Ch. 3 Word notes A & P ch 3 cells notes
advertisement

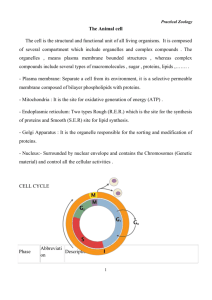
Cells Cells are the basic building block of life. - Composed of - Carbon –oxygen-hydrogennitrogen - Surrounded by interstitial fluids - Concentration important- must be isotonic - If hypertonic –greater concentration of molecules outside the cell - If – hypotonic concentration of lower molecules outside the cell - If isotonic – concentration equal inside and outside the cell - To maintain homeostasis interstitial fluid needs to be isotonic. - Hypertonic- molecules move into cell and water moves out (expands) - Hypotonic – molecules move out of the cell and water moves in ( contracts) - Isotonic – there is equilibrium inside and s\outside the cell - The movement of any molecules from an area of high to low concentration is passive transport ( down concentration gradient) - Diffusion is passive transport of molecules easy to move MITOSIS - Cell Division- cell’s life cycle: 2 main phases o Interphase – most of life : grow, carry on regular activity o Cell Division – period when cell reproduces itself prepares by duplicating DNA exactly - Transcription- Replication of DNA (know as template) - Mitosis- Events of cell division when an exact copy of the cell is made - Prophase- First stage: chromatin coils and shortens to become chromosomes, spindle fibers and centrioles appear. - Chromatids- Two sections of the chromosome and they separate into each daughter cell - Centromeres- Holds the chromatids together and help divide - Metaphase- when chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell - Anaphase- 2 chromatids begin to pull apart - Telophase- Chromatids uncoil and become chromatin and a true nucleus chromatin forms around the -cytokinesis- cytoplasm is divided in 2 new cells (called cleavage after the cells split) Protein Synthesis - gene: segment of DNA that carries info to build one protein chain - enzymes: regulate chemical reactions in cells - DNA is “encoded” with its information inside the sequences of steps - Each triplet codon (set of 3 steps/bases) requires a specific amino acid - Amino acid: building blocks of proteins: joined during protein synthesis - A,C,T,G put in different orders make different genes using 3 of them - Ribosome: manufacturing sites of proteins - Ribonucleic acid :RNA decoder and messenger for nucleus - tRNA: transfer RNA: transfer messages - rRNA: helps from ribosome’s ( r=ribosomal) - mRNA : carries messages to ribosome’s (m=messenger) - Two major Phases: - Transcription :MRNA is made at the DNA gene (only MRNA and DNA) - Translation: info in MRNA is “decoded” and used to form proteins (all RNA invloved) - Codons: corresponding triplet sequences on mRNA - Anticodon: special 3 step sequence on head of RNA - Each tRNA at the beginning of the mRNA which are lined up and joined by enzymes and amino acids are by the mRNA and joined by enzymes tRNA is then released and moves to another amino acid. When last condon is read protein is released. Body Tissues Human Body , a single cell divides endlessly to become specialized for particular function. - Groups of cells that are similar in structure and function are called Tissues Four Primary Tissue Types - epithelium (covering) - connective tissue (support) - nervous tissue (control) - muscle (movement) They all form “Fabric” of Body Tissues Organized into organs and arrangement of tissues determine organ’s structure and what it can do. Epithelial tissues, or Epithelium Lining, covering, and glandular tissues of the body. Epithelial functions include Protection, absorption, filtration, and secretion. -Epithelia cells fit closely to form continuous sheets. Bound together by cell junctions. - Membranes always have one free surface or edge. Apical Surface is exposed to the body’s cavity of internal organ. (slick & smooth). - Lower surface rest on a Basement membrane, structure less material secreted by the cell. -No blood supply, depend on diffusion. -Regenerates by itself if nourished right. Classification of Epithelium Simple epithelium: 1 layer of cells, classification by cell arrangement. Columnar: cells that are shaped like columns. Cuboidal: Cells that cube- shaped, like dice. Squamous: cells that are flattened like, fish scales. Stratifiedepithelium: More than 1 layer, named for the cells at the free surface of the epithelial membrane. Simple epithelia: Most concerned with absorption, secretion, and filtration, very thin protection is not 1 of their specialties. Simple Squamous Epithelium: A single layer of thin squamous cells resting on a basement membrane closely together, like floor tiles. Simple Squamous Epithelium forms: Serous membranes serosae. Types of Connective Tissue Most rigid to softest bone, cartilage, dense connective and loose connective. Bone- Osseous Tissue Bone cells sitting in cavities called lacunae and surrounded by layers of a very hard matrix that contains calcium salts and large amounts of collagen fibers -rock like hardness -protects and supports Cartilage- less hard and flexible - hyaline cartilage many collagen fibers hidden by a rubbery matrix with a glassy blue-white appearance. - Forms larynx (voice box) structures - attaches ribs to breastbone - Elastic cartilage only where elasticity is desired (ear) - Fibro cartilage- highly compressed forms cushion like disks between vertebrae. - Tendons- attach skeletal muscles to bone. - Ligaments- connects bones to bones at joints. - (D.C.T.) Dense Connective tissueDense fibrous collagen fibers are the main matrix. Between fibers are rows of fibroblasts that manufacture the fibers. D.C.T. forms Strong, ropelike structures, such as tendons and ligaments. D.C.T. makes up the lower layers of the skin Loose Connective tissue Loose Connective tissue fibers are softer than any other connective tissue. Arelar Tissue- most widely distributed tissue it cushions the organs, provides a reservoir of water and salts. When the tissue is inflamed and soaks up water like a sponge and becomes puffy is called edema. Adipose tissue- Commonly called fat, stored oil occupies most of a fat cells volume Fat cells volume and compresses the nucleus, displacing it to one side. This tissue forms beneath the skin insulates the body and protects it form heat and cold, protects the kidneys and cushions the eye sockets. Reticular Connective tissue- Network of interwoven fibers, it is limited to certain sites it form the stoma or internal supporting frame work supports many blood cells in lymphoid organs such as the spleen and bone marrow. Blood- vascular tissue is a connective tissue because it consists of blood cells. The fibers of blood are soluble protein molecules that become visible clotting. Blood carries nutrients, wastes and gases. Tissue Repair - skin, mucous, cilia, and strong aids - some of bodies defenses - when injury happens inflammatory, immune, and healing begins - Inflammation prevents further injury - Immune Fights bacteria, viruses, toxins - Two major ways to repair - Regeneration replacement of destroyed tissue fibrosis repair connective tissue scar tissue - Depends on type of tissue damage or severity - When injury occurs - Capillaries allow fluid to help clotting - Clotting proteins construct clot - Stop blood loss - Granulation tissue forms - Grows in damaged area - Bleed a lot - Contain phagocytes - Disposes of clot - Epithelium regenerates under scab - Covers scar - Different tissues regenerate in different ways scar tissues very strong, lacks flexibility - Can’t do what original tissues did. DEVELOPMENTAL ASPECTS OF CELLS & TISSUES Most cells except neurons under go mitosis. Cells exposed to abrasion wear away, like skin and intestinal cells. Amitotic tissues are hurt by injury because the cells can’t be replaced. The aging process begins once maturity has been reached. It is believed that” chemical insults” are responsible for it, but no one knows for sure. Another factor could be that could cause aging is radiation. X rays or ultraviolet waves and still another reason could be that our genes are genetically programmed to start the aging process. The effects of getting older starts to become obvious when we get wrinkles and our skin start to sag. That is because our epithelial membranes become thinner. Skin loses it’s elasticity. Hormones also decrease. The bones weaken, tissues ability to repair itself decreases, and muscles and nervous tissues begin to atrophy.