Chapter 7 Reading Guide
advertisement

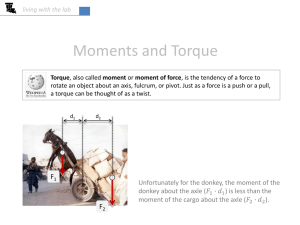
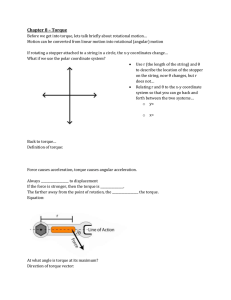
Reading Guide Chapter 7 – Rotational Motion 7.1 The rotation of a Rigid Body 1. A rigid body is an object whose __________________ and __________________ do not change 2. The three basic types of motion of a rigid body are: 3. Why does every point on a rotating body have the same angular velocity? 4. What is the formula that relates linear velocity to angular velocity? 5. So two points of a rotating object will have different _____________ if they have different _____________ from the axis of rotation, but all points have the same ________________________ 6. What is the formula and units for angular acceleration? 7. List the corresponding angular formula for the following linear formulas 𝑑 V= 𝑡 _______________ d = vit + ½ at2 a= 𝑣𝑓−𝑣𝑖 𝑡 8. What is the relationship between the tangential and angular acceleration Do Stop to think 7.1 7.2 Torque 9. What three things does a force depend on to cause a rotation or a twisting motion? 10. What is torque the equivalent of? 11. Define radial line 12. Forces that are parallel to the radial line has ________ effect on the wrench’s rotation, and thus contributes _________________ to the torque 13. Only forces that are perpendicular ___________ to cause rotation 14. The formula for torque is _____________ 15. How does the formula change if the force is directed at an angle? 16. How is torque different from force? 17. Torques are calculated about a ______________, ____________ or _______________ 18. What is the moment arm? 19. When is torque positive? When is it negative? Do stop to think 7.2 Net Torque 20. How is net torque determined? Do stop to think 7.3 7.3 Gravitational Torque and the center of gravity 21. How can the center of gravity be found? 22. Find the tactics box for calculating the center of gravity and write down the four steps Do stop to think 7.4 7.4 Rotational Dynamics and Moment of Inertia 23. What does torque do? 24. How can the moment of inertia be determined for a collection of particles? 25. Newton’s second law can be rewritten for rotation. State Newton’s 2nd law for rotation 26. What happens to an object when net torque is zero? 27. Give the rotational variable that corresponds to the following linear variables Fnet m A Fnet=ma Do stop to think 7.5 7.6 Rolling Motion 28. Rolling Motion combines two motions – what are they? 29. What point on a rolling object is instantaneously always at rest? ______________ 30. What is meant by rolling without slipping? Do stop to think 7.6