Word
advertisement

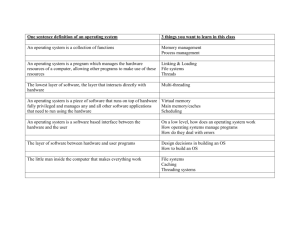
Ch. 3 – Operating Systems Operating System Software •Operating System (OS) – Software that ______________________________________ of a computer What is an operating system (OS)? Software which manages the overall operation of the computer system including: ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Software files (programs) which are stored on the hard disk • _________________________ with the internal programs • ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ Kernel •Kernel – The internal part of the operating system. –Those software components that perform the basic functions required by the computer. • ________________________________________________ • ________________________________________________ • ________________________________________________ 1 The functions of an operating system 1. Manages and Interacts with Computer Hardware 2. Provides and Manages System Security 3. Provides the System Interface 4. Provides the Interface for Application Software 1. Manages and Interacts with Computer Hardware Manages the CPU What software programs the ___________________ and when Manages RAM - What is ________________________ and where it is stored - Virtual memory - OS will send message when RAM is full Provides the interface for storage devices and _____________________________________ on those devices - in charge of formatting disks - creates sectors and clusters - creates F.A.T. or V.T.O.C. - sends message when disk is full or there is some other problem with writing data to the disk - virtual memory - CD-ROM, DVD-ROM - Flash drive Provides the Interface for Input and Output Devices keyboard, mouse, printer, device drivers = software programs which allow the hardware device to be used by the operating system and by application software Advantages/Disadvantages of Server Operating Systems Advantages _____________________________ for the installation and administration of all software and data More cost effective - less expensive than multiple computers (PCs, Macs) Disadvantages ___________________________ Loss of individual user control of their own software, data, and peripherals 2 2. Provides and Manages System Security Single-user Operating Systems __________________________________ user has full authority (usually) Server Operating Systems __________________ capability protection of user’s data stored on the server’s central hard disk drives protection and security for software programs 3. Provides the System Interface System Interface or shell = the interface between the user and the computer ___________________________________________ Linux, UNIX, DOS, older OS’s 4. Provides the Interface for Application Software Operating systems are _________________________________ Operating systems are designed and developed for a specific CPU or “family of CPUs” Application software is developed for an operating system MS Word for Windows 7 Windows 7 Intel CPU MS Word for the Macintosh Macintosh OS X Intel CPU 3 Virtualization, Cloud Computing and Big Data Virtualization Virtualization - Various techniques and methods of creating a virtual (rather than actual) version of something, such as: Computer hardware platform Operating System (OS) – _____________________________ Storage device Network resources Virtual Machine Software that supports multiple operating systems on a single computer. Each operating system is it’s own “virtual machine” with it’s own: • ________________________________________________ • ________________________________________________ • ________________________________________________ • ________________________________________________ VM A computer can run: Multiple operating systems simultaneously including the _____________________________________ Zero Client (thin clients) just: Connect to the network Begins a networking protocol to communicate with the VM server Displays the server's output: Operating system, applications and data Basically the full OS and applications are run in _____________________ Fewer client “computers” means: Less cost – fewer “computers” Do not have to constantly upgrade computers or buy new computers Easier installation of software and upgrading current software _______________________________________________ Easier management of client computers Access ______________________ from any device on the network. 4 Cloud Computing Centralization – Looks familiar…. The mainframe computer has now become the “cloud”. Cloud computing – Ability to run a program on many connected computers at the same time. The popularity of the term is from the ability host application services so that the client can access from a remote location. Also known as ___________________________ over a network A data center is a specialized facility used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. Cloud computing is ______________________________ in which large groups of remote servers are networked to allow the centralized data storage, and online access to computer services or resources. Big data Big data - The collection of data sets so large and complex that it becomes _____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ or traditional data processing applications. Challenges: How to capture, organize, store, search, share, transfer, analyze, and visualize. How to use larger data sets of information, analyze the information and use it to "spot business trends, determine quality of research, prevent diseases, link legal citations, combat and prevent crime, and _________________________________________________. Big Data (2012) Big Data Example Analyzing Data – RapidMiner Meta Data _________________________________ is data that describes other data. A metadata record is a file of information which captures the basic characteristics of a data or information resource. Metadata is traditionally in the card catalogs of libraries. Metadata describes how and when and by whom a particular set of data was collected, and how the data is formatted. 5