Noun Functions
advertisement

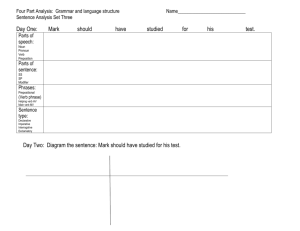
Noun Functions Following are the steps for finding the six noun functions. A noun can only have one function in a sentence. Mark out nouns once you have determined their functions to eliminate confusion. 1. To start, look for prepositions. Usually 2-3 words after the preposition, you will find a noun. That noun is the object of the preposition. A prepositional phrase requires a preposition and its object. Example: The fire crackled in the fireplace. prep. o.p. 2. Find the verb. 3. Locate the subject by asking who or what in front of the verb. Example: Tilly should give Reanna the ink pen. verb--should give Who or what should give? Tilly is the subject. 4. Determine if the verb is action or linking. 5. If the verb is action, look for a direct object by saying the subject + the verb + what or whom? Example: Tilly should give Reanna the ink pen. S + V + what or whom? Tilly should give what or whom? The answer, pen, is the direct object. 6. If you have a direct object, you might also have an indirect object. To find the indirect object, say S+ V + DO + to whom or what or for whom or what? The answer is the indirect object. Example: Using the previous sentence, one would say Tilly should give the pen to whom or what or for whom or what? Here, the indirect object would be Reanna. 7. If the verb is linking, see if you have a word on the other side of the verb that renames the subject. If you do, that word is the predicate nominative. Example: Jim is a student in my 5th hour class. The linking verb is is. Jim = student, so student is the predicate nominative. 8. Finally, if no other noun function is found, look to see if the word renames another noun close to it without using a linking verb. If it does, it is an appositive. Example: Mr. Lee, the math teacher, gives nightly homework. The word teacher renames Mr. Lee without a linking verb present, so it is an appositive. Hint: Sometimes words that seem to be nouns can function as adjectives, adverbs, or even verbs. Be careful; look at how they function with the rest of the sentence! Examples: Mr. Lee, the math teacher, gives nightly homework. (The word math is an adjective here.) Every night, I have homework. (The word night is an adverb here.) When will you pen your novel? (The word pen here is a verb.)