Ma T1 A1 Planning MK - St Peter`s Church of England Primary
advertisement

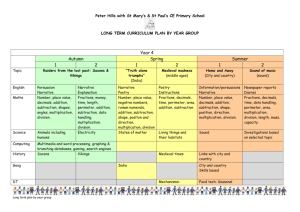
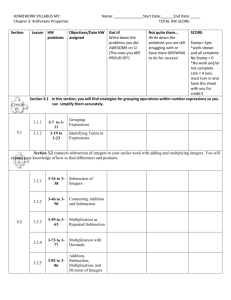
St Peter’s C of E Primary School: Maths Planning Sheet YEAR 5 BLOCK A UNIT 1 (AUTUMN) COUNTING, PARTITIONING AND CALCULATING Objectives / I Can Statements Red is Using and Applying 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Explain reasoning using diagrams, graphs and text; refine ways of recording using images and symbols. I can write down how I solved a problem, showing every step. Count from any given number in whole-number and decimal steps, extending beyond zero when counting backwards; relate the numbers to their position on a number line. I can find missing numbers in a sequence that includes negative numbers. *I can describe, explain and generate rules for a sequence. Explain what each digit represents in whole numbers and decimals with up to two places, and partition, round and order these numbers. I can say what any digit represents in a number with up to seven digits. *I can compare and order numbers. Use understanding of place value to multiply and divide whole numbers and decimals by 10, 100 or 1000. I can multiply or divide a whole number by 10, 100 or 1000. Recall quickly multiplication facts up to 10 × 10 and use them to multiply pairs of multiples of 10 and 100; derive quickly corresponding division facts. I know my tables to 10. I can use them to work out division facts and to multiply multiples of 10 and 100. Identify pairs of factors of two-digit whole numbers and find common multiples (e.g. for 6 and 9). I can find a pair of factors for a two-digit number. Use knowledge of rounding, place value, number facts and inverse operations to estimate and check calculations. I can estimate and check the result of a calculation. Extend mental methods for whole-number calculations, for example to multiply a twodigit by a one-digit number (e.g. 12 × 9), to multiply by 25 (e.g. 16 × 25), to subtract one near multiple of 1000 from another (e.g. 6070 – 4097). I can work out some calculations in my head or with jottings. I can explain how I found the answer. Use knowledge of place value and addition and subtraction of two-digit numbers to derive sums and differences and doubles and halves of decimals (e.g. 6.5 ± 2.7, half of 5.6, double 0.34). I can work out sums and differences of decimals with two digits. Use efficient written methods to add and subtract whole numbers and decimals with up to two places. I can explain each step when I write addition and subtraction calculations in columns. Speaking and Listening Objectives (3 WEEKS) Curricular Target Present a spoken argument, sequencing points logically, defending views with evidence and making use of persuasive language. I can describe each stage of my calculation method (e.g. for 18 × 25). I can explain why it is a good method for this calculation. Vocabulary problem, solution, calculate, calculation, equation, operation, answer, method, explain, reasoning, reason, predict, relationship, rule, formula, pattern, sequence, term, consecutive place value, digit, numeral, partition, decimal point, decimal place, thousands, ten thousands, hundred thousands, millions, tenths, hundredths, positive, negative, above/below zero, compare, order, ascending, descending, greater than (>), less than (<), round, estimate, approximately add, subtract, multiply, divide, sum, total, difference, plus, minus, product, quotient, remainder, factor, multiple calculator, display, key, enter, clear, constant pound (£), penny/pence (p), units of measurement and their abbreviations, degree Celsius (°C) Prior Learning Count from any given number in whole-number steps. Use positive and negative numbers in practical contexts; position them on a number line. Add or subtract mentally pairs of two-digit whole numbers, e.g. 47 + 58, 91 – 35. Use efficient written methods to add and subtract two- and three-digit whole numbers and £.p. Recall multiplication and division facts to 10 × 10. Multiply or divide numbers to 1000 by 10 and then 100 (whole-number answers). Use written methods to multiply and divide TU × U, TU ÷ U. Use decimal notation for tenths and hundredths in the context of money and measurement. Order decimals to two places and position them on a number line. Use a calculator to carry out one- and two-step calculations involving all four operations; interpret the display correctly in the context of money. Use the relationship between m, cm and mm. St Peter’s C of E Primary School: Maths Planning Sheet Class: Block: A1 Swans Probing Question: What does this digit represent? Curricular targets: WALT/I Mental/Oral/Skills can… Activity Monday WALT partition and compare whole numbers Tuesday WALT represent numbers with 1 d.p. Term: 1 Date: 6th – 10th September 2010 Week: 1 Focus children: Kasie, Olivia, Ashley, Zac W, Joe Main Teaching Input Main Activity Teacher Guided LA Level 3c/3b Use place value chart to demonstrate the value of digits in whole numbers. Model how to partition the numbers. Use this to order the numbers. Practise reading the numbers in words. HA – practise reading large numbers in words. Student – work with LA group to support with task. Start with numbers with 3 or 4 digits. Complete 2x, 5x and 10x tables tests (multiplication and division). Model how to use fraction rods to represent decimals with 1 d.p. Give children numbers to represent. Discuss how these can be represented in different ways and the value of each rod. LA – talk through examples, discussing value of each rod and recording on whiteboard. Student – work with MA group, discussing value of each rod. Wednesday WALT multiply and divide whole numbers by 10 and 100 Either complete 3x, 4x and 6x tables tests (multiplication and division) if successful yesterday, or complete grid to practice 2x, 5x and 10x tables. Use children holding number cards to demonstrate what happens when numbers are multiplied or divided by 10. Model how 0 is used as a place holder. Model again using place value chart. Use ITP ‘Moving Digits’ to practise multiplying and dividing by 10 and 100. Thursday WALT use written methods of calculation Either complete 7x, 8x and 9x tables tests (multiplication and division) if successful yesterday, or complete grid to practice 2x, 5x and 10x tables or 3x, 4x and 6x tables. Briefly model expanded written methods for each operation. HA – discuss steps and potential difficulties and then create poster to remind class. Student – work with LA group to ensure they are using place value grid effectively and understand how value of each digit changes. Observe and assess. Can children explain the method they are using? MA Level 3a/4c Partition and compare numbers with 5 or 6 digits. HA Level 4b/4a Plenary Key Questions Extend to numbers with up to seven digits. What can you tell me about the digit 7 in these numbers? Tell me a number that is between 23,454 and 24,211. What did you have to think about? Give decimal numbers to represent and compare using fraction rods. Take photos to stick in books as evidence. Record different ways to use rods to make the same number. How could I represent 2.7? How else could I do it? Model recording on board. Use place value sheet and digit cards to support. Start by multiplying and dividing by 10 only. Use ITP ‘Moving Digits’ to check answers together. Extend to numbers that already contain zeros and decimals. What happens to the digits of a number when it is divided by 10 or 100? Does this rule apply to decimal numbers as well? Complete chart, multiplying and dividing numbers by 10 and 100. Choose easy, medium or hard calculation for each operation to show what they are able to do, showing written method of working out. Ask a few children to model the methods they used. Use website 1 to practice times tables Model how to use word problem frame – LA – support with language. Solve easier word Solve medium word Solve harder word Friday and using scale to place answer on a identifying calculation, estimating answer, Begin to build up bank of problems, using problems, using word problems, using WALT solve number line. working out answer (choosing mental or words for each operation to word problem problem frame. word problem word written method), checking calculation (using add to maths display. frame. frame. problems inverse) and coming up with answer using (including any units needed). addition and subtraction Homework: ‘Aim high’ game (from Scholastic 100 Maths Homework activities Y5) – place value game using digits 0-9 to make highest number. Complete comment sheet. Websites: Check answers together, discussing any misconceptions or common difficulties. 1. http://www.mathsframe.co.uk/placecalcsmulti.swf St Peter’s C of E Primary School: Maths Planning Sheet Class: Block: A1 Term: 1 Week: 2 Date: 13th – 17th September 2010 Swans Probing Question: What is the most efficient method to use for this calculation? Focus children: Kasie, Olivia, Ashley, Zac W, Joe Curricular targets: I can calculate mentally with integers and decimals (e.g. U.t + U.t) I can quickly recall multiplication facts up to 10 x 10, use to multiply pairs of multiples of 10 and 100 and quickly derive corresponding division facts WALT/I Mental/Oral/Skills Main Activity Plenary can… Activity Main Teaching Input Teacher Guided LA MA HA Key Questions Level 3c/3b Level 3a/4c Level 4b/4a Use bead strings to add decimals (U.t + Model expanded and compact methods of HA: Ensure correct Complete easier Complete medium Complete harder Check answers using a Monday U.t). column addition. vocabulary for compact addition addition calculations, addition calculator. WALT use a method (e.g. “9 and 8 is 17 calculations, using choosing expanded or calculations, using column so I’ll carry one ten”, not expanded method. compact method. compact method. method for “carry 1”). addition Tuesday WALT use the grid method for multiplication Complete next times table test or practise grid. Model grid method for multiplication, using expanded method of addition to add up the parts of the answer. Wednesday WALT use a number line for subtraction Use bead strings to subtract decimals (U.t – U.t). Model using a number line for subtraction, using expanded method of addition to add up the parts of the answer Thursday WALT use jottings for division Complete next times table test or practise grid. Model how to use jottings for division, e.g. 48 ÷ 3 10 x 3 = 30 6 x 3 = 18 Also model this as two jumps on a number line, jumping forwards. Friday WALT solve word problems Use bead bar to count on and back in 0.1s, 0.2s, etc. Model how to estimate first by rounding numbers. Homework: Websites: 1. HA: Model how to multiply multiples of ten. Extend to HTU x TU if appropriate. LA: Use ITP Grouping to show how division can be worked out on a number line. Complete easier multiplication questions (TU x U). Complete medium multiplication questions (HTU x U). Complete harder multiplication questions (TU x TU and HTU x TU). Check answers using a calculator. Complete easier subtraction questions, using number line marked in 10s. Complete medium subtraction questions, using number line method. Complete harder subtraction questions, using number line or written counting up method. Check answers using a calculator. Complete easier division questions, using number line. Complete medium division questions, using number line or jottings. Complete harder division questions, using jottings. Check answers together. Solve easier word problems, using word problem frame. Solve medium word problems, using word problem frame. Solve harder word problems, using word problem frame. Check answers together, discussing any misconceptions or common difficulties. St Peter’s C of E Primary School: Maths Planning Sheet Class: Block: A1 Term: 1 Week: 4 Date: 27th September – 1st Swans Probing Question: Focus children: Lorenzo, Ashleigh M, Joe, Kray, Zac W, Ashley O, Cali, Tyler Curricular targets: I can calculate mentally with integers and decimals (e.g. U.t + U.t) I can quickly recall multiplication facts up to 10 x 10, use to multiply pairs of multiples of 10 and 100 and quickly derive corresponding division facts WALT/I Mental/Oral/Skills Main Activity can… Activity Main Teaching Input Teacher Guided LA MA HA (Red) (Yellow/Green) (Blue) Level 3c/3b Level 3a/4c Level 4b/4a Use bead bar to count on and back in 0.1s, Model how to complete counting back sequence Yellow: Discuss strategies Counting back Use sheet with Counting back Monday 0.2s, etc. and how to identify rule for a sequence. for mental subtraction. from 2-digit similar problems, from 3-digit WALT count Encourage children to look for patterns, such as numbers in steps counting back from numbers in back from a noticing odd and even numbers in the of less than 10. 3-digit numbers in steps of more 2- or 3-digit sequences, and explain that these patterns can Use multilink if steps of less than 10. than 10. number be used to help check answers. needed. Tuesday WALT use negative numbers Complete next times table test or practise grid. Wednesday WALT continue sequences involving decimals Show beginning of sequence using IWB ‘Counting stick’. What is the next number? How do you know? What is the rule for the sequence? What will the 10th number be? Thursday WALT find factors of numbers Complete next times table test or practise grid. Friday WALT use negative and decimal numbers Give out laminated thermometers. Put the Powerpoint file ‘Random Temperatures’ on slideshow view. Ask ch to say stop, hit "s" to stop on a temperature, ch mark temperature on their thermometer laminates. Hit "s" again to start presentation again. October 2010 Plenary Key Questions Check answers in pairs. Draw vertical number line. Write numbers -5 to 5 alongside. Class count back from 5 to –5, then up to 5. Give out ‘Negative number cards’. In pairs, children pick 8 cards and put them in order. Use ‘Negative Number Lift’ on Learning Clips to demonstrate elevator moving between floors, including underground (negative). Hand out cards –5 to 5. Ask children to come out and position themselves in order. Use ITP ‘Increasing number grid generator’. Begin with 10-column grid and hide all numbers, selecting start number and step size. Reveal three numbers that are well apart on the grid. Where is __? How do you know? Hide all numbers, and set start number and step size. Reveal three numbers in top row, for example the 3rd, 6th and 8th. What sequence might be shown here? Give me next number in the sequence … number hidden in this cell… Explain rule for the sequence. Model how to find all factors of a number, recording factors in pairs. Green: Extend by asking questions about the thermometers, e.g. what would the temperature be if it was 2 degrees higher? Answer questions and complete number lines on sheet from Learning Clips, which has visual image of elevator floors to support. Complete number lines on Activity sheet 8.1 (from NNS Unit Plan). Fill in missing temperatures on thermometers. Continue sequences involving negative numbers, writing sequences in maths book. Check answers with a partner. Use ‘Ordering negative numbers’ game to practise ordering negative numbers. Red: use bead strings to practise counting in 0.1s and showing and ordering decimal numbers. Continue sequences involving counting up in 0.1s (Nature trails sheet). Continue whole number sequences and then related decimal sequence (Snooker sequences sheet). Continue decimal sequences (Jungle fever sheet). Use counting stick from 0 to 1. Ask children to read number that is pointed to. Ask children to point to given numbers. Repeat with ends being e.g. 2 and 3. Red: model how to use multiplication square to find factors. Record factors of given numbers (easier). Use multiplication square to support. Record factors of given numbers (medium). Introduce task and share possible ways to show understanding. Observe all groups and record useful evidence for APP. Homework: Websites: 1. Counting stick http://www.topmarks.co.uk/Interactive.aspx?cat=20 2. Negative Number Lift http://www.learningclip.co.uk/Block.aspx?prodid=1040 3. Ordering negative numbers http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/online/negnumorder.swf Record factors of given numbers then find common factors of pairs of numbers. Display learning objectives from Block A1. In pairs, children create a poster to show their understanding of these objectives. Display Venn diagram on whiteboard with labels ‘Factor of 20’ and ‘Factor of 12’. Give a number to each child and ask them to come up and write number in correct place. Display posters and discuss how they show understanding.