Membrane Transport Animations
advertisement

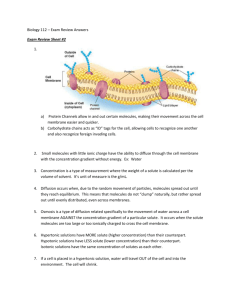
Membrane Transport Animations Name: ___________________________________ Period: __ Using the following website to fill out and answer the questions on this worksheet. http://www.northland.cc.mn.us/biology/Biology1111/animations/transport1.html The animation viewer is small so you may want to zoom in on the animation to better see what is going on. Pay attention. The “back” button can only be used at the end of the animation segment. You may need to watch each segment more than one time to answer the questions. From the Main Menu, Click on Passive Transport. Passive Transport 1. Passive transport is the movement of molecules across the cell that does not require an ____________________________________________________. (What does expenditure mean?) 2. What are the three types of passive transport? a. ________________________________________ b. ________________________________________ c. ________________________________________ Click “Next” Cell Membrane 3. Fill in the blanks of the following two diagrams. ____________________ ____________ __ ____________ __________ Watch the rest of the animation, follow along carefully. If you read this, draw an arrow by your name. 4. Why is the cell membrane described as a lipid bilayer? 5. Why is it important to note that the lipid bilayer is fluid? 6. Label the diagram to the right: a. Which part of the lipid bilayer is polar (hydrophilic — water liking)? b. Which is non-polar (hydrophobic — water non-liking)? 7. Which type of molecules have difficulty passing through the membrane? Why do you think so? 8. Which type of molecules pass easily through the membrane? Why do you think so? Click Next or Click on “Simple” Simple Diffusion 9. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of ____________________________________ to an area of ___________________________________________. 10. The term ___________________________________________refers to the relative density of one chemical substance versus another. Click Next 11. The rate of diffusion is dependent on these four things: a. b. c. d. 12. Simple Diffusion ends when equilibrium is met. a. What is meant by “equilibrium”? b. Since we are talking about living things, what is better / more accurate word choice to describe this condition in living cells ___________________________________. (Check the Intro to Chapter 7.) Click Next or Click on Facilitated Facilitated Diffusion 13. Facilitated diffusion is the ___________________________ of molecules down a concentration gradient with the aid of ________________________________________. 14. Does facilitated diffusion require the use of energy (ATP)? ________ 15. List the characteristics of some molecules that make them need help getting across the cell membrane? 16. How does a protein “facilitate” the diffusion of the molecule? 17. Sketch two protein channels in a membrane showing facilitated diffusion (one showing before and one after). Click Next or Click on Osmosis Osmosis 18. Define the term Osmosis. 19. Compare and contrast Simple Diffusion and Osmosis. What is similar? What is different? Diagram or T-chart for this please. Use a Venn 20. Compare a hypertonic solution to a hypotonic solution. Draw a picture or two showing what is going on. 21. Water travels across a cell membrane… (Circle one) a. from a hypotonic environment to a hypertonic environment or b. from a hypertonic environment to a hypotonic environment. 22. Explain why water molecules move across a cell membrane. Click Next Active Transport 22. ________________________________ is the pumping of molecules ______________their _________________________________________ with the expenditure of energy (ATP). 23. Why is active transport necessary? 24. Explain the difference between Passive and Active Transport. 25. Why do cells need to move molecules against the concentration gradient into the cells or out of the cells? 26. Describe the three different types of Active Transport used by cells to get molecules inside. 1. 2. 3. 27. What are the three different kinds of Endocytosis? Use the back of this page for more space & drawings. a. b. c. Membrane Transport Animations Name: ____Key____________________________ Period: __ Using the following website to fill out and answer the questions on this worksheet. http://www.northland.cc.mn.us/biology/Biology1111/animations/transport1.html The animation viewer is small so you may want to zoom in on the animation to better see what is going on. Pay attention. The “back” button can only be used at the end of the animation segment. You may need to watch each segment more than one time to answer the questions. From the Main Menu, Click on Passive Transport. Passive Transport 27. Passive transport is the movement of molecules across the cell that does not require an energy______. (What does expenditure mean?) 28. What are the three types of passive transport? a. Simple diffusion________________________________________ b. Facilitated diffusion________________________________________ c. osmosis________________________________________ Click “Next” Cell Membrane expenditure of 29. Fill in the blanks of the following two diagrams. (Integral proteins and lipid bilayer) ____________________ In ____________ __ ____________ __________ Watch the rest of the animation, follow along carefully. If you read this, draw an arrow by your name. 30. Why is the cell membrane described as a lipid bilayer? It is made of lipid molecules arranged in two layers. 31. Why is it important to note that the lipid bilayer is fluid? This fluidity provides for permeability. 32. Label the diagram to the right: a. Which part of the lipid bilayer is polar (hydrophilic — water liking)? b. Which is non-polar (hydrophobic — water non-liking)? 33. Which type of molecules have difficulty passing through the membrane? Why do you think so? Polar molecules have difficulty passing through. Probably because the non-polar middle of the membrane repels them. 34. Which type of molecules pass easily through the membrane? Why do you think so? Non-polar molecules pass through easily, because the non-polar middle doesn’t repel them? Click Next or Click on “Simple” Simple Diffusion 35. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of _high concentration__________________ to an area of _low concentration____________. 36. The term _Concentration gradient_________________________refers to the relative density of one chemical substance versus another. Click Next 37. The rate of diffusion is dependent on these four things: a. Steepness of the concentration gradient b. Temperature (the warmer it is, the faster the rate of molecular movement) c. Charge (electrical charge of the molecule) d. Diameter of the diffusing molecule (the smaller the molecule, the faster the rate.) 38. Simple Diffusion ends when equilibrium is met. a. What is meant by “equilibrium”? The concentration of molecules is the same all over/ on both sides of a membrane. b. Since we are talking about living things, what is better / more accurate word choice to describe this condition in living cells _Dynamic equilibrium________________. (Check the Intro to Chapter 7.) Click Next or Click on Facilitated Facilitated Diffusion 39. Facilitated diffusion is the _passive transport _______ of molecules down a concentration gradient with the aid of _special(ized) transport proteins_______________________. 40. Does facilitated diffusion require the use of energy (ATP)? Yes it does.________(What is ATP?) 41. List the characteristics of some molecules that make them need help getting across the cell membrane? They may be too big, have too much of an electrical charge, or be in scarce supply. 42. How does a protein “facilitate” the diffusion of the molecule? Facilitate means make it easier, and the protein changes shape so the molecule can pass through the membrane. 43. Sketch two protein channels in a membrane (before and after) showing facilitated diffusion. OK then. Click Next or Click on Osmosis Osmosis 44. Define the term Osmosis. Osmosis is the passage / movement of water molecules across a membrane from (an area of) high concentration to a (an area of) low concentration. 45. Compare and contrast Simple Diffusion and Osmosis. What is similar? What is different? Diagram or T-chart for this please. Simple diffusion: Any molecules, moving through any liquid or gas, Osmosis: water molecules only, moving through a membrane, down a concentration gradient down a concentration gradient. Use a Venn 46. Compare a hypertonic solution to a hypotonic solution. Draw a picture or two showing what is going on. OK then. 47. Water travels across a cell membrane… (Circle one) a. from a hypotonic environment to a hypertonic environment or b. from a hypertonic environment to a hypotonic environment. 22. Explain why water molecules move across a cell membrane. The water molecules move across the cell membrane because they are more concentrated than the cytoplasm if they are in a hypotonic solution and less concentrated than they are in the cytoplasm in a hypertonic solution Click Next Active Transport 48. _Active transport_______________________ is the pumping of molecules _against____their ___concentration gradient_________________________ with the expenditure of energy (ATP). 49. Why is active transport necessary? Because some molecules needed by the cell cannot be supplied by simple or facilitated diffusion. 50. Explain the difference between Passive and Active Transport. Passive transport requires no energy from the cell because molecules are moving down the concentration gradient. Active transport requires an input of energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient. 51. Why do cells need to move molecules against the concentration gradient into the cells or out of the cells? Living cells often require molecules in large supply that are naturally scarce in their environment. 52. Describe the three different types of Active Transport used by cells to get molecules inside. 1. Ion pumps 2. Co-transport 3. Endocytosis 27. What are the three different kinds of Endocytosis? Use the back of this page for more space & drawings. a. Phagocytosis b. Pinocytosis c. Receptor-mediated endocytosis