Managing Tropic Storms - thegeographyofblackwoodgcse
advertisement

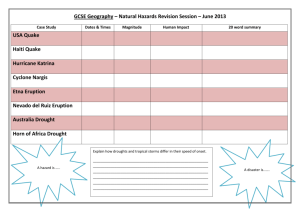
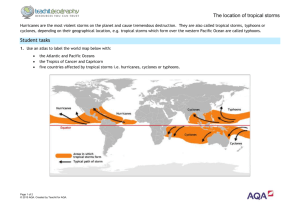
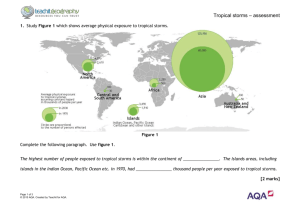
Theme 8: Weather and Climate Managing Tropic Storms Above: this TRACKS the nature of a hurricane and its force (power) as it approaches the Caribbean and mainland of the USA Aim of task: to produce a DETAILED mind map about the strategies used by both MEDC’s and LEDC countries as to how to manage the effects of TROPICAL STORMS. Learning Intentions: 1. To describe the characteristics of a tropical storm 2. to locate the regions of the world where tropical storm exist 3. to compare the effects of tropical storms in a LEDC to a MEDC 4. to analyse the methods used by MEDC and LEDC countries using a case study example where possible Tick when completed MIND Maps: these are an excellent tool which can develop a learners appreciation of a subject. Its visual content makes it great for REVISION purposes and its lack of detailed writing makes them relatively easy to build up. In addition, websites such as bubbl.us allow pupils to save and return to the mind map, adding more content along the way. www.thegeographyofblackwoodgcse.wikispaces.com Theme 8: Weather and Climate Revision Summary: Tropical Storms Conditions required for formation: Over Oceans Ocean temperature over 27°c Water heated to a depth of several metres Close to the East Coast of continents Late summer or early Autumn, when sea temperatures are at their highest (noticed how hurricanes always hit America around September/October!) Causes of tropical storms 1. Air on surface of ocean is heated (it also contains lots of moisture) 2. Hot, humid air rises, cools and condenses. Clouds form. 3. Rising air creates low pressure. Air rushes in to fill gap left by rising air. 4. Rotation of the earth means winds do not blow straight. Winds circle towards the centre. 5. The storm continues to feed itself. 6. Whole system moves in towards land. 7. When the system crosses the land it losses its source of heat and moisture. The tropical storm losses its energy and dies out. Managing the effects of tropical storms Reducing the effects of tropical storms includes: Studying tropical storms once they form (and tracking them) Providing an early warning system (air raid LEDC, news report MEDC) Long-term planning in areas prone to tropical storms such as engineered shelters and evacuation centres, strengthening levees and better education Case Study You will have to know at least one case study about tropical storms. If you can learn two, one in an LEDC (e.g. Bangladesh) and one in an MEDC (e.g. one in America - Hurricane Katrina) Make sure you know why tropical storms cause more problems in MEDCs than LEDCs. What might the examiner ask? 1. What is a tropical storm? 2. Describe how LEDC’s deal with the effects of a tropical storm. Use a case study you have studied to illustrate your knowledge. 3. Why are tropical storms much more damaging in an MEDC than a LEDC? 4. Using a case study of your choice explain how a Hurricane can effect a place 5. What modern technologies can be used to reduce the impacts of a tropical storm? www.thegeographyofblackwoodgcse.wikispaces.com Theme 8: Weather and Climate Tropical Storms Other Weather Hazards Case Study Drought Forest Fires Heavy rain (Storm) Arctic conditions Landslides (heavy rain) La Nina (and El Nino) Barcelona Australia UK Iceland Brazil South Pacific Low Technology vs High Technology Satellites, thermal imaging and engineered concrete sea walls are expensive methods that many LEDC’s simply cannot afford. Below is a scheme used by farmers in the Sahel region of Africa (Desertification is causing already dry un-watered land to become desert) www.thegeographyofblackwoodgcse.wikispaces.com Theme 8: Weather and Climate The Met Office provides a comprehensive range of services to warn government, emergency responders, businesses and the public about weather-related hazards. By providing early warning systems, weather risks can be managed to minimise disruption and safeguard lives. National Severe Weather Warning Service (NSWWS) — delivered over the web and by email alerts, this provides colour coded warnings of impending severe weather. PWS Advisors — this team can be called upon to provide advice for emergency responders. Flood Forecasting Centre — the Met Office and the Environment Agency work in partnership to provide advice on flood risk. Hazard Manager — a one-stop information source for the emergency response community. Other services include: UK Coastal Monitoring and Forecasting Service; FireMet; health forecasting (heatwaves, cold weather, UV warnings, as well as services for people with respiratory or mental health issues); animal health forecasting (such as spread of vectorborne diseases, like bluetongue); services to manage road, rail, marine and aviation risks. www.thegeographyofblackwoodgcse.wikispaces.com