National 5 Biology - Unit 3 Life on Earth Key Area Key Terms
advertisement
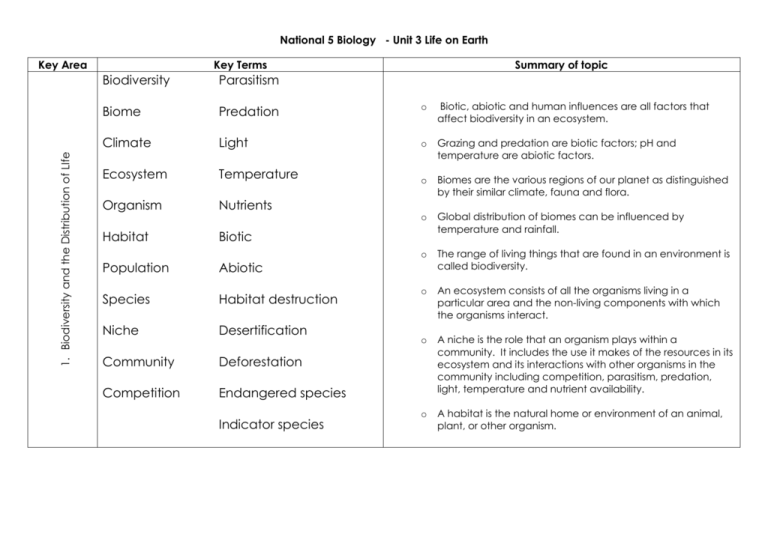
National 5 Biology - Unit 3 Life on Earth 1. Biodiversity and the Distribution of LIfe Key Area Key Terms Summary of topic Biodiversity Parasitism Biome Predation o Biotic, abiotic and human influences are all factors that affect biodiversity in an ecosystem. Climate Light o Grazing and predation are biotic factors; pH and temperature are abiotic factors. Ecosystem Temperature o Organism Nutrients Biomes are the various regions of our planet as distinguished by their similar climate, fauna and flora. o Habitat Biotic Global distribution of biomes can be influenced by temperature and rainfall. o The range of living things that are found in an environment is called biodiversity. o An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a particular area and the non-living components with which the organisms interact. o A niche is the role that an organism plays within a community. It includes the use it makes of the resources in its ecosystem and its interactions with other organisms in the community including competition, parasitism, predation, light, temperature and nutrient availability. o A habitat is the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism. Population Abiotic Species Habitat destruction Niche Desertification Community Deforestation Competition Endangered species Indicator species Key Area Key Terms Summary of topic Species: A species is a group of biologically similar organisms which can reproduce to produce fertile offspring. Population: A population is a group of interbreeding organisms of a species in a particular area. Producer: A producer is the organism in a food chain which fixes energy and produces organic compounds which are then available to other species in the food chain. Plants are producers as they use energy from sunlight to produce glucose from carbon dioxide through photosynthesis. Consumer: Consumers are organisms which are not able to fix energy and must consume other organisms in order to obtain organic molecules. Herbivore: Herbivores are animals which only consume plants. Carnivore: Carnivores are animals which only consume other animals. Omnivore: Omnivores are animals which consume both plants and animals. Energy 2. Energy in Ecosystems Organism Food chain Carnivores Food web Omnivores Producers Predator Consumers Prey Decomposers pollution herbivores 3. Sampling techniques and measurements Key Area Key Terms Quadrat Light meters Sampling pH meters Pitfall traps Abiotic Tree beating Biotic Errors Keys Reducing errors Summary of topic o Sampling plants and animals using quantitative techniques including quadrats and pitfall traps. o Evaluation of limitations and sources of error in pitfall traps and quadrats. o Measuring abiotic factors including light intensity, temperature, pH and soil moisture. 4. Adaptation, natural selection and evolution of species Key Area Key Terms Summary of topic Mutation Variation Resistance Adaptation Species Environmental Speciation conditions Rapid selection/evolution Natural selection A mutation is a random change to genetic material. Mutations may be neutral, confer an advantage or a disadvantage. Mutations are spontaneous and are the only source of new alleles. Environmental factors, such as radiation and chemicals, can increase rate of mutation. Variation within a population makes it possible for a population to evolve over time in response to changing environmental conditions. Natural selection/survival of the fittest occurs when more offspring are produced than the environment can sustain. Only the best adapted individuals survive to reproduce, passing on the genes that confer the selective advantage. Speciation occurs after a population becomes isolated and natural selection follows a different path due to different conditions/selection pressures. 5. Human impact on the environment Key Area Key Terms Summary of topic o Increasing human population requires an increased food yield. o o o Fertilisers can leach into fresh water, causing algal blooms. This leads to a reduction in oxygen levels. Pesticides sprayed onto crops can accumulate in the bodies of organisms over time. As they are passed along food chains, toxicity increases and can reach fatal levels. Indicator species are species that by their presence or absence indicate environmental quality/levels of pollution. Biological control and GM crops may be alternatives to mitigate the effects of intensive farming on the environment. Human population Nutrients Intensive farming Reducing pollution Monoculture Pesticides o Fertilisers Indicator species Algal blooms Biological control o o o