LECTURE 08 CH 14-1 POPULATION GROWTH AND REGULATION 2
advertisement

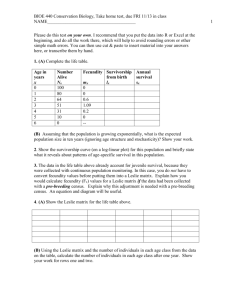
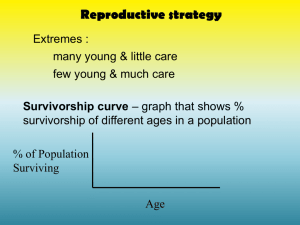
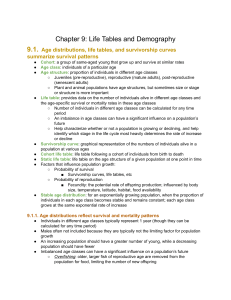
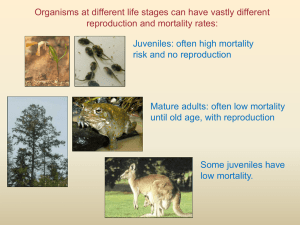
LECTURE 08 POPULATION GROWTH AND REGULATION 2 For this lecture, bring PRINTOUT of this and last Tuesday’s lecture outline ** PG. 221 FROM LAB MANUAL ** Completed Problem Set 1 (problems 1-7); Problem Set 2 (problem 2) Learn what bolded words below mean by looking at relevant figures; study Table 11.1 MAJOR CONCEPTS 1. The age structure of a population reflects its history of survival, reproduction, and potential for future growth. 2. How fast a population grows depends on its age structure. 3. A life table summarizes age-specific schedules of survival and fecundity. 4. A life table can be used to estimate net reproductive rate (Ro), geometric rate of increase (), generation time (T), and per capita rate of increase (r). 5. A survivorship curve summarizes the pattern of survival over time in a population. I. Age structure: proportion of individuals in each age class. 227-9 Influences population growth rate. Stable and growing populations have very different shapes. 11.6 Shape of age structure shifts when populations change birth/death rates 11.7 II. Life Table analysis for differential equations 229-231 Includes complexity of age-specific survival and fecundity Table 11.1, Table 11.4 Summarizes demographic information by age class Fecundity Probability of survival III. Life table: provides calculations of: 234-235 Table 11.7 T = mean generation time Ro = net reproductive rate (per lifetime); when Ro = 1, population is stable r = ln Ro/T = er Doubling time t2 = ln2 / ln t2 = ln2 / r ex = life expectancy IV. Cohort vs. static life tables (advantages and disadvantages) 231-234 11.8, 11.9, Table 11.6 Cohort: all individuals born at same time Shapes of survivorship curves (Type I, II, and III) 11.10 V. Use life table to project future population size and age structure Tables 11.2, 11.3 Get stable age distribution (SAD) with time, even with population growing Each age class grows (or declines) at same rate () fluctuates, then becomes constant with time Assumes birth and death rates are constant