Cytologic profile of rhabdoid tumor of the kidney
advertisement

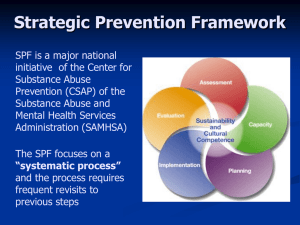
Acta Cytol. 2003 Nov-Dec;47(6):1055-8. Cytologic profile of rhabdoid tumor of the kidney. A report of 3 cases. Barroca HM, Costa MJ, Carvalho JL. Department of Anatomic Pathology, Hospital de S. Joao, Al. Hernani Monteiro-4200 Porto, Portugal. hbarroca@iol.pt BACKGROUND: Malignant rhabdoid tumor of the kidney (MRTK) is a rare malignant neoplasm that usually presents as an abdominal mass. The histogenesis is uncertain, and cases outside the kidney have been reported. An association with separate primary tumors of primitive neuroepithelial origin occurring in the midline of the posterior or middle cranial fossa has been reported in approximately 15% of cases. CASES: Three patients, a 7-month-old girl and two boys, aged of 6 and 2 months of age, underwent fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) for the diagnosis of renal masses. In 2 cases the smears revealed round to polygonal cells, singly or arranged in irregularly shaped clusters. The neoplastic cells did not differ much in shape and exhibited clear, empty nuclei with prominent nucleoli; the cytoplasm was abundant and sometimes eosinophilic. In the remaining case the aforementioned characteristics of the nuclei and cytoplasm were not as prominent, and sheets of fibrovascular stroma, with attached neoplastic cells, were seen. Diagnosis of MRTK was suspected in every case based upon morphology and immunocytochemistry; the diagnosis was histologically confirmed in the surgical specimens. CONCLUSION: MRTK may pose diagnostic problems due to its broad morphologic spectrum. Distinction from Wilms' tumor and clear cell sarcoma of the kidney is essential for therapeutic proposes. The results obtained in the FNAB study of these 3 cases demonstrate that diagnosis of MRTK may be proposed from fine needle aspiration smears using conventional methods together with ancillary ones (immunocytochemistry and electron microscopy). Publication Types: Case Reports Diagn Cytopathol. 2003 Oct;29(4):194-9. Flow cytometric S-phase fraction as a complementary biological parameter for the cytological grading of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Pinto AE, Cabecadas J, Nobrega SD, Mendonca E. Department of Morphologic Pathology, Portuguese Oncologic Institute, Lisbon Center, Portugal. apat@ipolisboa.min-saude.pt Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a technique that can overcome tissuesampling disaggregation problems related to DNA flow cytometry analysis. The aim of this study, with long-term follow-up (median, 72 mo), was to investigate the prognostic value of DNA ploidy and S-phase fraction (SPF) in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL), and additionally, the relevance of SPF in the grading of NHLs, using FNAC. The series comprised 76 patients with NHL (32 indolent and 44 aggressive tumors, including 14 Burkitt lymphomas) and 30 patients with reactive lymph node enlargement used as a control group. DNA flow cytometry was performed on fresh samples obtained by FNAC. NHL grading was done according to the updated Kiel classification. The 5-yr overall survival of patients with NHL was determined using the Kaplan-Meier method. All samples of the control group and 81.6% of the NHLs showed a DNA diploid pattern. Fourteen cases (18.4%) were DNA aneuploid with bimodal distribution: slight hyperdiploidy and near-tetraploidy. Despite the higher incidence of aneuploidy in aggressive than in indolent tumors (22.7% vs. 12.5%), no correlation between DNA ploidy and NHL grading was observed. In contrast, SPF revealed a strong correlation with grading (P=0.0001). The mean SPF values varied from 6.5% in indolent NHLs, to 20.4% in aggressive not-otherwise-specified (NOS) NHLs, and to 35.3% in Burkitt lymphomas. Nearly all aggressive NHLs had an SPF >15%, while the vast majority of indolent NHLs showed an SPF <10%. The mean SPF value in the reactive node group was 6.6%. NHL grading significantly was correlated to survival (P=0.004) only if the Burkitt lymphomas, which showed the best prognosis, were analyzed as an independent group. There was a trend that did not reach statistical significance (P=0.072) for a worse clinical outcome of patients with aneuploid tumors. When mean SPF values were used as cutoff points to divide both indolent NHLs and aggressive NOS NHLs into two proliferative subgroups, no differences in relation to survival were found (P=0.763 and P=0.994, respectively). Also, no proliferative difference was verified between indolent NHLs and the reactive lymph node group (P=0.223). These results show that flow cytometric SPF is a valuable complementary parameter for grading NHLs on FNAC samples, but it appears to give no additional prognostic information on subset analyses. Copyright 2003 Wiley-Liss, Inc. Int J Biol Markers. 2003 Jan-Mar;18(1):7-12 Overall survival in advanced breast cancer: relevance of progesterone receptor expression and DNA ploidy in fine-needle aspirates of 392 patients. Pinto AE, Andre S, Mendonca E, Silva G, Soares J. Department of Pathology, Portuguese Oncological Institute, Lisbon, Portugal. apat@ipolisboa.min-saude.pt Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is essential for making a diagnosis in advanced breast cancer. The determination of hormone receptors in the material obtained is useful for predicting patient response to endocrine therapy, but the prognostic value of hormone receptor expression as well as the clinical utility of DNA flow cytometry are controversial. The aim of this prospective study with long-term follow-up (median: 81 months) was to evaluate these biomarkers in relation to overall survival in a series of 392 patients with advanced breast cancer (stage IIB, n=106; IIIA, n=66; IIIB, n=174; and IV, n=46) using FNAC. Estrogen and progesterone receptor expression was found in 65.1% and 46.1% of the tumors, respectively. Hormone receptors were not found to be associated with clinical staging. DNA aneuploidy was present in 70.9% of the cases and the median S-phase fraction (SPF) was 9.4%. There was a significant correlation of aneuploidy and high SPF with lack of hormone receptors. In univariate analysis, advanced disease stage, absence of hormone receptors, DNA aneuploidy and high SPF showed a statistically significant correlation with poor clinical outcome. In multivariate analysis, disease stage, progesterone receptors and DNA ploidy retained independent prognostic significance in relation to overall survival. These data indicate that progesterone receptor expression and DNA ploidy are independent prognostic factors in advanced breast cancer. Acta Cytol. 2003 Jan-Feb;47(1):5-12 Preoperative diagnosis of suspicious parathyroid adenomas by RT-PCR using mRNA extracted from leftover cells in a needle used for ultrasonically guided fine needle aspiration cytology. Cavaco BM, Torrinha F, Mendonca E, Pratas S, Boavida J, Sobrinho LG, Leite V. Center for the Investigation of Molecular Pathobiology, Departments of Imagiology and Endocrinology, Cytology Laboratory, Francisco Gentil Portuguese Oncology Institute, Lisbon, Portugal. OBJECTIVE: To determine the usefulness of reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) detection of parathormone (PTH) gene mRNA in needle aspirates to confirm the parathyroid nature of suspicious cervical lesions in patients with hyperparathyroidism. STUDY DESIGN: Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) was performed on 12 patients with suspected parathyroid adenomas. The aspirates were subjected to cytologic and chromogranin A examination. Messenger RNA was isolated from left-over cells within the needle, and RT-PCR was used to amplify mRNA encoding PTH. RESULTS: The 12 aspirates were positive by PTH RTPCR, and molecular diagnosis was confirmed by histologic examination. The lower sensitivity of cytologic and immunocytochemical methods was demonstrated, respectively, by 67% and 50% of positive results. Sensitivity assays demonstrated that with our system, PTH RT-PCR products are obtained from as few as 10 pg of parathyroid mRNA. CONCLUSION: The present study showed that RT-PCR-based analysis of PTH gene transcripts in aspirates, obtained by US-guided FNAC of cervical lesions suspicious for parathyroid adenoma, is a feasible, sensitive and specific method for preoperative diagnosis of parathyroid adenomas. Publication Types: Evaluation Studies Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Aug 15;9(9):3413-7. Title : Detection of gene promoter hypermethylation in fine needle washings from breast lesions. Authors: Jeronimo C, Costa I, Martins MC, Monteiro P, Lisboa S, Palmeira C, Henrique R, Teixeira MR, Lopes C. Department of Genetics, Portuguese Oncology Institute-Porto, 4200-072 Porto, Portugal. cjeronimo@hotmail.com PURPOSE: Fine needle aspiration (FNA) is used widely in diagnostic assessment of breast lesions. However, cytomorphological evaluation depends heavily on the proficiency of cytopathologists. Because epigenetic alterations are frequent and specific enough to potentially augment the accuracy of malignant disease detection, we tested whether hypermethylation analysis of a panel of genes would distinguish benign from malignant breast FNA washings. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: FNA washings were collected from 123 female patients harboring suspicious mammary lesions. Sodium bisulfite-modified DNA was amplified by methyl-specific PCR (MSP) for CDH1, GSTP1, BRCA1, and RARbeta to detect gene promoter CpG island methylation. Paired samples of 27 breast cancer tissue and 7 fibroadenomas and 12 samples of normal breast tissue, collected postoperatively, were also analyzed. MSP results were compared with conventional cytomorphological diagnosis. RESULTS: FNAs were cytomorphologically diagnosed as benign (25 cases), malignant (76 cases), suspicious for malignancy (6 cases), and unsatisfactory (16 cases). Percentages of methylated CDH1, GSTP1, BRCA1, and RARbeta in FNA washings were 60, 52, 32, and 16%, and 65.8, 57.9, 39.5, and 34.2% for benign and malignant lesions, respectively. These differences did not reach statistical significance. In all of the paired benign lesions tested, there was absolute concordance. Sixty-seven percent (18 of 27) of FNA washings displayed hypermethylation patterns identical to malignant paired tissue. No methylation was found in the normal breast samples for any of the genes. CONCLUSIONS: Detection of gene hypermethylation in FNA washings by MSP analysis is feasible, but the selected gene panel does not discriminate between benign and malignant breast lesions. Acta Cytol 2004;48:57-63 Title: Thyroid Cell Proliferation in Graves' Disease: Use of MIB-1 Monoclonal Antibody Authors: Gláucia M. F. S. Mazeto, M.D., Ph.D., Maria Luiza C. S. Oliveira, Ph.D., Carlos R. Padovani, Ph.D., Mário R. G. Montenegro, M.D., Ph.D., Flávio F. Aragon, Ph.D., and Fernando C. L. Schmitt, M.D., Ph.D., M.I.A.C. Objective: To measure thyroid cell proliferation in patients with Graves' disease (GD) before and during treatment with antithyroid drugs. Study Design: Patients were assessed by fine needle aspiration biopsy before (n=20) and after 4 (n=19) and 12 months of treatment (n=15) with propylthio-uracil or methimazole. Cell proliferation index (CPI) was estimated by immunocytochemistry using MIB-1. CPI was studied in relation to the cytologic parameters of the smears; clinical parameters, such as Wayne's Clinical Index (WCI) and time without treatment; laboratory parameters, such as 131I uptake and dosage of serum free thyroxin and thyroid-stimulating hormone; and thyroid ultrasound. Results: CPI varied from 0.00% to 25.00% before treatment, 0.00% to 23.00% at 4 months and 0.00% to 14.84% at 12 months. CPI median values were 6.50%, 4.30% and 3.30%, respectively (before and after 4 months and 12 months of treatment). CPI had a positive correlation with WCI and FT4 at 12 months of treatment. Conclusion: Thyroid CPI in GD varies from case to case. However, due to its decreasing pattern during follow-up and its positive correlation with thyrotoxicosis severity, CPI may indicate the functional status of the gland and contribute to a better understanding of GD. Keywords:Graves' disease, thyroid diseases, aspiration biopsy, monoclonal antibodies, MIB-1 Acta Cytol 2004;48:187-193 Title: Comparison of Manual and Automated Methods of Liquid-Based Cytology: A Morphologic Study Authors: Venancio Avancini Ferreira Alves, M.D., Ph.D., Marluce Bibbo, M.D., Sc.D., F.I.A.C., Fernando Carlos Landèr Schmitt, M.D., Ph.D., M.I.A.C., Fernanda Milanezi, M.D., and Adhemar Longatto Filho, M.Sc., Ph.D., P.M.I.A.C. Objective: To evaluate the morphologic characteristics of gynecologic samples prepared by 3 different methods of liquid-based cytology. Study Design: Cytologic samples from representative cases of each diagnostic category of squamous epithelial lesion, prepared by automated and manual liquid-based systems, were analyzed by 3 laboratories in the United States, Portugal and Brazil. The systems included: ThinPrep(r) (automated, U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved; Cytyc Corp., Boxborough, Massachusetts, U.S.A.), Autocyte(r) PREP (South American system, manual; TriPath Imaging, Inc., Burlington, North Carolina, U.S.A.) and DNACITOLIQ(r) (manual; Digene Brazil, São Paulo, Brazil). A panel of 16 morphologic parameters was evaluated: cellularity, clean background, uniform distribution, artifacts, cellular overlapping, architectural and cytoplasmic distortion, cytoplasmic vacuolization, cellular elongation, imprecise cytoplasmic borders, folded cytoplasmic borders, nuclear hyperchromasia, coarse chromatin, prominent nucleolus, irregular nuclear borders, atypical mitosis and inflammatory infiltrate. Negative, atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance, low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) and high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) cases were included. Cases without biopsies were confirmed by consensus. Results: Cellularity was adequate in all samples. Clean background was observed in the vast majority of samples with all liquid-based systems. Uniform distribution was frequently found in ThinPrep(r) and Autocyte(r) PREP samples but not in DNACITOLIQ(r). Artifacts were not present in DNACITOLIQ(r) samples, rare in ThinPrep(r) and observed in 8 (34.7%) Autocyte(r) PREP. Cellular overlapping was observed in all 3 system samples: 11 (31.42%) cases in ThinPrep(r), 16 (69.56%) in Autocyte(r) PREP and 17 (68%) in DNACITOLIQ(r) System. Architectural and cytoplasmic distortion were present in 3 cases of HSIL (13%) and cytoplasmic vacuolization in 2 cases of LSIL and 1 HSIL of Autocyte(r) PREP. Cellular elongation was found in 13 (56.5%) Autocyte(r) PREP and in 5 (20%) DNACITOLIQ(r) samples. Inflammatory infiltrate was found in all 3 system samples but with more frequency in the Autocyte(r) PREP (69.56%) and DNACITOLIQ(r) System (72%). Conclusion: This study clearly indicated that in spite of the different methodologies, the 3 methods adequately preserved cellular structure for morphologic evaluation. The choice of method will depend on price, availability and procedures involved. Keywords:cervix neoplasms, cervix diseases, mass screening, Papanicolaou smear, ThinPrep(r), Autocyte(r) PREP, DNACITOLIQ(r) System