12L -final Plate Tectonics - Doral Academy Preparatory
advertisement

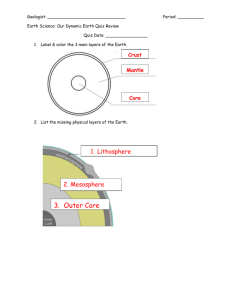
Plate Tectonics Continental Drift – 1. The first theory of continental drift was suggested by the German meteorologist Alfred Wegener in 1912 (1906/1915). 2. The hypothesis stated that the continents consist of _______________ rocks that rest on heavier crustal material— similar to the manner in which icebergs ________________ on water. Wegener contended that the positions of the continents are not always in the same position but are slowly_______________— at a rate of about one meter per century. 3. The theory of continental drift states that Earth’s continents were joined in a single large landmass (called Pangaea) that broke________________, and that the continents have drifted to their positions that they have today. What Evidence Did Alfred Wegener Have For The Theory of Continental Drift? 1. Shape of the Continents – The shape of the continents look like they should fit together like _______________ pieces. 2, Fossil Evidence - Wegener found that identical fossils, that could not ________________ or ____________ across 3,000 miles of ocean, were located directly opposite on widely separated continents. This had been realized previously but the idea of "land bridges" was the most widely accepted solution. Wegener found _________________ to be convincing evidence that a supercontinent had existed in the past. Example: Mesosaurus 3. Rock Type and Structural Similarities - We find similar _____________ types on continents on opposite sides of the Atlantic Ocean. Similar age, structure and rock types are found in the Appalachian Mountains in North America and mountains in Scotland and Scandinavia. When the continents are reassembled or put back together, the mountain chains from a continuous belt — having the same rock types, structures and rock _______________. 4. Climatic (climate) Evidence – Cold areas show evidence of once having been ____________ while hot areas show evidence of once being _______________. For example, coal needs a ____________ humid climate to form. It does not form in areas of extreme________________. Although Antarctica is extremely cold, it has huge ______________ deposits. Also warm-climate _______________________ plants and animals have been found in Antarctica and also the cold Arctic areas of North America. This indicates that at one time in the past, Antarctica and the Arctic areas of North America must have been physically closer to the_____________________. Wegener's idea of continental drift was not generally accepted because no one could come up with a reasonable mechanism (way) for the movement of the continents (How did the continents ___________________?). It was not until the 1960's that further data led to the development of the theory of plate tectonics that could explain the ___________________ of continents. The Theory of Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonic Theory – The Earth’s surface is composed of Lithospheric plates that “______________” atop the Asthenosphere and are in constant__________________. Lithoshere - The rigid and solid area that includes the ____________ and the uppermost portion of the______________. Asthenoshere - The lower part of the upper mantle that exhibits _______________ and plastic (flowing) properties. This is a far-reaching theory that has become the basis for understanding many geologic processes such as mountain_______________, _________________, and___________________. There are 12 major plates and many smaller plates which move in different__________________. Plates move slowly but continuously on the order of a few cm/year. This plate motion causes them to_________________, pull_______________, or scrape against each_________________. Plate Boundaries There are 3 distinct types of boundaries: 1. divergent — plates move _________________ from one another 2. convergent — plates _____________________ into one another (collision) 3. transform — plate grind ____________________ one another Each plate is bounded by a variety of plate boundaries. New plates can be created by forces that split plates apart such as at the East African Rift Valleys. Two plates may come ________________________ to form one plate such as may happen with the Himalayans. 2. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mB2pzhWUaiU&feature=related – 8min all types 3. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nfziy_860GU - convergent plates 4min 2a http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0mWQs1_L3fA all types – 1. http://www.teachersdomain.org/resource/ess05.sci.ess.earthsys.lp_platetectonics/ used first intro and further evidence and scientist What Forces Cause The Plates to Move? At the boundary of any moving plate earthquakes are formed. Below the lithosphere (which makes up the tectonic plates) is the asthenosphere. These plates in the lithosphere are made of rock that is lightweight compared with the_______________, hot, fluid layer underneath (________________________). This allows plates to ride and ____________________ on top of hot, denser, flowing rock. Plates move because ________________ is being released from deep inside the earth. Convection currents causes hot material to ______________ and expand (plates diverge –move apart) and _____________________ material to sink and contract (plates converge - move into each other). The plates move very _________________ on the surface, about 5cm per year. Convection currents are movements of fluids (________________and ____________) by unequal heating. Hot fluids ______________ and cold fluids_________________. What Geological Features do the Moving Plates Produce? Convergent Boundary – This forms when plates_____________. The pressure and violence at convergent boundaries produce folded or fault-block ______________, bands of________________, ________________activity, and ___________ (Japan). The movement of one plate under another is called subduction. Subduction happens at converging plate boundaries. When a plate undergoes subduction, the rocks in that plate are pushed deep into the _______________ where they are heated and changed into molten material called _____________ (A temperature hot enough to melt lithosphere is about a thousand degrees!). This molten material, which is under great_________________, can escape through weak spots in Earth’s crust as an erupting___________________. Where colliding ocean and continental plates occur deep ocean valleys called ___________________ are formed. These trenches are the deepest area of the ocean (the Mariana Trench in the western Pacific Ocean 10924 meters deep). Folded Mountains Fault-Block Mountains How colliding plates affect the rock cycle This process affects the rock cycle producing new ____________rock or ___________________ rock. New igneous rocks are produced as the ________________ inside the Earth or ____________________ erupting from a volcano cools to form rocks. Also the great ____________________ and _____________ produced by the converging plates can cause rocks to be into changed into metamorphic rocks (called contact metamorphism). Divergent Plates – This forms when two plates diverge, or _____________ from each other. Melted rock from the mantle can move to the surface at divergent boundaries and form new _______________. Most divergent boundaries are in the oceans (Atlantic Ocean has been forming for about 180 million years). Here, they build undersea __________________ ranges called mid-oceanic ridges. Also major ___________________ occur and where the molten rock pushes up above the ocean ____________________ islands form (Iceland). How plates moving apart affect the rock cycle As the molted magma hardens under the surface or reaches the ocean floor as lava new ________________ rock is formed. Transform Boundary – This forms where two plates slide ________________ each other. The sliding causes rocks along the boundary to grind past each other from time to time, causing jolts that you feel as _____________________. In the United States the San Andres Fault is an example of two plates sliding past each other. Volcanoes And Earthquakes Are Closely Linked To The Margins Of The Tectonic Plates. Anytime there is movement along a plate boundary _________________ occur. The movements occur along faults, which are large ______________ in the Earth’s crust. Rocks on either side of a fault are under great _________________ and get locked together. When too much pressure builds up, the rocks suddenly slide past each other and release the_________________. The longer the plates lock up before releasing energy the ___________________ the earthquake. Volcanoes occur when plates converge (come _____________) or diverge (move ________________) from each other. Location of Plate Boundaries. Location of Major Earthquakes Locating of Major Volcanic Areas What Evidence Exists For The Theory of Plate Tectonics? 1. The same evidence for __________________ _________ that was discussed earlier. 2. As plates move apart new material is erupted out of __________________ and rock fissures to fill the gap. This is occurring at the mid-oceanic ridge. This causes a slow steady movement of the sea-floor crust away from the center. The movement is eastward toward Europe and Africa and westward toward North and South America. Measurements of the age of sea-floor rocks show very_______ rocks closest to the ridge and _____ rocks farther away from the ridge. The composition of rocks is on both sides of the ridge is the same. oldest rock oldest rock The above diagram shows the spreading of rock at the midoceanic ridge where the ______________ rocks are at the center and ___________________ at the edges. 3. Paleomagnetism - The Earth's _______________field produces invisible lines of force that extend from one pole to the other. A compass needle aligns itself with these lines of force — points toward the magnetic poles. When igneous rocks containing magnetic _____________ minerals crystallize and harden, the crystals in the rocks become __________________ in a direction of the Earth’s magnetic field. Earth's magnetic field periodically reverses polarity (direction of the _______________ and _______________ magnetic pole) — the north and south poles switch. Rocks crystallizing during one of these periods of magnetic reversal will be magnetized with a polarity opposite of __________________ that crystallize earlier. These ______________ rocks provide evidence of the different locations of the Earth’s magnetic poles at the time when the rocks were formed. An example is at the midoceanic ridge ___________________ rocks formed new patterns in two long bands on each side of the ridge where the rocks poured out. The __________________ ______________ of the rock then points toward the magnetic pole that existed when the rock formed. Scientists have studied magnetic volcanic rocks at the mid-ocean ridge. The rocks magnetic field acts as a "fossil compass." There is an exact copy of the direction of the Earth’s magnetic field on both sides of the ___________.