tropical Wet
heavy rainfall all year
temperature is high every day (high twenties)
thunderstorm or rain storm almost every day [afternoon]
weather is virtually the same each day
however it is not the hottest region on earth
with heavy precipitation you receive almost constant cloud cover
clouds will reduce solar radiation reaching the Earth’s Surface
radiant energy... from the earth... back to space is also... reduced
(Greenhouse Effect???)
this makes for high night time temperatures
air retains much moisture.....thus making it very humid
Tropical Wet and Dry
rain is heavy for several months.......slight during others
this region experiences... what we commonly refer to as... seasons
Summers are hot and wet
Winters are hot and dry.
Seasons exist in this region because it is farther from the equator than the wet
tropical subregion
This region is affected by the shift in the pressure cells and the prevailing winds as
a result of the tilt of the earth’s axis
Southeast Asia experiences the extreme conditions or a monsoonal climate
The Himalayan mountains and the Indian Ocean are key factors in this type of
climate
In winter the Northeast cool air descending from the Himalayas, expands, warms
(temperature rises) and humidity drops This results in very dry conditions.
In summer prevailing winds from the Southwest, are blowing off cooler waters of
the Indian Ocean The cool air moves toward hot rising air over the land resulting in
almost continuous rainfall
Dry Climates
These areas have extremely small amounts of precipitation. More water is
evaporated than falls
resulting in rivers unable to form, sparse vegetation and high winds
Two subregions : Arid or Desert ; Semi-arid, or steppe
Arid or Desert (sub region)
Found at latitudes 10 to 30 degrees (North and South).
Particularly on the west coast ....Leeward side of mountains
Deserts near the equator have high daytime temperatures and low night time
temperatures (absent of cloud cover). Examples are:
Sahara and Kalahari deserts in Africa
Arabian desert in Asia
Great Australian Desert in Australia
Mexican Desert also called the Chihuahuan desert in Mexico
Deserts on the west coast of continents do not have drastic changes in
temperature. They receive the influence of cold ocean currents. For Example,
Atacama desert in Chile
Kalahari desert and Namib deserts in Southwest Africa
Mojave desert found in the states of California Nevada, Arizona, and Utah
Sahara found in Northwest Africa
Great Australian Desert, Victoria, Gibson, Great Sandy Deserts, all found in
Australia
Deserts on the leeward or rainshadow sides of mountains. These are cold deserts
with lower temperatures than tropical deserts. Examples include;
Badlands in Alberta
American Great Plains on the U.S. West Coast
Gobi Desert in Central Asia
Patagonian desert in Argentina
Semi-Arid, or Steppe
Steppe is a transitional zone between Tropical wet and dry region and the
almost completely dry desert region.
Steppe has a high daytime but low night time temperature all year long.
Like the Tropical wet and dry it is affected by the shifting pressure belts and wind
systems
It receives moderate amounts of precipitation during summer. The Steppe receives
enough rain in the middle latitude areas to support grassland vegetation.