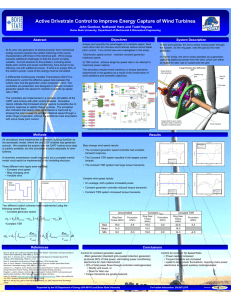
Design Optimization Study of
advertisement

Eric Sabelhaus 19 September 2006 AME 40463 Senior Design Generator Selection Study Purpose/Influence on Design Decisions: In our design concept, a bike pedal will be turned by the human user to power a generator. The purpose of this design study is to select a generator that will most effectively convert the mechanical power input from the pedals to electrical energy. The study will determine an appropriate gear tooth ratio that will most closely match the required generator rotational speed and torque. To measure the merit of each candidate generator, mechanical efficiency, cost, and size will be weighed, respectively, in decreasing order of importance. Variables: Design Variable (DV) 1 2 3 Generator type (batch) Design Parameter (DP) Power from pedals to input gear (PPEDAL) Output gear radius, rOUT (batch-purchased) Generator shaft rotational speed, ωG (continuous) State Variable (SV) Power to drive generator (PG) Generator Torque (TG) Constraint (C) Max. generator speed (ωG_M) Max. generator torque (TG_M) Gear Ratio (GR) Methods of Analysis: To simplify the analysis, the input gear will be a predetermined diameter based on a typical gear in a 21-speed bicycle. Additionally, the input gear rotational speed will be held constant at 60 rpm, a nominal value that a normal human can accomplish when pedaling. From known Voltage and Amp specifications of candidate generators, PG can be determined. Ideally, PG will be as near PPEDAL as possible to maximize power conversion. If PPEDAL >> PG, the generator will not be able to convert the human work to electrical energy, and if the converse is true, the high generator torque will bog down the worker and inhibit pedaling output. The output gear radius and generator shaft speed will be adjusted to optimize mechanical efficiency. Based on these values, the gear ratio can be calculated. The basic equations to be used in this study are: GR Output _ Circum. 2 r _ out r _ out Input _ Circum. 2 r _ in r _ in Torque r F Power Volts Amps Torque Quantitative Information to be Developed: Based on this study the output gear radius, generator shaft rotational speed, and gear ratio will be determined. Each generator will receive three ‘scores’ for its 1) mechanical efficiency, 2) cost, and 3) size. The generator earning the highest score will be selected. Schedule: Due Date Milestone 19/9 (Tue) Proposal due 26/9 (Tue) Generators identified 28/9 (Thur) Input radius, ωG selected 03/10 (Tue) Generator chosen, ordered 10/10 (Tue) Report draft completed 12/10 (Thur) Report due