Genetics Review _12_
advertisement

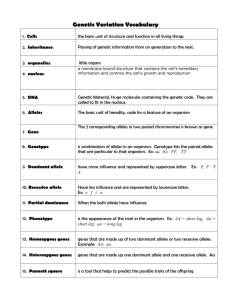
Genetics Review Vocabulary you will need to know: 1.Genotype: an organism’s genetic makeup. 2.Phenotype: an organism’s outward appearance. 3. Allele: Different forms of a gene, which produce variations in a genetically inherited trait. For example, different alleles produce different hair colors – brown, blond, red, etc… 4. Homozygous: pair of identical alleles for a character. For example, (BB) 4.Heterozygous: having 2 different alleles for a character. For example, (Bb) 5. Genes: parts of hereditary information passed from parents to children. For example Genes carry the blue-print for each individual for her or his specific traits. 6. Gamete: sex cells (sperm or egg cells). Males are represented by XY and females are represented as XX 7. Sex-linked disorder: gene for a trait is carried on one of the sex chromosomes. example color color blindness, hemophilia 8. Sexual reproduction: a new organism is formed from two organisms. For example, all organisms that have two parents such as humans, dogs, and birds. 9. Asexual reproduction: a new organism is produced from one organism. “Since the offspring from this process contain the same genetic material as one another (and the same as the original single parent), they can be described as a clone.” (http://www.biotopics.co.uk),For example, all organisms that divided by mitosis or binary fission (bacteria) or budding (hydra). 10. Dominant: mask recessive genes (shown as a capital letter - A) 11. Recessive: is masked by dominant genes (shown as a lower case letter - a) Dominant: dimples (D) Recessive: no dimples (d) Parents: Dd x dd D d d Dd dd d Dd dd Complete the Punnett Square: 50% Dd : 50% dd % Genotype 50% Dimples : 50% no dimples % Phenotype 1. Who is the father of Genetics? Gregor Mendel 2. Which type of reproduction results in more diversity in offspring? Sexual reproduction 3. What is the branch of mathematics that helps you predict the chance that something will happen? probability