SC2 - Biological systems
advertisement
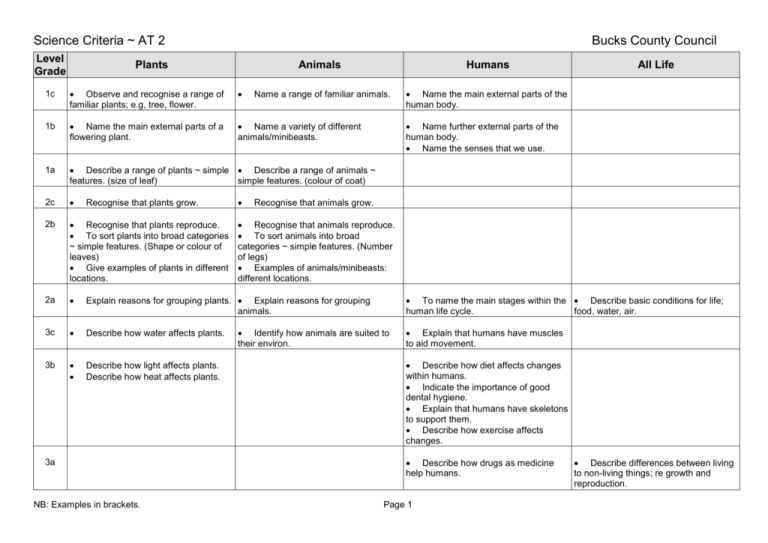
Science Criteria ~ AT 2 Level Grade Bucks County Council Plants Animals Humans Name a range of familiar animals. Name the main external parts of the human body. 1c Observe and recognise a range of familiar plants; e.g, tree, flower. 1b Name the main external parts of a flowering plant. Name a variety of different animals/minibeasts. 1a Describe a range of plants ~ simple Describe a range of animals ~ features. (size of leaf) simple features. (colour of coat) 2c 2b Recognise that plants reproduce. To sort plants into broad categories ~ simple features. (Shape or colour of leaves) Give examples of plants in different locations. 2a Explain reasons for grouping plants. Explain reasons for grouping animals. 3c Describe how water affects plants. 3b Describe how light affects plants. Describe how heat affects plants. Recognise that plants grow. 3a NB: Examples in brackets. All Life Name further external parts of the human body. Name the senses that we use. Recognise that animals grow. Recognise that animals reproduce. To sort animals into broad categories ~ simple features. (Number of legs) Examples of animals/minibeasts: different locations. To name the main stages within the Describe basic conditions for life; human life cycle. food, water, air. Identify how animals are suited to their environ. Explain that humans have muscles to aid movement. Describe how diet affects changes within humans. Indicate the importance of good dental hygiene. Explain that humans have skeletons to support them. Describe how exercise affects changes. Describe how drugs as medicine help humans. Page 1 Describe differences between living to non-living things; re growth and reproduction. Science Criteria ~ AT 2 Level Grade Bucks County Council Plants Animals 4c Humans Use predator and prey in context. Indicate the position of the heart. 4b 4a Use keys to identify and group Use keys to identify and group plants. animals/minibeasts. Identify the major organs of plants. (stamen, stigma) Indicate: food chains usually begin with green plants. Indicate the position of the major organs. (heart, lungs, stomach) 5c Compare: human/plant life-cycles. Explain: importance of plant organs to survival. Explain the importance of classification. Compare: human/plant life-cycles. Explain: importance of the major organs to health. 5b Describe main stages of life cycle of Explain: different animals in different plants. localities ~ environmental factors. Describe the function of the major organs of plants. (leaf, stamen, root hairs) Explain why different plants grow in different places, re environmental factors. Describe the function of the major organs. (heart, stomach, lungs) Describe main stages of life cycle of humans. Explain the importance of the heart to health. 5a Explain the importance of classification. Explain: importance of plant organs to survival. Compare: human/plant life-cycles. 6c Use keys to identify plants. Use keys to identify animals/minibeasts. Describe feeding relationships: re food chain or web. Use scientific names for major organs and systems. (heart, stomach) Explain: importance of the major organs to health. Compare: human/plant life-cycles. Describe life processes. (Photosynthesis) Distinguish between related processes. (pollination & fertilisation) NB: Examples in brackets. Page 2 All Life Science Criteria ~ AT 2 Level Grade 6b Plants 7b Animals Humans All Life Describe single cell structure. Describe single cell structure. Explain distribution and abundance in habitats affected by environmental factors. 6a 7c Bucks County Council Describe life processes. (Respiration) Identify differences between simple animal and plant cells. Construct models to show feeding relationships. (web, pyramid of numbers) Explain how feeding relationships affect population size. Explain process of photosynthesis in terms of main chemical change. Describe some causes of variation between living things. Identify common variations between individuals (height) that are affected by environmental factors. Identify common variations between individuals (eye colour) that are inherited. Explain process of respiration in terms of main chemical change. 7a Explain how cells are adapted to their function. (sperm, ovum, root hair) Recognise change in biological systems. (CO2 affects growth of crops, consequences of smoking) Explain how characteristics can be inherited. 8c 8b 8a Relate the cellular structure of organs to their associated life processes. (absorption of food in digestive system, gas exchange in lungs) Predict change in biological systems. (as above) Predict short-term effects of environmental change on ecosystems. Predict long-term effects of environmental change on ecosystems. Explain change in biological systems. (as above) Justify predictions; re effects of environmental change on ecosystems. NB: Examples in brackets. Page 3 Apply knowledge of how characteristics can be inherited. (selective breeding)