Science Grade 7 Unit 6 Earth and Human Activity
advertisement
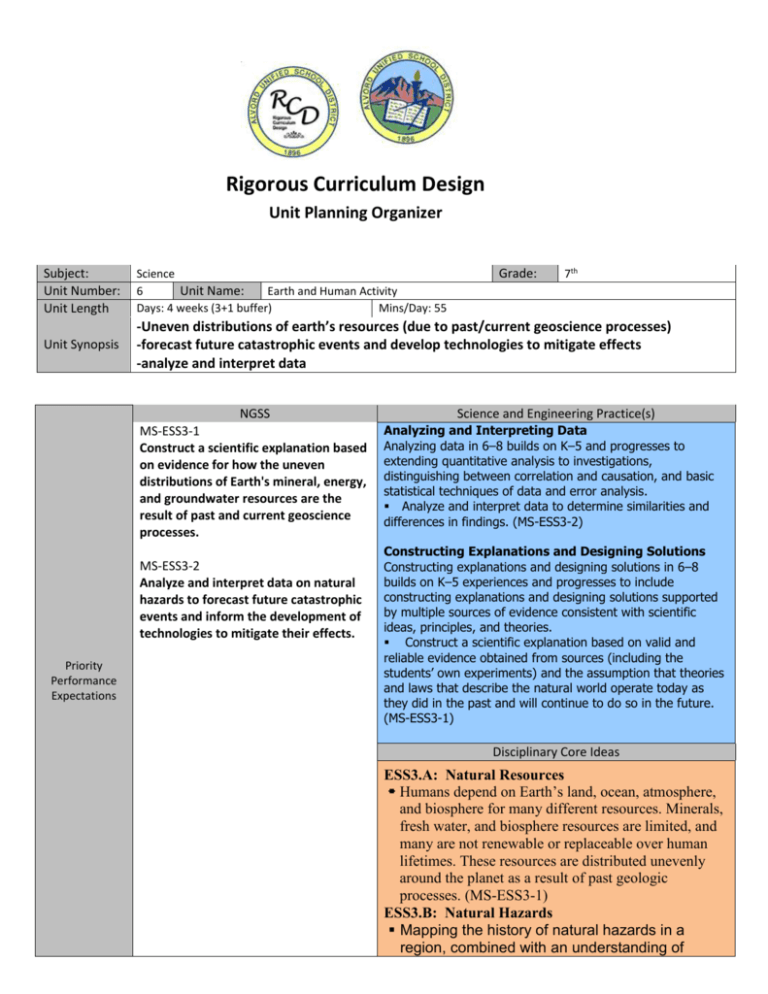
Rigorous Curriculum Design Unit Planning Organizer Science 6 Earth and Human Activity Unit Name: Days: 4 weeks (3+1 buffer) Mins/Day: 55 Unit Synopsis -Uneven distributions of earth’s resources (due to past/current geoscience processes) -forecast future catastrophic events and develop technologies to mitigate effects -analyze and interpret data NGSS MS-ESS3-1 Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for how the uneven distributions of Earth's mineral, energy, and groundwater resources are the result of past and current geoscience processes. MS-ESS3-2 Analyze and interpret data on natural hazards to forecast future catastrophic events and inform the development of technologies to mitigate their effects. Priority Performance Expectations Grade: 7th Subject: Unit Number: Unit Length Science and Engineering Practice(s) Analyzing and Interpreting Data Analyzing data in 6–8 builds on K–5 and progresses to extending quantitative analysis to investigations, distinguishing between correlation and causation, and basic statistical techniques of data and error analysis. Analyze and interpret data to determine similarities and differences in findings. (MS-ESS3-2) Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions Constructing explanations and designing solutions in 6–8 builds on K–5 experiences and progresses to include constructing explanations and designing solutions supported by multiple sources of evidence consistent with scientific ideas, principles, and theories. Construct a scientific explanation based on valid and reliable evidence obtained from sources (including the students’ own experiments) and the assumption that theories and laws that describe the natural world operate today as they did in the past and will continue to do so in the future. (MS-ESS3-1) Disciplinary Core Ideas ESS3.A: Natural Resources Humans depend on Earth’s land, ocean, atmosphere, and biosphere for many different resources. Minerals, fresh water, and biosphere resources are limited, and many are not renewable or replaceable over human lifetimes. These resources are distributed unevenly around the planet as a result of past geologic processes. (MS-ESS3-1) ESS3.B: Natural Hazards Mapping the history of natural hazards in a region, combined with an understanding of related geologic forces can help forecast the locations and likelihoods of future events. (MSESS3-2) Patterns Graphs, charts, and images can be used to identify patterns in data. (MS-ESS3-2) Crosscutting Concepts Cause and Effect Cause and effect relationships may be used to predict phenomena in natural or designed systems. (MS-ESS3- 1),(MS-ESS3-4) NGSS MS-ETS1-1. Define the criteria and constraints of a design problem with sufficient precision to ensure a successful solution, taking into account relevant scientific principles and potential impacts on people and the natural environment that may limit possible solutions. Supporting Performance Expectations MS-ETS1-2. Evaluate competing design solutions using a systematic process to determine how well they meet the criteria and constraints of the problem. MS-ETS1-3. Analyze data from tests to determine similarities and differences among several design solutions to identify the best characteristics of each that can be combined into a new solution to better meet the criteria for success. Math CCSS Literacy CCSS MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. (MS-ESS3-2),(MSESS3-5) 6.EE.B.6 Use variables to represent numbers and write expressions when solving a real-world or mathematical problem; understand that a variable can represent an unknown number, or, depending on the purpose at hand, any number in a specified set. (MS-ESS3-1),(MSESS3-2),(MS-ESS3-3),(MS-ESS34),(MS-ESS3-5) 7.EE.B.4 Use variables to represent quantities in a real-world or mathematical problem, and construct simple equations and inequalities to solve problems by reasoning about the quantities. (MSESS3-1),(MS-ESS3-2),(MS-ESS33),(MS-ESS3-4),(MS-ESS3-5) RST.6-8.1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts. (MSESS3-1),(MS-ESS3-2),(MS-ESS34),(MS-ESS3-5) RST.6-8.7 Integrate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text with a version of that information expressed visually (e.g., in a flowchart, diagram, model, graph, or table). (MS-ESS3-2) WHST.6-8.2 Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content. (MSESS3-1) WHST.6-8.9 Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. (MS-ESS3-1),(MS-ESS3-4) MS-ETS1-4. Develop a model to generate data for iterative testing and modification of a proposed object, tool, or process such that an optimal design can be achieved. NG ELD Standards Interdisciplinary Connections Interpretive 6Reading closely literary and informational texts and viewing multimedia to determine how meaning is conveyed explicitly and implicitly through language. Productive 10Writing literary and informational texts to present, describe, and explain ideas and information, using appropriate technology. Teacher Tip: Collaborative 1 Literacy / Science / History / Other Exchanging information and ideas with others through oral collaborative discussions on a range of social and academic topics. Unwrapped Priority Performance Expectations PE:MS-ESS3-1 Skills Construct PE:MS-ESS3-2 Skills Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for how the uneven distributions of Earth’s mineral, energy, and groundwater resources are the result of past and current geoscience processes Concepts Bloom’s DOK (Rigor Language Matrix) Demand A scientific explanation based on evidence for how the uneven distributions of Earth’s mineral, energy, and groundwater resources are the result of past and current geoscience processes Create 3 Analyze and Interpret data on natural hazards to forecast future catastrophic events and inform the development of technologies to mitigate their effects Concepts Bloom’s DOK (Rigor Language Matrix) Demand Analyze and Interpret Data on natural hazards Analyze 4 To forecast Future catastrophic events Create 4 And Inform The development of technologies to mitigate their effects Create 4 Learning Progressions of Skills and Concepts PE: DCI(s): Previous Course___________ NA PE: DCI(s): Previous Course___________ NA Current Course MS-ESS3-1 Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for how the uneven distributions of Earth's mineral, energy, and groundwater resources are the result of past and current geoscience processes. Current Course MS-ESS3-2 Analyze and interpret data on natural hazards to forecast future catastrophic events and inform the development of technologies to mitigate their effects Next Course_____________ HS.PS3.B – Conservation and transfer of energy HS.LS1.C – Matter and energy flow HS.ESS2.A – Earth systems HS.ESS2.B – Plate tectonics HS.ESS2.C – Water’s role in Earth’s surface processes HS.ESS3.A – Natural resources Next Course_____________ HS.ESS2.B – Plate tectonics HS.ESS2.D – Weather and climate (sun) HS.ESS3.B – Natural Hazards HS.ESS3.D – Global climate change PE: DCI(s): Previous Course___________ Current Course Next Course_____________ PE: DCI(s): Previous Course___________ Current Course Next Course_____________ PE: DCI(s): Previous Course___________ Current Course Next Course_____________ PE: DCI(s): Previous Course___________ Current Course Next Course_____________ Big Idea(s) 1. Geoscience processes account for uneven distribution of Earth’s resources. Corresponding Essential Question(s) 1. Why are Earth’s resources unevenly distributed? 2. Analyzing natural hazards allows us to prepare for 2. How can we reduce the impact of natural disasters? catastrophic events. Unit Vocabulary Words Academic Cross-Curricular Vocabulary (Tier 2) Content/Domain Specific Vocabulary (Tier 3) Resources Groundwater Non-renewable Geoscience Processes Hazards Hydrothermal Predict Catastrophic Technology Interior Processes (earthquake/volcanic eruptions) Disaster Exterior Processes (tsunamis and mass wasting) Forecast Petroleum Frequency Magnitude Mitigate Supporting Vocabulary (Tier 2) Supporting Vocabulary (Tier 3) Resources for Vocabulary Development (Strategies, Routines and Activities) Instagram vocab Vocabulary Vocabulary activity Flipbook/Foldable Examples/nonexamples Vocabulary Vocabulary around Matchbooks/Frayer the World Vocabulary Matrix model/Looping Vocabulary Vocabulary Web Vocabulary Flashcards Snowball Fight Vocabulary Focus Word Wall Mnemonics 21st Century Skills Creativity and Innovation Initiative and Self-Direction Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Social and Cross-Cultural Skills Communication and Collaboration Productivity and Accountability Flexibility and Adaptability Leadership and Responsibility Globally and Financially Literate __________________________ Communicating and Collaborating __________________________ Connections between 21st Century Skills, NGSS, and Unit Overview: Costa & Kallick, 2008 Unit Assessments Pre-Assessment Post-Assessment Scoring Guides and Answer Keys Assessment Differentiation Emerging English Language Learners Students with Disabilities Accommodations Reference IEP to ensure appropriate testing environment Modifications Expanding Engaging Scenario Overview (Situation, challenge, role, audience, product or performance) Description: Suggested Length of Time Days: Mins/Day: Engaging Learning Experiences Synopsis of Authentic Performance Tasks Authentic Performance Tasks Task 1: Description Problem Solving: Suggested Length of Time Days: Task 2: Task 3: Task 4: SEP: Mins/Day: Problem Solving: Days: SEP: Mins/Day: Problem Solving: Days: SEP: Mins/Day: Problem Solving: Days: SEP: Mins/Day: Authentic Performance Task 1 Suggested Length Name: Days: Mins/Day: Priority Standards NGSS Science and Engineering Practice(s) Disciplinary Core Idea(s) Performance Expectations / Standards Addressed Crosscutting Concept(s) NGSS Teaching and Supporting Standards CCSS Math CCSS Literacy NG ELD Bloom’s DOK Learning Progression Scoring Rubric Instructional Strategies SWD ELs Accommodations Emerging All Students Enrichment Expanding Modifications Bridging Authentic Performance Task 2 Suggested Length Name: Days: Mins/Day: Priority Standards NGSS Science and Engineering Practice(s) Disciplinary Core Idea(s) Performance Expectations / Standards Addressed Crosscutting Concept(s) NGSS Supporting Standards CCSS Math CCSS Literacy NG ELD Bloom’s Teaching and Learning Progression Scoring Rubric DOK Instructional Strategies SWD ELs Accommodations Emerging All Students Enrichment Expanding Modifications Bridging Authentic Performance Task 3 Suggested Length Name: Days: Mins/Day: Priority Standards NGSS Science and Engineering Practice(s) Disciplinary Core Idea(s) Performance Expectations / Standards Addressed Crosscutting Concept(s) NGSS Supporting Standards CCSS Math CCSS Literacy NG ELD Bloom’s Teaching and Learning Progression Scoring Rubric All Students Instructional Strategies SWD ELs Enrichment DOK Accommodations Emerging Expanding Modifications Bridging Authentic Performance Task 4 Suggested Length Name: Days: Mins/Day: Priority Standards NGSS Science and Engineering Practice(s) Disciplinary Core Idea(s) Performance Expectations / Standards Addressed Crosscutting Concept(s) NGSS Supporting Standards CCSS Math CCSS Literacy NG ELD Bloom’s Teaching and Learning Progression Scoring Rubric All Students Instructional Strategies SWD ELs Accommodations Emerging Enrichment DOK Expanding Modifications Bridging Engaging Scenario Detailed Description (situation, challenge, role, audience, product or performance) All Students Instructional Strategies SWD ELs Accommodations Emerging Expanding Modifications Bridging Scoring Guide: Feedback to Curriculum Team Enrichment Reflect on the teaching and learning process within this unit of study. What were some successes and challenges that might be helpful when refining this unit of study? Successes Challenges Student Perspective Teacher Perspective