Selection of rotations with model measuring
advertisement

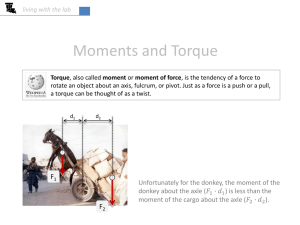
Case # (was this your first case or ??) Case type: class __ dental and skeletal with protrusion and excess anterior overjet Age __ Male/Female Transition to IP @ 6 months Your Name, practice location, POS OC#17 Initial Records __ year old Chinese Male presented with the chief complaint of _________. Start Panoramic x-ray Start Cephalometric x-ray: (to do this page, print the dentalcad tracing, then scan into adobe photoshop, label, then “insertimage-from file” in MS Word, resize the photo) Start Model Measuring (to do this, print model measuring from dentalcad, then scan, name, “insert-image” from file in Microsoft word, resize photo) Treatment Decision A discussion of your treatment decision, what else you considered, and reasoning….. For example: Non-Extraction was the initial diagnosis, which would have NOT solved the chief complaint of this patient, who was complaining of protrusion (with straight teeth). The patient had already gone through non-extraction orthodontics previously. I consider this retreatment diagnosis as a missed diagnosis. In the past, a change in diagnosis to bicuspid extraction would have been made. Instead, the upper incisor brackets were changed to Labial root torque brackets, and 21x25N was engaged and retied for the next 6 months to test the ability to do more cases non-extraction. IP Appliance Design Say something about incisor torque, cuspid torque, molar buccal tubes, archwires, rotations, positioning that you used for this case (and maybe what you did not use). For example: Single patient standard Roth IP Appliance was used for this case. At 6 months, a change to Labial root torque brackets was made to reduce the upper incisor proclination and associated “overjet” felt by the patient. There was also a change to mesial rotation brackets on 14M and 25M. Other rotation brackets could have been used, but were not diagnosed using the “manual” method (no software and no model measuring). Ovoid non-extraction #1 (expanded) archwires were applied for the first 6 months. At 6 months, the lower archwire was changed to Ovoid non-extraction #2, the archform to maintain the original shape and size. In the upper arch, 21x25N is not available in the IP Shapes and sizes, so this was ovoid non-extraction #1 for the entire treatment. Changes in the incisor torque would be due to the bracket-archwire interface. There is no difference in the anterior expansion 3-3 between these archwires. The upper posterior constriction did not cause a posterior crossbite. This is the overlay of the upper non-extraction #1 and #2 archwires. Selection of rotations with model measuring More rotation brackets would have been selected had model measuring been available at the time of treatment. This would have led to less under-corrections on the final result. Rotations by this method are: 35M, 33D,41D,43D,44M in the lower arch, and 15M,14M,13D,11M,21D,22M,24M, 25M in the upper arch. Results Alignment and wire progression to rectangular wires consumed the first 14 months due to the severe upper left second bicuspid (25) rotation. This was followed by some lower arch finishing (only step bends to compensate for height bracket error). There were NO finishing bends made in the upper arch. Several rotations were not fully corrected due to a) combination labial root torque and rotation brackets were not available at the time of treatment and b) 21x25N is too stiff an archwire to deflect fully into the bracket slots. A better archwire would have been 18x25N heat activated. The case was debanded at 20 months. 13 months photos [Not required, but if you have progress photos or models or xrays that are significant to the case understanding, please include] The reason for extraction, the protruded upper incisor with the feeling of excess overjet was now corrected after 6 months of 21x25N and labial root torque brackets. 13 Months Cephalometric x-ray Skeletal overlay: start vs. 13 months [Skeletal, dental overlays are completed on your “finished” case and possibly different stages of treatment. Comments on what these show is added. Scan, same, insert-image-from file, resize.] The mandible rotated down and back, avoiding the protrusive interference resulting from detorquing and extrusion of the upper incisor. This also increased the class II dental seen on the lateral views. Dental Overlays: start vs. 13 months (6 months of 21x25N in Labial root torque brackets) There was NOT a loss of molar anchorage due to the added labial root torque applied to the upper incisors. The increase in class II dental was due to mandibular rotation, an avoidance response to the incisive protrusive interference. After the root contacted the labial cortical plate, the crown had to move palatal as a result of the torquing applied through the archwire and bracket. 10 degrees of change in the upper incisor inclination is NOT seen with the previous straight wire appliances. Comparison of Labial Cortex close-up: start vs. 13mo Final Records Comparison of the study models: Final vs. start The archforms were maintained. The severe upper bicuspid rotations were not fully corrected. Final Panoramic x-ray Final Cephalometric x-ray Skeletal overlay: 13 months vs. final Some counterclockwise rotation of the mandible took place in the last year of treatment, a recovery of the clockwise rotation seen in the first year. Dental overlays: 13 months vs. final Upper incisor labial root torque was complete after 6 months of rectangular nickeltitanium wires, with no further detorquing noted in the last year. Skeletal overlay: Start vs. final The mandibular rotation seen in the first year did not fully recover in the second year. Dental overlays: start vs. final There was a change of 11 degrees of labial root torque as a result of the full size nickel-titanium archwire engaged into the Labial root torque bracket. There is an additional 10 degrees of labial root torque (+2 degrees) in the La bracket relative to the standard Roth (+12 degrees) on the central incisor prescription. The crown of the tooth moved lingual after the root could no longer move forward as a result of contacting the labial cortical plate.