Chapter 6 Word Study
advertisement

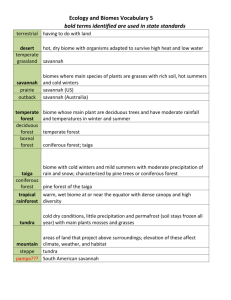
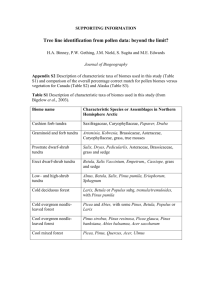
Your Name ______________________________Period ______ Date __________ Environmental Science Chapter 6 Word Study - Biomes Directions: Study the following words by reading and rereading them each evening so you will be prepared for the word study test each week. You may use one index card to write as many words and definitions on as possible to use for the test. The card must written in ink, be in your handwriting, and have your name, your class period, and the chapter recorded in the top, right corner with no obvious erasures or mark outs. ALL WORDS MUST BE NUMBERED. If all the criteria are met, you may use your index card during the test. It will then be stapled to your test. 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) 5.) 6.) 7.) 8.) 9.) 10.) 11.) 12.) 13.) biome – a large region characterized by a specific type of climate and certain types of plant and animal communities / example: tundra climate – the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time latitude – the distance north or south from the equator; expressed in degrees longitude – the distance east or west from the equator; expressed in degrees altitude – the height of an object above a reference point, such as sea level or the Earth’s surface tundra – a treeless plain that is located in the Arctic or Antarctic and that is characterized by very low winter temperatures; short, cool summers; and vegetation that consists of grasses, lichens, and perennial taiga – a region of evergreen, coniferous forest below the arctic and subarctic tundra regions temperate deciduous forest – a forest (or biome) that is characterized by trees that shed their leaves in the fall tropical rain forest – a forest or jungle near the equator that is characterized by large amounts of rain and little variation in temperature and that contains the greatest known diversity of organisms on Earth emergent layer – the top foliage layer in a forest where the trees extend above surrounding trees canopy – the layers of treetops that shade the forest floor epiphyte – a plant that uses another plant for support, but not for nourishment / examples: orchids, mosses, lichens understory – a foliage layer that is beneath and shaded by the main canopy of a forest 14.) temperate rain forest – a forest community (biome), characterized by cool, humid weather and abundant rainfall, where tree branches are draped with mosses, tree trunks are covered with lichens, and the forest floor is covered with ferns 15.) taiga – a region of evergreen, coniferous forest below the arctic and subarctic tundra regions 16.) savanna – a plain full of grasses and scattered trees and shrubs; found in tropical and subtropical habitats and mainly in regions with a dry climate, such as East Africa 17.) temperate grassland – a community (or biome) that is dominated by grasses, has few trees, and is characterized by cold winters and rainfall that is intermediate between that of a forest and a desert 18.) chaparral – a type of vegetation that includes broad-leafed evergreen shrubs and that is located in areas with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters 19.) desert – a region that has little or no vegetation, long periods without rain, and extreme temperatures 20.) tundra – a treeless plain that is located in the Arctic or Antarctic and that is characterized by very low winter temperatures; short, cool summers; and vegetation that consists of grasses, lichens, and perennial herbs 21.) permafrost – in arctic regions, the permanently frozen layer of soil or subsoil 22.) migration – in general, any movement of individuals or populations from one location to another; specifically, a periodic group movement that is characteristic of a given population or species 23.) perennial – a plant that usually lives and reproduces more than one year 24.) annual – a plant that usually germinates, flowers, and dies in a year or a season