Student Targets
DuPage ROE Biology Essential Curriculum Objectives
Scientific Process
Objective 1 Recognize the role biology plays in current events.
Student Targets
I can describe different applications of biology.
I can identify the role that biologists play in current events.
Objective 2 Use the process of scientific reasoning to investigate scientific problems.
Student Targets
I can describe the process a scientist uses to explain a problem.
I can recognize a controlled experiment.
I can identify the variables in an experiment.
I can recognize a good hypothesis that is based on observations that can be tested.
I can recognize a good conclusion that is based on experimental data.
I can distinguish between a fact and an assumption.
Objective 3 Distinguish between an observation and an inference when given a scientific statement about an experiment.
Student Targets
I can identify inferences.
I can identify observations.
I can differentiate between inferences and observations.
Objective 4 Analyze and interpret experimental data.
Student Targets
I can make a prediction from given data.
I can identify a data point on a graph.
I can identify increasing and decreasing trends or patterns from data tables and graphs.
I can draw a logical conclusion from a given set of data.
Objective 5 Analyze and interpret visual representations of biological processes.
Student Targets
I can look at a figure of a biological process and explain what is happening.
Objective 6 Analyze a given data set and recognize correct graphical representations of a data set.
1
DuPage ROE Biology Essential Curriculum Objectives
Organization of Cells
Objective 1 Identify the basics components of cell theory.
• All living things are made of cells.
• Cells are the basic unit of structure and function.
• All cells come from pre-existing cells.
Student Targets
I can recite the three components of the cell theory.
I can identify the main points of the cell theory when given a list of things that are true about cells.
Objective 2 Compare and contrast eukaryotic with prokaryotic cells.
• presence of a nucleus
• presence of membrane bound organelles
• both living
• both have plasma membranes and ribosomes
Student Targets
I can explain what a eukaryotic cell is and give examples (plant and animal cells).
I can explain what a prokaryotic cell is and give an example (bacteria).
I know which type of cell has a nuclear membrane and membrane bound organelles.
I can identify a diagram of a eukaryotic cell and a prokaryotic cell.
I can draw a Venn diagram of eukaryotic cells and a prokaryotic cells, contrasting the differences and showing the similarities.
Objective 3 Categorize cell organelles according to their contribution to overall cell functions.
• Transport (plasma membrane)
• Energy (chloroplast, mitochondria)
• Manufacturing of macromolecules (ribosome)
• Homeostasis ( plasma membrane)
• Structure (cell wall)
Student Targets
I can identify the following cell organelles in a cell diagram. Plasma membrane
Chloroplast
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Cell wall
I can name the cell organelles that are responsible for moving substances into and out of cell.
I can name the organelles of a cell that are responsible for collecting and storing energy.
I can name the organelles of a cell that are instrumental in the manufacture of macomolecules in the cell.
I can explain how a cell maintains homeostasis and identify the cell organelles that are responsible.
I can describe why plant cells maintain a definite shape.
2
DuPage ROE Biology Essential Curriculum Objectives
Objective 4 Compare and contrast plant cells and animal cells.
Student Targets
I can identify a plant cell by reading a description of the cell.
I can identify an animal cell by reading a description of the cell.
I can draw a plant or animal cell and label the distinguishing organelles.
I can draw a Venn diagram of plant cells and an animal cell, contrasting the differences and showing the similarities.
Objective 5 Predict from descriptions or diagrams which of the following processes are occurring:
Diffusion - osmosis - passive transport – active transport
Student Targets
I can summarize the process of diffusion using six words or less.
I can describe the differences and similarities between diffusion and osmosis.
I can analyze a data table and interpret which cell process (passive transport or active transport) will take place in a given environment.
I can analyze a diagram of a cell in an environment and predict which cell process (passive transport or active transport) will take place.
I can describe an everyday situation that is an example of diffusion
Objective 6 Recognize that the cell cycle provides for genetic continuity, cell division, growth, and repair.
Student Targets
I can draw a diagram of the cell cycle and describe what is happening in the cell at each stage.
I can name the stages of the cell cycle.
I can describe the process of DNA synthesis and use the following terms correctly:
Replication
Chromatin
Chromosome
Chromatid
Centromere
Base pairs
Diploid
I can identify the phases of mitosis, when shown a cell in the process of division.
I can explain summarize why the process of mitosis is important to the living organism.
I can describe how the cell cycle is regulated within an organism
I can use a data table to construct a graph.
I can connect graphs to their corresponding data tables.
3
DuPage ROE Biology Essential Curriculum Objectives
Genetics
Objective 1 Recognize how the terms traits, genes, alleles, and chromosomes are related.
Student Targets
I can define the terms trait, gene, allele, and chromosome
I know the difference between a gene and an allele
I understand how alleles influence traits
I know that genes are found on chromosomes
Objective 2 Identify the sex of a human based on its genotype.
Student Targets
I can distinguish a male (XY) and female (XX) genotype
I can analyze a Karyotype to determine sex
Objective 3 Predict the phenotype of an organism given its genotype.
Student Targets
I know the difference between genotype and phenotype
I know that an organism’s genotype determines it’s phenotype
I can tell when a dominant or recessive allele will be expressed
Objective 4 Indicate whether a genotype is homozygous or heterozygous.
Student Targets
I can define the terms homozygous and heterozygous
I can tell the difference between a homozygous and heterozygous genotype.
Objective 5 Use a Punnett square to solve genetic problems for single trait and sex-linked traits.
Student Targets
I can create a Punnett square given parental information
I can interpret the results of a Punnett square
I can explain how sex-linked disorders are inherited
I know how sex-linked traits are different than autosomal traits
I can compare and contrast the inheritance patterns of sex-linked traits in males and females
Objective 6
Interpret a pedigree to determine an individual’s genotype / phenotype.
Student Targets
I can summarize the information provided in a pedigree
I can determine the genotypes and phenotypes of individuals in a pedigree
4
DuPage ROE Biology Essential Curriculum Objectives
Objective 7 Explain how meiosis results in sex cells
Student Targets
I know that the process of meiosis produces sperm and eggs
I can compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis
I understand the importance of meiosis in maintaining the chromosome number over multiple generations
Objective 8 Explain how DNA’s structure allows it to code for genes and replicate.
Student Targets
I can describe the structure of a DNA molecule
I know base pairing rules
I can diagram DNA replication
Objective 9
Explain DNA’s role in the production of proteins.
Student Targets
I can describe the process of protein synthesis
Given a strand of DNA, I can determine the amino acid sequence of a protein
Objective 10 Describe how a mutation is a change in the DNA or chromosome and the possible effects on an organism or population.
Student Targets
I can define the term mutation
I can recognize mutations given different DNA sequences
I know that a change in DNA sequence may or may not result in a change in the organism
I understand the various effects mutations can have
Evolution
Objective 1 Recognize and identify examples of evolution as change in the genetic makeup of a population over time.
Student Targets
I can define evolution.
I recognize that when the genetic makeup of a population changes evolution has occurred.
Objective 2 Recognize that natural selection is a mechanism for evolutionary change. (State the basic principles of natural selection)
Student Targets
I can explain why variation is important to evolution.
I can summarize the process of natural selection.
I can explain why competition occurs in a population.
5
DuPage ROE Biology Essential Curriculum Objectives
Objective 3 Recognize the factors that lead to speciation.
Student Targets
I can explain how new species come from other species.
I can explain how speciation occurs through geographic isolation.
Objective 4 Recognize evidences that support the theory of evolution (e.g. molecular, homology, embryology, fossil, etc.)
Student Targets
I can list evidence for evolution.
I can explain how DNA evidence supports common ancestry of organisms.
Ecology
Objective 1 Distinguish between different levels of organization within the biosphere (such as organism, population, community, ecosystem…).
Student Targets
I can list the different levels of organization within the biosphere in order (most general to most specific or vice versa).
I can match a specific level of organization with its description / example.
I can identify level from a photograph or drawing of a level of ecosystem or within an ecosystem.
Objective 2 Describe the interdependence between living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the environment.
Student Targets
I can define biotic an abiotic.
I can identify biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem.
I understand how abiotic factors cam impact biotic factors.
I understand how biotic factors cam impact abiotic factors.
I can give an example of interdependence of biotic/ abiotic factors in ecological cycles.
I can predict the effect of a change in one component on another component in an ecosystem (from a story or a graph).
Objective 3 Predict the effects on an ecosystem given limitations and disruptions (such as limiting factors, natural disasters, climate change, introduction of non-native species, human impact, population changes, pollution).
Student Targets
I can define and identify limiting factors in an ecosystem.
I can predict possible outcomes of global warming / cooling (climate change).
I can identify examples of natural disasters.
I can predict possible outcomes of the introduction of invasive non-native species.
I can predict possible outcomes of human population growth.
6
DuPage ROE Biology Essential Curriculum Objectives
I can predict possible the impact of pollution on an ecosystem.
I can distinguish between significant impacts caused by nature and those caused by humans.
I can predict possible outcomes when given a disruption scenario.
Objective 4 Recognize the relationship between organisms and the flow of energy in an ecosystem (such as trophic levels, producers, consumers, food chains, food webs, transfer of energy, ecological pyramids)
Student Targets
I can categorize the different ways that organisms get their energy.
I can describe what happens to the amount of available energy as you move up the food chain.
I can link different types of living things in a food chain.
I can describe why energy flow, mass, and populations in ecology are best represented by a pyramid.
I can tell the difference between a food chain and a food web.
I can predict what will happen to a food chain/ web if an organism increases / decreases in number.
I can identify organisms by trophic level.
I can explain the difference between producers and consumers.
I can explain the difference between herbivores and carnivores.
Objective 5 Distinguish between interactions among organisms within an ecosystems (such as competition, predation and other relationships).
Student Targets
I can define and give examples of competition, predation, and symbiosis (parasitism, commensalism, mutualism).
Classification
Objective 1 Identify what criteria necessary for organisms to be considered members of the same species
Student Targets
I can state the definition for fertile.
I can recognize the different groups/ breeds/variations that exist within a species.
I can identify two species that produce hybrids.
I know that two organisms are the same species if they can interbreed in nature and produce fertile offspring.
Objective 2 Demonstrate how the major categories of biological classification scheme shows that some organisms are more closely related than others
Student Targets
I can list the taxonomic levels of classification in order of specificity.
I can name the broadest group and most specific group of the taxonomic classification levels.
I know that domain is the broadest group and species is the most specific group.
I can use the taxonomic levels to determine how closely related two organisms are.
7
DuPage ROE Biology Essential Curriculum Objectives
Objective 3 Recognize the necessity of scientific names.
Student Targets
I can write a scientific name using the rules for scientific names.
I know that scientific names are universally accepted and refer to one species.
I know that scientific name refers to one species.
I can describe the confusion caused by common names.
I can identify genus and species from the scientific name.
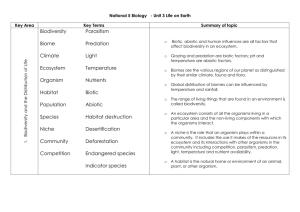
Biodiversity
Objective 1 Distinguish the three levels of biodiversity (genetic, species, ecosystem).
Student Targets
I can define genetic diversity.
I understand that genetic diversity is genetic differences between individuals of a population.
I can define species diversity.
I understand that species diversity is the numbe of different species occupying an area.
I can define ecosystem diversity.
I understand that ecosystem diversity is the variety of habitats an area contain.
I can describe several different examples of:
1. Genetic diversity (population of pandas),
2. Species diversity (varying organisms in a rain forest)
3. Ecosystems diversity (marsh, prairie).
Objective 2 Identify how humans benefit from biodiversity
Student Targets
I can list several examples of how biodiversity benefits human populations
Objective 3 Identify human impacts on biodiversity
Habitat destruction- habitat restoration
Invasive Species
Population growth (human)
Pollution
Over Harvesting
Student Targets
I can discuss the reasons for a species endangerment based on HIPPO
I can explain the impact of biodiversity loss on a local environment
I can list examples and explain how humans have negatively impacted biodiversity
I can describe the effects of biodiversity loss on both human populations and other species
8
DuPage ROE Biology Essential Curriculum Objectives
Biochemistry
Objective 1 Identify reactants and products in biochemical reactions.
Student Targets
Given an equation, I can identify the reactants
Given an equation, I can identify the products
I can identify the meaning of an arrow in an equation for a chemical reaction
Objective 2 Identify the structure and function of macromolecules including Carbohydrates, Nucleic Acids,
Lipids, and Proteins).
Student Targets
I can name the 4 types of organic macromolecules
I can identify elements present in carbohydrates, nucleic acids, lipids, and proteins
I can identify/name the subunits in carbohydrates, nucleic acids, lipids, and proteins
I can identify/describe the functions of carbohydrates, nucleic acids, lipids, and proteins
I can describe what the terms “organic” and “macromolecule” mean
Objective 3 Describe the function of enzymes.
Student Targets:
I can describe how enzymes affect chemical bonds and activation energy
I can read an enzyme activity graph
I can label all the parts of an enzyme
I can describe what a substrate is
I can describe factors that affect enzyme activity, such as pH, temperature, inhibitors
Objective 4 Recognize the relationship between photosynthesis and cell respiration.
Student Targets:
I can name which organelles are responsible for photosynthesis, cell respiration
I can recognize the reactants and products for photosynthesis
I can recognize the reactants and products for cellular respiration
I can explain how photosynthesis and respiration are interconnected
Structure and Function
Objective 1 Identify the basic structures and functions that allow organisms to obtain and use energy
(including: unicellular, multicellular, animal, and plant).
Student Targets
I can identify function, structures and processes used by plants, animals, protists and fungi to obtain nutrition (e.g.; root and vascular systems, mycelium, digestive systems, etc.).
I can describe the role of mitochondria and chloroplasts in energy production and relate this to the formation of ATP.
9
DuPage ROE Biology Essential Curriculum Objectives
Objective 2 Identify the basic structures and functions that allow organisms to exchange gasses (including: unicellular, multicellular, animal, and plant).
Student Targets
I can identify structures and processes used to exchange gases in organisms (e.g. diffusion across a membrane, respiratory systems, stomata, vascular processes, etc..),
I can explain the importance of surface area, volume and membrane thickness in the exchange of gases.
Objective 3 Identify the basic structures and functions that allow organisms to rid itself of waste products
(including: unicellular, multicellular, animal, and plant).
Student Targets
I can explain the importance of waste elimination as it relates to homeostasis.
I can identify organelles, tissue and organs involved in the removal of waste products from an o rganism (e.g. vesicles, vacuoles, skin, kidney, lungs, etc…)
Objective 4 Identify the basic structures and functions behind the transport of essential materials in an organism (including: unicellular, multicellular, animal, and plant).
Student Targets
I can identify the structures in an organism used to transport gasses, nutrients and waste throughout the organism. (e.g. vascular systems in plants and animals)
Objective 5 Identify the basic structures and explain the functions that allow an organism to pass on genetic information for the survival of the species (including: unicellular, multicellular, animal, and plant).
Student Targets
I can describe structures and processes involved in sexual and asexual reproduction (e.g. binary fission, budding, f ertilization, etc…)
I can explain the advantages and disadvantages of sexual versus asexual reproduction.
10