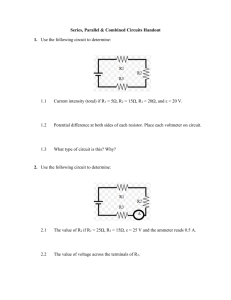
file_77_1420522885POWER TECHNOLOGY (71) 3th & 4th ALLl
advertisement

1 BANGLADESH TECHNICAL EDUCATION BOARD 4-YEAR DIPLOMA-IN-ENGINEERING PROGRAM POWER TECHNOLOGY SYLLABUS THIRD & FORTH SEMESTER 2 POWER TECHNOLOGY (71) THIRD SEMESTER Sl. No Subject code MARKS Name of the subject T P C Theory Practical Total Cont. Final Cont. Final assess exam. assess exam. 30 120 25 25 30 120 25 25 1. 2. 7131 6734 Engineering Thermodynamics General Electricity 3 3 3 3 4 4 3. 6632 Computer Application -2 0 6 2 - - 50 50 100 4. 5. 5931 5922 Math-III Physics-II 3 3 3 3 4 4 30 30 120 120 50 25 25 200 200 6. 5722 English-II 2 2 3 20 80 50 - 150 7. 5811 Social Science-1 2 0 2 20 80 - - 100 15 23 23 150 600 225 175 1150 Total 200 200 POWER TECHNOLOGY (71) FOURTH SEMESTER Sl. No Subject code MARKS Name of the subject T P C Theory Practical Total Cont. Final Cont. Final assess exam. assess exam. 30 120 25 25 30 120 25 25 1. 2. 7141 7142 Engine Details Engineering Mechanics 3 3 3 3 4 4 200 200 3. 7144 2 6 4 20 80 50 50 200 4 6744 Automotive suspension, Brake & Transmission system Electrical Machines 2 3 3 20 80 25 25 150 5 6 6811 7042 Basic Electronics Machine Shop Practice 2 1 3 6 3 3 20 10 80 40 25 50 25 50 150 150 7 5821 Social Science-2 2 0 2 20 80 - - 100 Total 14 21 22 140 560 200 200 1150 3 PT-7131 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS T 3 P 3 C 4 AIMS To provide the students with an opportunity to acquire knowledge, skill and attitude in the area of engineering thermodynamics with special emphasis on. heat and temperature Application of heat thermodynamic systems thermodynamic laws and processes properties of gas, vapor and steam thermodynamic cycles transmission of heat SHORT DESCRIPTION Definition and Scope of thermodynamics; Heat and heat units; Temperature and its scales; Thermodynamic systems; Thermodynamic laws & processes; Properties of gas; vapor and steam; Entropy and enthalpy; Thermodynamic air cycles; Thermodynamic vapor cycles; Refrigeration and heat pumps; Transmission of heat. theory: INTRODUCTION 1. Understand the scope of thermodynamics 1.1. Define thermodynamics. 1.2. Outline the importance of thermodynamics in engineering field. 1.3. Identify different applications of thermodynamics in engineering field. Heat & temperature 2. Understand the basic concept of heat & temperature 2.1. Define heat. 2.2. Mention the units of heat. 2.3. Convert one heat unit to another heat units. 2.4. Define absolute temperature in rankine and kelven scale. 2.5. Relate rankine and kelvin scales of temperature. 2.6. Distinguish between heat and temperature. 2.7 Explain heat is a low grade energy and work is a high grade energy . 2.8 Solve problems on converting heat units and temperature scale. SPECIFIC 4 HEAT OF GASES 3 Understand the concept of specific heat of gases . 3.1 Define specific heat , thermal capacity and water equivalent. 3.2 Describe the terms specific heat at constant pressure (Cp) and specific heat at constant Volume (Cv) 3.3 Mention Rgnault’s law. 3.4 Relate two specific heats (Cp and Cv). 3.5 Explain the ratio of two specific heats (γ) 3.6 Mention the standard value of Cp, Cv, and γ for some common 3.7 Explain the molar specific heats of a gas. 3.8 Solve problems on Cp, Cv, and γ. gases. LATENT HEAT AND SENSIBLE HEAT 4 Understand the concept of latent heat and sensible heat. 4.1 Define sensible heat and latent heat. 4.2 Explain the terms freeing and boiling point temperature in different scale. 4.3 Explain different types of latent heat. 4.4 List the values of different latent heat for water and Ice in different units. 4.5 Computer the formulae to calculate sensible sensible heat and latent heat. 4.6 Solve problems on sensible heat, latent heat and total heat. THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEMS 5 Understand the aspects of thermodynamic systems. 5.1 Define thermodynamic system, boundary and surrounding. 5.2 Explain the different system i,e open system, closed system and with example. 5.3 List the properties of thermodynamic systems. 5.4 Describe the control volume. 5.5 Compare the thermodynamic system and control volume. LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS 6 Understand the laws of thermodynamics. 6.1 Sate the laws of thermodynamics. 6.2 Explain the 1st law of thermodynamics. 6.3 Mention the corollaries of 1st law of thermodynamics. isolated system 5 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 Explain the 2nd law of thermodynamics. Mention the corollaries of 2nd law of thermodynamics. Mention the physical significance of 1st and 2nd law of thermodynamics. Explain the 3rd law of thermodynamics. Explain the Zeroth law if thermodynamic. Solve problems on laws of thermodynamics. LAWS OF PERFECT GASES 7 Understand The laws of perfect gases. 7.1 Dentine perfect gas. 7.2 Explain the variables of perfect gases. 7.3 State boyle’s law, Charle’s law and Gay-Lussac law, Avogdro’s law. 7.4 Explain the general gas equation, characteristic gas equation and universal gas constant or molar constant. 7.5 Solve problems using gas laws and equations. INTERNAL ENERGY & ENTHALPY 8 Understand the internal energy and enthalpy of gases. 8.1 Define internal energy. 8.2 Define enthalpy. 8.3 Explain the internal energy of gas heated at constant volume and constant pressure. 8.4 Relate between internal energy and enthalpy. 8.5 Explain Joules law. 8.6 Solve problems on change of internal energy. METHODS OF HEATING AND EXPANDING OF GASES 9. Understand the thermodynamic processes of perfect gases. 9.1 Define thermodynamic process. 9.2 Explain the flow processes and non-flow processes of gases. 9.3 Describe the various non-flow thermodynamic processes with p-v and t-s diagrams. 9.4 Determine the work done by the gases during above process. 9.5 Explain the steady and unsteady flow processes. 9.6 Describe the steady flow energy equations. 9.7 Solve problems on thermodynamic processes. ENTROPY OF GASES. 10. Understand the entropy of perfect gases. 10.1 Define entropy. 6 10.2 Mention the importance of entropy. 10.3 Describe the principle of increase of entropy. 10.4 Establish the relation between heat & entropy. 10.5 Explain the general expression for change of entropy of a 10.6 perfect gases during various thermodynamic processes. 10.7 Solve problems on entropy of different thermodynamic processes. VAPOR AND STEAM 11 Understand the properties of vapor and steam 11.1 Name the three-state of a substance. 11.2 Distinguish between the steam and vapors. 11.3 Discuss the triple point of a substance. 11.4 List the properties of vapors. 11.5 Explain the formation of steam at constant pressure. 11.6 Describe the important terms for steam (wet steam, dry saturated steam, superheated steam, dryness fraction specific volume of steam, etc) 11.7 Explain the method of using steam table. 11.8 Explain the mollier diagram, 11.9 Find out the different properties of steam from steam table at certain pressure and temperature . THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES 12 Understand the aspects of thermodynamic cycles. 12. 1 Define thermodynamic cycle. 12. 2 List the assumption in thermodynamic cycles. 12. 3 Explain the reversible and irreversible cycles. 12. 4 State the meaning of air standard cycle. Gas power cycle and vapor power cycle. 13 Understand the aspects of non-conventional thermodynamic air cycles. 13.1 List the non-conventional air cycle . 13.2 Describe the cannot cycle with P-V and T-S diagrams. 13.3 Describe Stirling and Ericsson cycles with P-V and T- S 13.4 Determine air standard efficiencies of carnot cycles. 13.5 Solve problems on Carnot cycles. 14 Understand the aspects of conventional air cycles. 14.1 List the conventional air cycles. 14.2 Describe the conventional air cycles i,e Otto cycle, diesel cycle dual cycle and Brayton cycle with on PV and T-S diagrams. 14.3 compare oHo, Diesel and Dual cycles. 14.4 Determine the air standard efficiency of Otto & Diesel cycle. 14.5 Compare the theoretical Otto and diesel cycles with the actual Otto and Diesel cycles. 14. 6 Solve problems on Otto & Diesel cycle 7 15 Understand the aspects of thermodynamics vapor cycles 15.1 Define vapor cycle. 15.2 Describe the Rankin cycle with incomplete evaporation and modified Rankine cycle with superheated steam. 15.3 Define reheat, regenerative and reheat-regenerative vapor cycles. 15.4 Explain the reheat, regenerative and reheat-regenerative vapor cycles with P-V and T-S diagrams. 15.5 Compare the reheat, , regenerative and reheat-regenerative vapor cycles. 15.6 Describe the binary vapor cycle and topping cycle. REFRIGERATION AND HEAT PUMPS 16. Understand the features of refrigeration and heat pumps. 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 16.6 16.7 State the meaning of heat engine refrigeration and heat pump cycles. Describe the reverse cannot cycle with P-V and T-S diagrams. Describe the vapor compression mechanical refrigeration cycle. Determine the Co-efficient of performance COP (heating & refrigerating) Describe the capacity of the refrigerating Machine Describe the vapor absorption refrigeration cycle Solve problems on COP and TR. TRANASMISSION OF HEAT 17. Understand the modes of heat transfer. 17.1 Define conduction, convection and radiation of heat. 17.2 Describe the coefficient of thermal conductivity. 17.3 Deduce the formula of the conductive heat flow through flat surface and thick cylinder. 17.4 Deduce the formula of the heat flow by convection through 17.5 Deduce the formula of the radiant heat transmission. 17.6 Solve problem on the three modes of heat transfer. tube. 18. Understand the features of heat exchanges 18.1 Define heat exchanger. 18.2 Mention the classification of the heat exchangers. 18.3 Explain the operation of parallel flow, counter flow and cross flow heat exchangers 18.4 Explain Log mean Temperature Difference (LMTD) 18.5 Explain the operation of direct contract heat exchanger with 18.6 Explain the operation of regenerative heat exchanger with 18.7 Explain the operation of recuperative heat exchanger. Practical: example. example 8 1. Verify Boyle’s law with Boyle’s law test apparatus i.e. P1V1=P2V2……………..= constant. 2. Verify Gay – Lussac law by measuring pressure of the refrigeration cylinder in different temperature i.e. p1 P2 …………..= constant. T1 T2 3. Observe the 4-stroke Otto Cycle with a model. 4. Observe the 4-stroke diesel Cycle with a model. 5. Observe the 2-stroke diesel Cycle with a model. 6. Determine the mechanical equivalent of heat by Joule’s apparatus to verify first law of thermodynamics. 7. Observe the heat transfer modes (Conduction, convention and radiation) with refrigerator or an engine. 8. Observe Rankine cycle with a steam engine model. 9. Observe the refrigeration cycle to verify second law of thermodynamics. 10.Determine the amount of heat exchange by a parallel and counter flow heat exchangers. Reference Book:1. Engineering Thermodynamics 2. Engineering Thermodynamics - R. S. Khurmi - P.K. Nag 3. Heat and Thermodynamics -Brij lal N. Subrahmanyam 4. Thermal Engineering - A.S. Sarao Publishers: Mc- GRAW- HILL BOOK COMANY New York- st, louis San Francisco Dallas Tononto, London Sydney. 9 6732 GENERAL ELECTRICITY T 3 AIMS P 3 C 4 To provide the concepts of basic network theorem. To provide understanding and skill on single phase AC circuits. To provide understanding and skill on poly phase system. To provide understanding of power & power factor in AC circuits. To develop understanding and skill on DC machines. To develop understanding and skill on AC machines. To develop understanding and skill on electrical measurements and measuring instruments. SHORT DESCRIPTION Network theorems – Kirchhoffs law, Thevinins theorem, Nortons theorem; super position theorem; AC fundamentals; Alternating quantities; Single phase AC circuits; RLC series & parallel circuit, Power and power factor in AC circuit; Poly phase system; Star/delta connection; Power and energy; DC Generator; DC Motor; Alternator; Transformer; Induction motor; Electrical measuring instruments and measurements. DETAIL DESCRIPTION Theory: Network Theorem’s (DC only) 1. Apply the principle of circuit theorems 1.1 Explain kirchhoffs current and voltage law. 1.2 Solve problems on KCL and KVL 1.3 Explain thevinins theorem. 1.4 Solve problems related to thevinins theorem. 1.5 Explain Nortons theorem. 1.6 Solve problems related to Nortons theorems. 1.7 Explain superposition theorem. AC fundamentals 2. Understand the AC fundamentals. 2.1 Explain the generation of AC voltage. 2.2 Express the deduction of the equation, e=E max Sinwt. 2.3 Define cycle, frequency and time period. NP 2.4 Show the relation, f= . 120 2.5 Explain the phase and phase difference with diagram. 2.6 Solve problems relating to AC generation. 3. Understand the concept of alternating quantities. 10 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Define instantaneous, maximum, average and rms values of alternating quantities. Define form factor and peak factor. Solve problems relating to instantaneous, average and rms values. Define Ohmic resistance and skin effect. Compare ohmic & effective resistance. Distinguish between AC and fluctuating DC. AC CIRCUIT 4. Understand the parameters of alternating current circuits. 4.1 Explain the resistance, inductance and capacitance. 4.2 Distinguissh between inductive and capacitive effect. 4.3 State the formulae of inductive and capacitive reactance. 4.4 Solve problems on inductive and capacitive reactance. 4.5 Describe pure resistive, inductive and capacitive circuits. 4.6 Explain the term waveform, phase angle and phasor diagram. 4.7 Show the relationship between current and voltage of pure resistive, inductiive and capacitive circuits by waveform. 4.8 Draw the phasor diagram of pure resistive, inductive and capacitive circuits. 4.9 Solve problems on pure resistive, inductive and capacitive circuit. 5. Understand the concept of AC series/parallel circuit containing RL and RC. 5.1 Sketch a circuit containing resistance and inductance in series/parallel. 5.2 Explain the vector & phasor diagram of RL series/parallel circuit. 5.3 Find the impedance, current and voltage drop in RL series/parallel circuits. 5.4 Draw the impedance triangle of RL series/parallel circuits. 5.5 Sketch a RL series/parallel circuits. 5.6 Explain the vector & phasor diagram of RC series/parallel circuit. 5.7 Find the impedance, current and voltage drop in RC series/parallel circuits. 5.8 Draw the impedance triangle of RC series/parallel circuits. 5.9 Solve problems relating to RL & RC circuit. 6. Understand the concept of RLC series/parallel circuit. 6.1 Sketch a circuit containing resistance, inductance, and capacitance in series/parallel. 6.2 Explain the vector & phasor diagram of RLC series/parallel circuit. 6.3 Draw the impedance triangle of RLC series/parallel circuits. 6.4 Calculate the inductive reactance, capacitive reactance, total impedence, current & voltage drops in RLC circuit. 6.5 Describe the resonance and resonance frequency in RLC circuit. 6.6 Solve problems relating to RLC circuit. 7. Understand the concept of power & power factor in AC circuit. 7.1 Define power, power factor, active and reactive power. 7.2 Calculate the power and power factor of resistive and reactive circuits. 7.3 Calculate the power and power factor, active & reactive power of RL, RC and RLC circuit. 11 8. Understand the concept of poly phase power system. 8.1 State the meaning of the term AC poly phase power system. 8.2 Mention the advantage of poly phase system over 1-phase system. 8.3 State the generation of poly phase emf. 8.4 State the sequence of poly phase power system. 9. Understand the features of 3-phase star connected power system. 9.1 Sketch a 3-phase 3-wire & 3-phase 4-wire star connected system. 9.2 Draw the phasor diagram of a 3-phase 3-wire star connected system. 9.3 Express the formulae, I L= Ip and VL=3Vp 9.4 Identify neutral wire in a 3-phase star connected system. 9.5 Solve problems on 3-phase star connected power system. 10. Understand the features of 3-phase delta connected system. 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 Sketch the circuit diagram of a 3-phase delta connected system. Sketch the phasor diagram of a 3-phase delta connected system. Explain the formulae VL= Vp and IL=3 Ip Solve problems on delta connected balanced load system. Compare the advantages of star connection system with those of delta connection system. DC GENERATOR 11. Understand the features of DC Generator. 11.1 State the principle of operation of a simple DC generator. 11.2 Identify different types of DC generators. 11.3 Interpret the nameplate information of a DC generator. 11.4 Identify the different parts of DC generators. 11.5 Identify armature, pole, brush, field coil, commutator and yoke of DC generator. 11.6 Describe the principle of operation of DC generators. 11.7 Describe the emf equation of DC generators. 11.8 Explain the building up voltage of DC shunt generators. DC MOTOR 12. Understand the features of operation of DC motor 12.1 Explain the working principle of DC motor. 12.2 Identify different parts of DC motor. 12.3 Explain the principle of operation of DC motors. 12.4 Draw connection diagrams of DC series, shunt and compound motor. 12.5 Explain the term back emf of DC motor. 12.6 Express the formula of the mechanical power developed in DC motor. 12.7 List at least five uses of DC motor. ALTERNATOR 13. Understand the features of AC generator/alternator. 12 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 13.5 Explain the working principle of AC generator/alternator. Identify different types of alternator. Express the deduction of the emf equation of an alternator. Explain the efficiency and regulation of alternator. Describe different losses of alternator. TRANSFORMER 14. Understand the principle of operation of transformer. 14.1 Explain the working principle of transformer. 14.2 Explain the transformer action. 14.3 Express the derivation of the emf equation of transformer. 14.4 Define transformation ratio. 14.5 Solve problems related to transformation ratio and emf equation of transformer. 14.6 Interpret the nameplate data of a transformer. INDUCTION MOTOR 15. Understand the features of 3-phase induction motor. 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 15.5 15.6 15.7 State the meaning of induction motor. Identify different types of 3-phase induction motor. Identify different parts of 3-phase induction motor. Explain the working principle of 3-phase induction motor. State the necessity of starter for starting 3-phase induction motor. State different methods of starting squirrel-case and slip-ring induction motor. Interpret the nameplate data of a 3-phase induction motor. 16. Understand the features of 1-phase induction motor. 16.1 Explain the working principle of a capacitor type 1-phase induction motor. 16.2 Identify different parts of capacitor type 1-phase induction motor. 16.3 Name different types of 1-phase induction motor. 16.4 Explain the working principle of a Universal motor. 16.5 Uses of different types of 1-phase induction motor. MEASURING INSTRUMENT 17. Understand the features of electrical measuring instruments. 17.1 State electrical measuring instruments. 17.2 Identify different types of electrical measuring instruments. 17.3 Describe the working principle of indicating instrument (Permanent magnet moving coil ammeter, voltmeter) 17.4 Differentiate between indicating, integrating and recording instruments. 17.5 List the practical applications of different types of measuring instruments. 13 17.6 17.7 17.8 Sketch connection diagram of Ammeter, Voltmeter, Wattmeter and Energy meter in an electric circuit. Describe the construction and working principle of Megger. State the uses of Megger. Practical 1. 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Show skill in verifying Kirchhoffs laws. Select experiment circuit, components, meters and necessary materials. Construct a series-parallel circuit. Select the series section of the circuit. Verify Kirchhoffs voltage law. Select the parallel section of the circuit. Verify Kirchhoffs current law. 2. Find the maximum and rms values of current, voltage and frequency by oscilloscope. 2.1 Identify the control & function knobs of oscilloscope. 2.2 Prepare the oscilloscope to measure the values. 2.3 Check all connections. 2.4 Observe the AC signal and meaasure the maximum value, rms values and frequency. 2.5 Note down the observations. 3. Draw the vector diagram of a RLC series circuit determining the value of resistance, inductance capacitance and power factor. 3.1 Sketch the circuit diagram for determining resistance, capacitance and inductance of RLC series circuit. 3.2 Select equipments, tools & materials required for the experiment. 3.3 Connect the circuit according to the circuit diagram using proper equipment. 3.4 Check all the connection points before energizing the circuit. 3.5 Apply the proper voltage & record readings from the meters. 3.6 Find the value of resistance & phase angle from relevant data. 3.7 Sketch the vector diagram with the relevant data as obtained. 4. Draw the vector diagram of a RLC parallel circuit determining the value of resistance, inductance and capacitance 4.1 Sketch the circuit diagram of a RLC parallel circuit. 4.2 Select the equipment, tools & materials for the experiment. 4.3 Connect the circuit according to the circuit diagram. 4.4 Check all the connection points before energizing the circuit. 4.5 Connect the power supply to the circuit and record the readings from the meter. 4.6 Determine the values of resistance, inductance, capacitance and phase angle from the relevant data. 4.7 Sketch the vector diagram with the help of relevant data as obtained. 5. Measure line and phase voltage & current in a 3-phase star/delta connected load. 5.1 Sketch the circuit diagram for a 3-phase star/delta connected load. 5.2 Select the instrument, tools and materials required for the experiment. 5.3 Connect the circuit according to the circuit diagram. 14 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 Check all the connection points before energizing the circuit. Record the readings of the instruments. Compare the recorded values with calculated values. Note down the observations. 6. Construct vector diagram measuring current, voltage and power in a balanced 3-phase delta connected inductive load. 6.1 Sketch the circuit diagram for measuring current, voltage and power of a 3-phase delta connected load. 6.2 Select the necessary equipment, tools and materials. 6.3 Connect the circuit according to the circuit diagram. 6.4 Check all the connections before energizing the circuit. 6.5 Record the readings from the meters used in the circuit. 6.6 Draw the vector diagram for the circuit. 7. Construct vector diagram measuring current, voltage and power in a balanced 3- phase star connected inductive load. 7.1 Sketch the circuit of a star connected power system for measuring current. voltage and power of the circuit. 7.2 Select the instrument, tools and materials required for the circuit. 7.3 Connect the circuit components as per diagram. 7.4 Check all the connection points before energizing the circuit. 7.5 Record the readings from the meters used in the circuit. 7.6 Draw the vector diagram. 7.7 Note down the observations. 8 Start a DC shunt motor by 3-point starter. 8.1 Sketch the circuit diagram. 8.2 Select the instrument, tools and materials required for the job. 8.3 Connect the motor starter according to the circuit diagram. 8.4 Apply proper supply voltage to the circuit. 8.5 Manipulate the starter to have the desired speed. 8.6 Note down the observations. 9. Draw the no-load characteristic curve (relationship between excitation current and generated voltage) of an alternator. 9.1 Sketch the circuit diagram for the experiment. 9.2 Select the equipment, tools and materials required for the experiment. 9.3 Connect the equipment/machine according to the diagram. 9.4 Apply the proper supply voltage to the circuit. 9.5 Record the values of the excitation current and corresponding generated voltage. 9.6 Plot the characteristic curve from the recorded data. 9.7 Note down the observations. 10. Verify the turn ratio of a transformer. 10.1 Sketch the circuit diagram for the experiment. 10.2. Select the machine, instrument and tools required for the experiment. 15 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.7 Connect the circuit according to the circuit diagram. Apply the voltage to primary side of the transformer. Record the values of voltage and currents on both sides of the transformer. Calculate the voltage and current ratio. Note down the observations. 11. Disassemble and assemble a 3-phase induction motor. 11.1 Select the necessary tools and a 3- phase inductor motor. 11.2 Dismantle the parts of the motor. 11.3 Identify the parts of the motor. 11.4 Sketch the main parts of the motor. 11.5 Fix the parts of the motor at original position. 11.6 Note down the observations. 12. Start a 3-phase induction motor using star-Delta Starter. 12.1 Sketch the circuit diagram. 12.2 Select the tools, necessary materials and a 3-Phase induction motor. 12.3 Connect the motor according to the circuit diagram. 12.4 Apply the voltage to the motor starter. 12.5 Start the motor operating the motor starter. 12.6 Observe the operation. 13. Study the construction of ammeter and voltmeter. 13.1 Select the tools and materials for disassembling meters. 13.2 Select ammeter and voltmeter. 13.3 Disassemble the parts of the instruments. 13.4 Identify the controlling and damping system. 13.5 Identify different parts. 13.6 Identify the types of the meter. 13.7 Note down the observations. REFERIENCE BOOK 1. A text book of Electrical Technology. - B.L. Theraja 2. Introduction to Electrical Engineering. - V. K Mehta. 3. AC Machine -Siskind 4. Electrical Measurements - Goldings 16 6632 Computer Application -II T 0 P 6 C 2 OBJECTIVES To develop skill on spreadsheet applications. To develop skill on creating graphs. To assist in the efficient use of database packages. To develop skill on computerized database management. To develop skill on programming with database management. SHORT DESCRIPTION Spreadsheet Analysis Package: Applications of spreadsheet; Using worksheet; Apply formula and functions in worksheet; Creating & printing graphs; Create simple macros. Database management package: Creating the database; Editing the database; Searching the records; Customizing the data entry form; Creating the query; Arranging the records; Generating reports. Database management language: Creating a command file; Writing simple database program using decision-making commands. DETAIL DESCRIPTION SPREAD SHEET ANALYSIS PACKAGE: 1 Apply the basic skills of a spreadsheet software package 1.1 Run a spreadsheet software package. 1.2 Identify and use different areas (working area, border area, control panel, mode indicator, and status indicator) of the worksheet screen. 1.3 Identify the function of different keys (typing key, calculator key, text key, cursor key, etc.)of the keyboard. 1.4 Move around the worksheet using keys and combination of key. 1.5 Identify and use the on-screen help facility. 1.6 Identify and use the types of data, numbers, labels and formula. 1.7 Demonstrate menus, submenus, pop-up menu, etc. 2 Manage workbooks and windows. 2.1 Make and use workbooks. 2.2 Access different types of files. 2.3 Open files as read only. 2.4 Demonstrate the options for saving files. 2.5 Display a workbook in more than one window. 2.6 Work with more one workbook. 2.7 Close a workbook. Create a worksheet and use simple commands. 3 17 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Activate entries in a worksheet. Use edit key (F2) to correct or to modify entries. Activate the command menus and select commands. Save the worksheet. Exit from spreadsheet . Retrieve a previously saved worksheet. Modify the worksheet. Save a modified worksheet. 4 Apply formula, function and using templates. 4.1 Use simple formulae to solve arithmetical computation. 4.2 Use arithmetical operators in formula. 4.3 Edit formula. 4.4 Use mathematical function to solve simple equations. 4.5 Make and use workbook templates. 4.6 Make changes in existing workbook templates 4.7 Validate numbers, dates, times & text. 4.8 Show custom validation. 5 Solve engineering problems using formula and functions 5.1 Use mathematical functions to compute trigonometric values, absolute values, random number, square root, logarithmic values, etc for solving engineering problems. 5.2 Use logical functions to perform an operation depending on a condition in engineering problem. 5.3 Use statistical function to compute summation, average, minimum value, maximum value, etc in engineering problem. 6 Work with cell pointer to a particular cell. 6.1 Use GOTO key to move the cell pointer to particular cell. 6.2 Use the ABSOLUTE KEY to change cell address from one from to another in formula or in functions. 6.3 Enter range in formulae or in functions by typing directly or by using cell pointer. 6.4 Create a range name. 6.5 Use range name in formula & functions. 6.6 Copy, Move & Erase cell range. 7 Format a worksheet. 7.1 Change the width of a column, a range of column, and change the columns width globally. 7.2 Insert blank columns and blank rows in a worksheet. 7.3 Delete columns and blank rows in a worksheet. 7.4 Format the display of data of a worksheet globally or by referring a range of cells (e.g. currency format, exponential format, comma format, etc.). 7.5 Format the display of data and of a worksheet globally or referring of cells. 7.6 Protect worksheet, function, formula, important text and unprotect a range for entering entries. 18 7.7 7.8 8 Work with window for viewing worksheet in different ways and freeze rows or columns. Create, change and delete a style. Exercise on Sorting, Searching and Worksheet Printing. 8.1 Create a database program 8.2 Sort a database in different ways. 8.3 Search a record from the database using search criteria. 8.4 Extract records from the database that match a given criteria. 8.5 Delete records that a given criteria from the database using available database commands. 8.6 Show the Print Preview and adjust Page setup option. 8.7 Create and use page headers of footers. 8.8 Set print area, print titles and different print option 8.9 Print portion of worksheet and multiple worksheets 8.10 Print ranges from different worksheets on the same pages. 9 Create and Print graphs. 9.1 Create bar, line, X-Y and pie graphs. 9.2 Add color, titles, legend, gird and levels to the graph. 9.3 Add visual impact with colors. 9.4 Create linked pictures. 9.5 Save the graph and assign names to different graphs of a single worksheet. 9.6 Print graphs (low or high quality graphs.) 9.7 Plot graphs using a plotter using different colors. 9.8 Change graphs size, print & plot them. 10 Create Macros and using macro commands. 10.1 Create simple macros (e.g. to change the width of a cell, to format a cell display, to erase a range of cells etc.) using keystroke commands. 10.2 Create a macro to convert values into labels vice versa. 10.3 Create a macro for inserting blank rows between two rows of data in a worksheet. 10.4 Create a macro for deleting the inserted blank rows in a worksheet. DATABASE MANAGEMENT PACKAGE: 11 Create the new database. 11.1 Identify the practical database in real world. 11.2 Identify the fields and records of a database. 11.3 Identify the different phases of database design. 11.4 Collect the data form a typical field. 19 11.5 11.6 11.7 Determine the category of a typical field. Design a typical Paper- pencil database form raw data. Run a generalized database management package and identify its display Screen 11.8 Identify the different options of the selected packages. 11.9 Use the on-screen help facilities of DBMS package 11.10 Create and save the table structure. 12 Change the table structure and edit database. 12.1 Modify and Edit the table structure. 12.2 Verify the structure (i.e. data of update, number of records. etc) 12.3 Enter or append the new records in the database. 12.4 Use the key combinations for editing. 12.5 Use the available options to edit fields. 12.6 Delete unwanted records and files. 12.7 Save & close database file. 12.8 Use different modes to append and edit records of database. 13 Search, display and arrange the records of database. 13.1 View a database using list and display command 13.2 Retrieve the database records with different conditions. 13.3 Search within a field. 13.4 Keep the track of specific records. 13.5 Keep the database up-to-date. 13.6 Sort a database on single or multiple fields. 13.7 Sort with qualifier (i.e. sort with specific subset of records). 13.8 Index the database on single or multiple fields. 13.9 Use the function to index on different field types. 13.10 Use the commands for selective indexing and to control the order of records. 14 Create the customized data entry form. 14.1 Draw a typical data entry screen with paper-pencil work. 14.2 Design the screen with all fields. 14.3 Move the field to make the entry form logical and easy to use. 14.4 Change the field width. 14.5 Add or delete field (if necessary). 14.6 Change the display characteristics of fields. 14.7 Use picture functions template and range to format the displayed data. 14.8 Use different options and commands in design menu. 14.9 Draw lines and boxes on the form. 15 Create the query. 15.1 Display and identify query design screen. 15.2 Build a simple query 15.3 Save & apply the query. 15.4 Use the query design menu options. 15.5 Use the symbols and operators to build query. 20 15.6 15.7 15.8 15.9 16 17 Search the records with matching on two or more fields. Select the records within range using range operators. Find the records with inexact and complex matching. Sort the records within queries. Generate the custom reports. 16.1 Send the reports to the screen or to a file. 16.2 Use the print menu options and dos-prompt options. 16.3 Produce a quick and selective report. 16.4 Plan the design of the report. 16.5 Design a custom columnar report. 16.6 Find the parts of a report specification. 16.7 Make the changes to the report specification. 16.8 Save & run the report. Work with multiple database and relationship. 17.1 Merge the data form one file to another. 17.2 View the files to relate two or more database files. 17.3 Set up the relationship. 17.4 Modify the relationship. 17.5 Create the report from relational database. DATABASE MANAGEMENT LANGUAGE: 18 Create a simple command file using expression and function. 18.1 Identify the database editor. 18.2 Use the commands to assign different types of data values to variables. 18.3 Save the memory variable. 18.4 Display the memory variable. 18.5 Release & restore the memory variable. 18.6 Use the mathematical expression. 18.7 Use the mathematical, relational, logical and string operators. 18.8 Use the common function such as EOF, BOF DATE, UPPER & LOWER< CTOD, DTOS, SPACE, TRIM, STR, etc. in command file. 18.9 Use the commonly use commands such as SET TALK, SKIP, RETURN in command file. 18.10 Use the commands to display a string of characters and wait for user response. 18.11 Use commands to display or print text. 19 Design & write simple programs. 19.1 Identify the basic steps to design a program. 19.2 Write the pseudocode for simple program. 19.3 Convert the pseudocode into actual program code. 19.4 Verify & documents the simple program. 19.5 Save the command file and then exit. 19.6 Run the program. 20 Use the decision making commands in Programs. 21 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 20.5 20.6 20.7 20.8 20.9 20.10 Use DO WHILE ---- ENDDO, IF ---- ENDIF and DO CASE ---- ENDCASE to control program flow. Use SCAN ---- ENDSCAN command instead of DO WHILE ---- ENDDO. Use IF, ELSE and ENDIF commands to branch to the part the program. Use nested IF ---- ENDIF statements. Write simple program using decision making commands. Use immediate IF function. Write simple program using immediate IF function. Use CASE ---- ENDCASE statement instead more than three IF ---- ENDIF statements. Use the EXIT, CANCEL, WAIT and ZAP command in database program. Use macro function within programs. 22 MATHEMATICS III 5931 T P C 3 3 4 AIMS To make understand the basic concept and techniques of composition and resolution of vectors and computing the resultant of vectors. To enable to use the knowledge of gradient of a straight line in finding speed, acceleration etc. To enable to use the knowledge of conic in finding the girder of a railway bridge, cable of a suspension bridge and maximum height of an arch. To provide ability to apply the knowledge of differential calculus in solving problem like slope, gradient of a curve, velocity, acceleration, rate of flow of liquid etc. To enable to apply the process of integration in solving practical problems like calculation of area of a regular figure in two dimensions and volume of regular solids of different shapes. SHORT DESCRIPTION Vector Co-ordinate Geometry Differential Calculus Integral Calculus : Addition and subtraction, dot and cross product. : Co-ordinates of a point, locus and its equation, straight lines, circles and conic. : Function and limit of a function, differentiation with the help of limit, differentiation of functions, geometrical interpretation dy of dx , successive differentiation and Leibnitz theorem, partial differentiation. : Fundamental integrals, integration by substitutions, integration by parts, integration by partial fraction, definite integrals. DETAIL DESCRIPTION Vector 1 Apply the theorems of vector algebra. 1.1 Define scalar and vector. 1.2 Explain null vector, free vector, like vector, equal vector, collinear vector, unit vector, position vector, addition and subtraction of vectors, linear combination, direction cosines and direction ratios, dependent and independent vectors, scalar fields and vector field. 1.3 Prove the laws of vector algebra. 1.4 Resolve a vector in space along three mutually perpendicular directions 23 1.5 2 solve problems involving addition and subtraction of vectors. Apply the concept of dot product and cross product of vectors. 2.1 Define dot product and cross product of vectors. 2.2 Interpret dot product and cross product of vector geometrically. 2.3 Deduce the condition of parallelism and perpendicularity of two vectors. 2.4 Prove the distributive law of dot product and cross product of vector. 2.5 Explain the scalar triple product and vector triple product. 2.6 Solve problems involving dot product and cross product. CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY 3 Apply the concept of co-ordinates to find lengths and areas. 3.1 Explain the co-ordinates of a point. 3.2 State different types of co-ordinates of a point. 3.3 Find the distance between two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2 ). 3.4 Find the co-ordinates of a point which divides the straight line joining two points in certain ratio. 3.5 Find the area of a triangle whose vertices are given. 3.6 Solve problems related to co-ordinates of points and distance formula. 4 Apply the concept of locus. 4.1 Define locus of a point. 4.2 Find the locus of a point. 4.3 Solve problems for finding locus of a point under certain conditions. 5 Apply the equation of straight lines in calculating various parameter. 5.1 Describe the equation x=a and y=b and slope of a straight line. 5.2 Find the slope of a straight line passing through two point (x1, y1,) and (x2, y2 ). 5.3 Find the equation of straight lines: i) Point slope form. ii) Slope intercept form. iii) Two points form. iv) Intercept form. v) Perpendicular form. 5.4 Find the point of intersection of two given straight lines. 5.5 Find the angle between two given straight lines. 5.6 Find the condition of parallelism and perpendicularity of two given straight lines. 5.7 Find the distances of a point from a line. 6 Apply the equations of circle, tangent and normal in solving problems. 6.1 Define circle, center and radius . 6.2 Find the equation of a circle in the form: 24 i) ii) x2 + y2 =a 2 (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 =a 2 iii) x 2 + y 2 + 2gx + 2fy + c=0 6.3 Find the equation of a circle described on the line joining (x1, y1) and (x2, y2). 6.4 Define tangent and normal. 6.5 Find the condition that a straight line may touch a circle. 6.6 Find the equations of tangent and normal to a circle at any point. 6.7 Solve the problems related to equations of circle, tangent and normal. Understand conic or conic sections. 7.1 Define conic, focus, directrix and eccentricity. 7.2 Find the equations of parabola, ellipse and hyperbola. 7.3 Solve problems related to parabola, ellipse and hyperbola. 7. DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS FUNCTION AND LIMIT 8. Understand the concept of functions and limits. 8.1 Define constant, variable, function, domain, range and continuity of a function. 8.2 Define limit of a function 8.3 Distinguish between f(x) and f(a). 8.4 Establish i) lim sinx x =1 x0 . ii) lim tanx x =1. x0 9. Understand differential co-efficient and differentiation. 9.1 Define differential co-efficient in the form of dy f(x+h)-f(x) = lim dx h h 0 9.2 10. Find the differential co-efficient of algebraic and trigonometrical functions from first principle. Apply the concept of differentiation. 10.1 State the formulae for differentiation: 25 i) ii) iii) iv) v) 10.2 11. sum or difference product quotient function of function logarithmic function Find the differential co-efficient using the sum or difference formula, product formula and quotient formula. Find the differential co-efficient function of function and logarithmic function. Apply the concept of geometrical meaning of 11.1 dy Interpret dx geometrically. 11.2 dy Explain dx under different conditions 11.3 dy dx Solve the problems of the type: A circular plate of metal expands by heat so that its radius increases at the rate of 0.01 cm per second. At what rate is the area increasing when the radius is 700 cm ? 12 Use Leibnitz’s theorem to solve the problems of successive differentiation. 12.1 Find 2nd, 3rd and 4th derivatives of a function and hence find n-th derivatives. 12.2 Express Leibnitz’s theorem 12.3 Solve the problems of successive differentiation and Leibnitz’s theorem. 13 Understand partial differentiation. 13.1 Define partial derivatives. 13.2 State formula for total differential. 13.3 State formulae for partial differentiation of implicit function and homogenous function. 13.4 State Euler's theorem on homogeneous function. 13.5 Solve the problems of partial derivatives. INTEGRAL CALCULUS 14 Apply fundamental indefinite integrals in solving problems. 14.1 Explain the concept of integration and constant of integration. 14.2 State fundamental and standard integrals. 14.3 Write down formulae for: i) Integration of algebraic sum. ii) Integration of the product of a constant and a function. 14.4 Integrate by method of substitution, integrate by parts and by partial fractions. 26 14.5 15 Solve problems of indefinite integration. Apply the concept of definite integrals. 15.1 Explain definite integration. 15.2 Interpret geometrically the meaning of 15.3 Solve problems of the following types: i) 2 0 2 cos xdx ii) 1 0 sin 1 f x dx b a x 1 x2 P* =Practical continuous assessment 2 dx 27 5922 PHYSICS–II T P C 3 3 4 AIMS To provide a foundation in scientific principles and processes for the understanding and application of technology. To develop an understanding of fundamental scientific concepts through investigation and experimentation. To provide a common base for further studies in technology and science. To develop the basic knowledge of modern physics. Short description Thermometry; Calorimetry, Expansion of materials (effect of heat); Heat transfer; Nature of heat and its mechanical equivalent; Engine. Principles of light and Photometry; Reflection of light; Refraction of light ; lens. Concept of Electron and photon; structure of atom, Theory of Relativity. Detail description Theory : 1. Thermometry 1.1 Define heat and temperature. 1.2 Mention the units of measurement of heat and temperature. 1.3 Distinguish between heat and temperature. 1.4 Identify the sources of heat. 1.5 Identify the range of the Celsius scale determined by the boiling point and melting point of water 1.6 Compare the Celsius scale, Roamer scale, Fahrenheit scale, Kelvin scale and Rankin scale of temperature measurement. 1.7 State the construction and graduation of a mercury thermometer. 1.8 Describe the operation of different types of thermometers (e.g., maximum and minimum thermometer, clinical thermometer). 2. Heat capacity of materials (calorimetric) 2.1 State the heat as a form of energy. 2.2 Define specific heat capacity. 2.3 State SI units of measurement of specific heat capacity as J/Kgc0 or J/Kgk0. 2.4 Define thermal capacity and water equivalent. 2.5 Differentiate between thermal capacity and water equivalent. 2.6 Mention the specific heat capacity of different materials. 28 2.7 2.8.1 2.8.2 2.9 2.9.1 Prove the total heat gained by an object is equal to the sum of the heat lost by all the surrounding objects. Identify specific latent heat as the energy consumed or liberated when water vaporizes or condenses and when ice melts or freezes. Explain the effects of a change in pressure on the melting point and boiling point of water. Define various kinds of specific latent heat. Determine the latent heat of fusion of ice and latent heat of vaporization of water. 3. Effects of heat on dimension of materials 3.1 Show that different materials change in size at different amounts with the same heat source. 3.2 Explain the meaning of differential expansion in bimetallic strip, thermostats, compensated pendulum etc. 3.3 Explain the methods of overcoming problems caused by the expansion of materials in buildings, machinery, railway lines and bridges. 3.4 Define the co-efficient of linear, superficial and cubical expansion of solids. 3.5 Mention the units co-efficient of linear, superficial and cubical expansion of solids. 3.6 Mention the linear, Superficial and cubical expansion of a range of common engineering materials. 3.7 Define real and apparent expansion of liquid. 3.8 Define and explain the co-efficient of real and apparent expansion of liquid. 3.9 Distinguish between the co-efficient of real and apparent expansion of liquid. 3.10 Determine the co-efficient of real and apparent expansion of liquid. 4. Heat transfer 4.1 Identify the phenomenon of heat transferring from hot bodies to cold bodies. 4.2 Explain the methods of heat transfer by conduction, convection and radiation with examples of each type of transfer. 4.3 Define thermal conductivity (K) & rate of heat transfer. w w State the SI units of thermal conductivity as mk or mc 4.4 List the factors which determine the quantity of heat (Q) flowing through a material. 4.5 Show that the quantity of heat flowing through a material can be found from Q KA (H C)t = d 4.6 Outline the properties of materials which give thermal insulation. 4.7 Explain Characteristics of radiant heat energy. 4.8 Describe Emissive power and absorptive power of radiant heat. 29 4.9 4.10 4.11 4.12 5. 6. 7. State Stefan-Boltzman Law, State Newton’s law of cooling. State wiens law. Explain Green house effect. Nature of heat and its mechanical equivalent 5.1 Describe the caloric theory and kinetic theory of heat. 5.2 State the drawbacks of the caloric theory of heat. 5.3 Explain the mechanical equivalent of heat. 5.4 Explain the first law of thermodynamics . 5.5 Explain Isothermal and adiabatic change. 5.6 Explain Specific heat of a gas, Molar specific heat or molar heat capacity. 5.7 Relate between pressure and volume of a gas in adiabatic Change i, e;PV=const. 5.8 Difference between CP and Cv for an ideal gas (CP-Cv=R) 2nd law of thermodynamics 6.1 State and Explain Reversible process and irreversible process. 6.2 State & explain 2nd law of thermodynamics 6.3 Explain heat engine. 6.4 Explain the principle of work of a heat engine. 6.5 Identify thermal efficiency of a heat engine. 6.6 Explain the working principles of internal combustion and external combustion engines (with fair sketches) 6.7 Distinguish between internal combustion engine and external combustion engine. Entropy : Definition, unit and significant. 6.8 Explain Change of entropy in a reversible and irreversible process. 6.9 Give an example of increase of entropy in irreversible process. Preliminaries of light and photometry 7.1 Define light, medium (transparent, translucent, opaque), luminous & nonluminous bodies, parallel, convergent & divergent rays, beam. 7.2 Show the travel of light in straight line. 7.3 Define photometry, luminous intensity, luminous flux, brightness and illuminating power. 7.4 Mention the units of luminous intensity, luminous flux, brightness and illuminating power. 7.5 Mention relation between luminous intensity & illuminating power. 7.6 Explain inverse square law of light. 7.7 Describe the practical uses of light waves in engineering. 30 8. Reflection of light 8.1 Define mirror (plane & spherical ), image (real & virtual) and magnification of images. 8.2 Describe the reflection of light. 8.3 State the laws of reflection of light. 8.4 Express the verification of laws of reflection. 8.5 Define pole, principal axis, center of curvature, radius of curvature, principal focus in case of concave & convex mirrors. 8.6 Find the relation between focal length & radius of curvature of a concave & convex mirror. 8.7 Express the general equation of concave and convex mirror. 9. refraction of light 9.1 Define refraction of light Give examples of refraction of light 9.2 State the laws of refraction and Express the verification of laws of refraction 9.3 Define absolute and relative refractive index and Relate absolute and relative refractive index 9.4 Explain the meaning of total internal reflection and critical angle and Relate total internal reflection and critical angle. 9.5 Give examples of total internal reflection. 9.6 Describe refraction of light through a prism. 9.7 Express the deduction of the relation between refractive index, minimum deviation and angle of the prism. 9.8 Explain Dispersion of light. 9.9 Define lens and mention the kinds of lens. 9.10 Define center of curvature, radius of curvature, principal axis, 1st and 2nd Principal focus, optical center and power of lens. 9.11 Express the deduction of the general equation of lens (eoncave & convex). 9.12 Define Combination of two thin lenses and equivalent lens. 9.13 Identify and List uses of lens. 10. Electron and photon : 10.1 Describe Electrical conductivity of gases. 10.2 Describe Discharge tube. 10.3 Cathode ray : Definition and its properties 10.4 X-ray : Definition, properties & uses 10.5 Discuss Photo electric effect . 10.6 Derive Einstein’s photo electric equation 31 11. Structure of atom : 11.1 Atomic models : Thomson, Rutherford and Bohr model. 11.2 Bohr Hydrogen atom & the theory of hydrogen spectra . 11.3 Define and explain Radio activity. 11.4 Describe Radio active rays. 11.5 Deduce radioactive decay law. 11.6 Define half-life & mean life of radioactive atoms. 11.7 Define nuclear fission & fusion. 12. Theory of relativity : 12.1 Express the theory of relativity. 12.2 Mention different Kinds of theory of relativity. 12.3 Explain special theory of relativity and its fundamental postulate. 12.4 Deduce Einstein’s mass -energy relation Practical: 1. Compare the operation of common thermometers. 2. Determine the co-efficient of linear expansion of a solid by Pullinger’s apparatus. 3. Measure the specific heat capacity of various substances.(Brass, steel). 4. Determine the latent heat of fusion of ice. 5. Determine the water equivalent by calorimeter. 6. Compare the luminous intensity of two different light sources. 7. Verify the laws of reflection. 8. Find out the focal length of a concave mirror. 9. Determine the refractive index of a glass Slab. 10. Determine the angle of Minimum deviation and refractive index of a glass prism by using I-D graph. 32 ENGLISH – II 5722 T P C 2 2 3 OBJECTIVES : After the completion of the course, learners will be able to develop Reading and writing skills Grammatical accuracy with emphasis on spelling & punctuation Information Collection Creative Writing Effective Communication and Correspondence CONTENTS Seen comprehension Fourteen: Human Resources Sixteen: Wonders Home and Abroad Seventeen: Modes of Communication Nineteen : Healthy Living Twenty: Jobs and Professions Twenty-one: Globalization 3 Marks 20 Enriching the workforce 1 2 6 The Sangsad Bhaban The Jamuna Multi-Purpose Bridge E-mail 5 The disabled among us 2 How can I be self-employed? 3 Self-help a key to success 1 The world as a global village 3 Modern technology and globalization 6 Globalization and English N.B: The Unit mentioned refers to the Text Book (1st Paper) English for Today for class 11 – 12 by National Curriculum & Text Book Board, Dhaka. GRAMMAR Unit One: Pronouns & Determiners Lesson 3 Marks 30 Title Modifier: Pick out modifiers, determiners, Infinitive, participles headword, in the sentence. Question : A beautiful girl of Thirteen dances well. : Headword: girl Pre modifier – a, beautiful Post modifier – of thirteen 33 Twelve: Further Use of Preposition 2 Patterns of Sentence Structure Fourteen: Idiom and Phrase Changing Speech 9 Use Appropriate Prepositions 3. Sentence Structure -----------Question a) Analyse sentences Exam : He goes to school. Ans: Sub : He Verb intransitive: goes b) Make Sentence according to the structure Question S+VI+Obi +Ob2 Answer : He called me a liar. Make Sentences with the idioms and Phrases in the following. (any five) Direct & indirect narration N.B: The Unit mentioned refers to the Text Book (2nd Paper) English Grammar and Composition for class XI - XII by National Curriculum & Text Book Board, Dhaka. COMPOSITION marks 30 Area of interest: With hints/ key words National, Social, Political Problems: Terrorism, Drug Addiction, Acid Violence, Dowry, Load shedding, Price Hike, Gender Discrimination, Traffic Jam, Deforestation etc. Calamities: Drought, Erosion, Flood, Cyclone, Earth quake, Landslide etc. National days and festivals: International Mother Language Day, Independence Day, Victory Day, Pahela Baishakh, May Day etc. Scientific Development: Satellite, Optical Fiber, E-mail, Internet & Agricultural Development. Environment Pollution: Water, Air, Sound, Global Warming. Heritage sites: The Sundarbans, National Memorial, Cox’s Bazar Sea Beach, Bhashani Novo Theatre. Industries: Garments, Textile, Poultry, Leather, Ceramics, Fertilizer. 1. 2. 3. Writing a short composition Writing a formal letter/CV. Writing Letter (Personal/Official) 34 4. 5. Writing Reports on work place of standard form/ instrument or Construction or fault on / instrument or Construction/ Repairing of instrument or Construction/ a situtation/event/incident. Writing letter to the print & Electronic media. Practical 1. 2. Asking Questions : WH, Yes/No, Tag questions Conversations on real life situations a) Today's market price b) About festival c) Preparation for the examination d) Last day of your Class. e) Visit to the place of interest f) Choice of profession g) Current Topics from Newspapers. 35 5811 Social science- I T 2 P 0 C 2 OBJECTIVES To provide opportunity to acquire knowledge and understanding on : importance of civics and its relationship with other social sciences the relationship of an individual with other individuals in a society social organizations, state and government rule of law, public opinion and political parties UNO and its roles the basic concepts and principles of economics and human endeavor in the economic system. the realities of Bangladesh economy and the current problems confronting the country. the role of Diploma Engineers in industries. occupations and career planning for Diploma Enginers. SHORT DESCRIPTION Civics and Social Sciences; Individual and Society; Nation and Nationality; Citizenship; state and government; Law; Constitution; Government and its organs; public Opinion; Political Party; UNO and its organs; Scope and importance of Economics; Basic concepts of Economics- Utility, Wealth, consunmption, income wages and salary and savings; Production – meaning, nature, factors and laws; Demand and Supply; Current economic problems of Bangladesh; Role of Diploma Engineers in the economic development of Bangladesh; Occupations and career planning; Engineering teem. Part-1 (Civics) 1. Understand the meaning and scope of civics and inter relations of social sciences. 1.1. Define social science. 1.2. State the meaning and scope of civics. 1.3. Explain the importance of civics in the personal and social life of an individual. 1.4. Describe the relationship of all social science (civics, Economics, political science, sociology, ethics) 2. Understand the relationship of the individual with the society, Nationality and nation, Rights and duties of a citizen. 2.1 Define the concept (individual, society, Nation, Nationality, citizen and citizenship). 2.2 State the relationship among the individuals in the society. 2.3 Differentiate between nation and nationality. 36 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 Describe the elements of nationality Describe the criteria of Bangladesh nationalism. Diferentiate between a citizen and an alien. Discuss the methods of acquiring citizenship and state the causes of losing citizenship Describe the rights of a citizen and state the need for developing good citizenship. 3. Appreciate the relationship between the state and government, law and organs of government. 3.1 Meaning the state, government and law 3.2 Discuss the elements of state. 3.3 Discuss the classification of the forms of government 3.4 Distinguish between cabinet form of Government and presidential form of government. 3.5 Describe the main organs of Government (legislature, Executive and judiciary) 3.6 Discuss the sources of law 4. Understand and the classification of constitution 4.1 Explain the deferent form of Constitution 4.2 Explain the merits and demerits of different forms of constitution and state the salient feature of Bangladesh constitution 5. Understand the importance of the formation of public opinion and the role of political parties in the affairs of state and government. 5.1 Define the public Opinion and political party. 5.2 Explain the importance of public opinion in the modern democratic society. 5.3 Discuss the role of different media in forming public opinion. 5.4 Discuss the importance of political parties in democracy. 6. Understand the role of UNO in maintaining world peace 6.1 Explain the major functions of UNO. 6.2 State the composition and functions of General Assembly. 6.3 Describe the Composition and functions of security council. 6.4 Discuss the role of Bangladesh in the UNO. 37 Part-2 (Economics) 1. Understand the importance of the study fundamental concepts of economics. 1.1 Discuss the definition of Economics as given by eminent economists. 1.2 Describe the scope and importance of economics of Technical Student. 1.3 Define commodity, utility, value, wealth, consumption, income, savings wages and salary. 1.4 Differentiate between value in use and value in exchange. 1.5 Explain wealth with its characteristics. 2. Understand the production process and the concept of the law of diminishing returns in the production process. 2.1 Discuss production mode and process 2.2 Explain the nature of different factors of production. 2.3 Discuss the law of diminishing returns. 2.4 State the application and limitations of the law of diminishing returns. 2.5 Describe the law of production (increasing constant and diminishing). 3. Appreciate the importance of the concept of elasticity of demand. 3.1 Illustrate the law of diminishing utility. 3.2 Define the marginal utility explain the law of dimishing marginal utility. 3.3 define the term, “demand” 3.4 Describe elasticity of demand and factors which determine the elasticity of demand 3.5 Describe elasticity of supply with the help a supply curve. 4. Understand national income and population control. 4.1 Explain national income. 4.2 Discuss GDP and GNP. 4.3 Discuss growth rates. 4.4 Explain features of Bangladesh population. 4.5 State measures to be undertaken to arrest high growth rate of population. 5. Understand the current issues and the avilability and use of natural resource in the economic development of Bangladesh 5.1 Identify major problems of rural and urban economy. 5.2 Explain income distribution in alleviating poverty in equality and discrimination. 5.3 Explain the migration of rural population to urban areas. 5.4 List of the Natural resource of Bangladesh and classify them according to sources of availability. 5.5 Explain the importance of the mine, forest and water resources and protential uses for sustainable development. 38 6. Understand the role of a Diploma Engineer in the Development of Bangladesh Economy. 6.1 Explain the concept of the term, “Engineering team” 6.2 Identify the functions of Engineers, Diploma Engineers, craftsmen forming the engineering team. 6.3 Discuss the role of a Diploma Engineer in the overall economic development of Bangladesh. 7. Appreciate the career prospects for Diploma Engineers in different production/service engineering organizations. 7.1 Explain the employment opportunities for diploma engineers in different sectors and sub Sectors of economy 7.2 Explain socio-economic status of a diploma Engineer. 7.3 Explain prospects of diploma Engineers in self-employment. 39 BANGLADESH TECHNICAL EDUCATION BOARD 4-YEAR DIPLOMA-IN-ENGINEERING PROGRAM POWER TECHNOLOGY SYLLABUS FORTH SEMESTER 40 7141 Engine Details (IC Engine) T P 3 3 C 4 AIMS To provide the students with an opportunity to acquire knowledge, skill and attitude in the area of internal combustion engines with special emphasis on : functions of internal combustion (IC) engines. types of internal combustion (IC) engines. dimensions of IC engines. working principle of IC engines. construction and operation of IC engine components. systems of IC engines. supercharging of IC engines. combustion process of IC engines. SHORT DESCRIPTION Functions & types of internal combustion (IC) engines; Construction and operation of engine components; Dimensions of IC engines; Working principle of IC engines; Valve trains; Lubricating system; Cooling system; Petrol engine fuel system; Diesel engine fuel system; Supercharging & scavenging; Combustion process of IC engines. DETAIL DESCRIPTION Theory : INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES 1 Dimension of IC engines 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Difine IC engine Cassify the IC engine on the basis of different terms. List the basic terms of IC engine dimensions. Explain the terms engine bore and stroke. Explain the terms piston displacement, clearance volume and compression ratio. Describe the volumetric efficiency and engine torque. Compute the formulae to calculate indicated power (IP), brake power (BP) and frictional power (FP). Solve problems on IP, BP and FP. 41 CONSTRUCTION & OPERATION OF IC ENGINE 2 Understand the construction & operational features of IC engine. 2.1 Identify the cylinder block, cylinder head and crankcase. 2.2 Mention the function of stationary and moving parts of an IC engine. 2.3 Identify the moving parts & stationery parts of an IC engine. 2.4 Describe the construction of piston, piston rings, piston pin, connecting rod and crankshaft. 2.5 Describe the operation of piston, piston rings, piston pin, connecting rod and crankshaft. 2.6 Describe the construction of engine bearing, valves, camshaft, valve lifter and manifolds. WORKING PRINCIPLES OF IC ENGINES 3 Understand the features of IC engines. 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 4 State the working principle of 2-stroke and 4-stroke SI & CI engines. Compare the SI and CI engines. Compare the 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines. List the advantages and disadvantages of CI and SI engines. List the advantages and disadvantages of 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines. VALVE TRAINS OF IC ENGINES Understand the features of valve trains of IC engines. 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 State what is meant by the valve mechanism/trains. Describe the daffarant valv opperting mechanism. Explain the operation of hydraulic valve lifter. Describe the fixed valve timing & variable valve timing (VVT-i) Outline the importance of valve timing. Explain the methods of valve timing. 42 LUBRICATING SYSTEM 5 Understand the engine lubricating system. 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 State the lubrication principles. Mention the purposes of lubricating system. List the types of lubricating system. Describe the construction of lubricating systems. Describe the operation of lubricating systems. Describe the oil pressure regulation. Outline the importance of crankcase ventilation. Mention the lubricating system troubles, possible causes and remedies. COOLING SYSTEM 6 Understand the features of cooling system. 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 Mention the necessity of cooling system. Identify the types of cooling system. Describe the operation of various cooling system. Describ the contruction of cooling water pump & radiator. Explain the use of antifreeze solution. Mention the cooling system flushing procedure. Mention the cooling system troubles and their remedies. CARBURETED GASOLINE ENGINE FUEL SYSTEM 7 Understand the features of conventional carbureted gasoline engine fuel system. 7.1 7.2 Listthe components of gasoline engine fuel system. Draw the flow diagram of SI engine fuel system. 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 Explain the mechanical, electrical and intank fuel pump system. State the basic principle of carburation. Explain the functions of a curburator. List the different circuits of a carburetor. Explain the air fuel ratios requirements with different carburetor circuits operation at different speeds. NON-CONVENTIONAL SI ENGINE FUEL SYSTEMS 8 Understand the features of non-conventional fuel systems. 43 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 Explain the gasoline injection system. List the advantages of gasoline injection system. Describe the construction of electronic fuel injection system. Describe the operation of electronic fuel injection system. State the onbard diagnosis system (OBD) of EFI engine. Mention the SI engine fuel system troubles, possible causes and remedies. 8.7 Describe the opertion of CNG fuel system. 8.8 Describe the opertion of LPG fuel system. DIESEL ENGINE FUEL SYSTEMS 9 Understand the features of diesel engine fuel systems. 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 9.8 9.9 9.10 Describe the requirements of a diesel injection system. Mention the classification of the diesel engine injection systems. Explain the diesel engine injection systems. Identify the components of a diesel engine fuel systems. Mention the function of low and high pressure pumps. Describe the operation of low and high pressure pumps. Mention the classification of the fuel injectors and nozzles. Identify the fuel injectors and nozzles. State the meaning of phasing and calibration. Mention the diesel engine fuel system troubles, possible causes and their remedies. SUPERCHARGING & SCAVENGING 10 Understand the aspects of supercharging & scavenging. 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.7 State the purpose of supercharging. Outline the necessity of scavenging in SI. & CI engines. Explain the effect of supercharging on SI & CI engines performance. Mention the classification of the superchargers and turbochargers. Describe the construction of superchargers and turbochargers. Describe the operation of superchargers and turbochargers. List the advantages and disadvantages of superchargers and turbochargers. COMBUSTION PROCESS OF SI ENGINE 11 Understand the combustion process of SI engine. 11.1 11.2 11.3 Mention the stages of SI engine combustion. State the meaning of normal and abnormal combustion. Describe the effect of engine variables on flame propagation. 44 11.4 11.5 11.6 11.7 11.8 Mention the classification of the SI engine combustion chambers. Describe the design features of different types of combustion chambers. List the advantages and disadvantage of various combustion chambers. State what is meant by the SI engine detonation. Mention the causes & effect of SI engine detonation and their remedies. COMBUSTION PROCESS OF CI ENGINE 12 Understand the combustion process of CI engine. 12.1 State the combustion phenomenon of CI engine. 12.2 Identify the delay period. 12.3 Explain the variables affecting delay period. 12.4 Describe the diesel knock. 12.5 Describe the methods of controlling diesel knock. 12.6 Explain the design features of CI engine combustion chambers. 12.7 List the advantages and disadvantage of various combustion chambers. Practical : 1 Study the IC engine components. 1.1 Identify the engine cylinder block, crankcase & cylinder head with all parts connected there in. 1.2 Identify the piston and connecting rod assembly. 2 Study the valve trains. 2.1 Identify the valve train components of an IC engine. 2.2 Adjust the valve clearance of a typical IC engine. 3 Study the lubricating system of IC engine. 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 4 Identify the pressure feed lubricating system and its components. Change the crankcase oil and re-fill with proper grade of lub oil. Remove the oil filter and replace it. Diagnose and correct lubricating system troubles. Study the cooling system of IC engine. 4.1 4.2 4.3 Identify the air and liquid cooling system components. Isolate the fan belt and replace it after proper inspection. Remove the thermostat from the system and fix up it after servicing. 5 Study the ptrol fuel pump . 6 5.1 Disassemble a fuel pump. 5.2 Assemble a fuel pump after necessary servicing. 5.3 Test the fuel pump. 5.4 Fix up the fuel pump in the system. Stady the opertion of carburator. 45 6.1 6.2 6.3 Disassemble the carburetor. Assemble the carburetor in sequential order. Adjust the carburetor to run on idle speed . 7 Study the CI engine injection system. 8 7.1 Identify the different components of CI engine fuel injection system. 7.2 Remove and replace a high pressure pump from engine. Stady the opertion of injector 8.1 Disassemble and assemble the injector. 8.2 Test the injector. 9 Perform phasing & calibration of high pressure diesel fule pump. 10 Set valve timing operation of an IC engine. REFERENCE BOOKS 1 Automotive Fundamentals Fredric C. Nash 2 Vehicle and Engine Technology Heinz Heisler 3 Automotive Mechanics Crouse-Anglin 4 Automobile Engineering Dr. Kirpal Singh 5 The Automobile Harbans Singh Reyat 6 A Course in Internal Combustion Engines M. L. Mather R. P. Sharma 7 Automobile Engineering__ 8 Automobile Engineering____ K.K. Ramalingan 9 Automobile Engineering ____ N.K. Giri 7142 R.B. Gupta. ENGINEERING MECHANICS T P C 2 3 3 46 AIMS To provide the students with an opportunity to acquire knowledge, skill and attitude in the area of engineering mechanics with special emphasis on: force system, moment and couple center of gravity moment of inertia friction stress & strain Torsion shear force & bending moment work, power and energy simple lifting machines and gear train SHORT DESCRIPTION Force system, Moment and couple, Center of gravity & centroid, Moment of inertia, Friction, Stress & strain, Torsion, Shear force and beading moment, Work, power & energy, Simple lifting machines and Gear train. DETAIL DESCRIPTION Theory : FORCE SYSTEM 1 Understand the composition and resolution of forces. 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 State the effect of forces. Mention the characteristics of forces. Learn the laws of forces. Define resolution of forces. Define resultant force and composition of forces. Find the resultant force graphically and analytically. Solve problems related to resultant forces. MOMENT AND COUPLE 2 Understand the aspects of moment and couple of forces. 2.1 Define moment and couple of a force. 2.2 Represent the moment of a force geometrically. 2.3 State the laws of moments. 2.4 State the Varignon’s principles of moments. 47 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 3 Proof the Varignon’s principles of moments Identify the clockwise and anticlockwise moment. Distinguish between clockwise couple and antniclockwise couple. Define leverage functions. Solve problems related to moment and couple of forces. Understand the aspects of equilibrium of forces. 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Mention different system of forces. Mention the various types of equilibrium of forces. State the principles of equilibrium of forces. State the Lami’s theorem. Express the derivation of Lami’s theorem. Describe different methods of the equilibrium of coplanar forces. Explain the conditions of equilibrium. Solve problems related to equilibrium of forces. CENTER OF GRAVITY 4 Understand the concept of center of gravity. 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Define center of gravity and centroid. Distinguish between center of gravity and centroid. Determine the center of gravity of simple geometrical figure geometrically and by integration. Identify the axis of reference and axis of symmetry. Determine the center of gravity of plain geometrical figure by first principle of moments. Calculate the center of gravity of compound geometrical figure or areas by moments. Calculate the center of gravity of solid bodies. MOMENT OF INERTIA 5 Understand the application of moment of inertia. 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 5.10 Explain the term moment of inertia. Mention the units of moment of inertia. Express the derivation of the formulae for moment of inertia of an area. Explain polar moment of inertia. Describe the methods for finding out the moment of inertia. Find the moment of inertia of a simple areas by integration. State the theorem of perpendicular axis as applied to moment of inertia. Proof the theorem of perpendicular as applied to moment of inertia. State the parallel axis theorem. Explain the radius of gyration and section modulus. 48 5.11 Calculate the moment of inertia and section modulus of simple solid bodies and composite sections. FRICTION 6 Understand the principles and application of friction. 6.1 Define friction. 6.2 State the laws of static and dynamic friction. 6.3 Explain coefficient of friction. 6.4 Determine the frictional force of a body lying on horizontal and inclined plane. 6.5 Identify the ladder and wedge friction. 6.6 Describe the screw friction. 6.7 Solve problems on wedge and ladder friction. STRESS AND STRAIN 7. Understand the aspect of stress and strain. 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 8. Define stress, strain, modulus of elasticity, modulus of rigidity, Bulk modulus, Poison’s ratio and principle of shear stress. Establish the relation between stress and strain. Explain the stress in composite bar, stress in nuts and bolts, and thermal stress. Describe the linear and lateral strain. Explain the stress-strain diagram. Solve problems on stress and strain. Understand the effects of torsion of solid and hollow shafts. 8.1 Explain torsion and torsion shear. 8.2 Deduce the equations used incase of designing solid and hollow shafts. 8.3 Deduce the equations of twist angle. 8.4 Solve problems using the equation of solid, hollow shafts and twist angle. SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENT 9. Understand the fundamentals of shear force and bending moment. 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Define beam. Identify the types of beam. Identify the types of loading on beam. Determine the support reactions of different types of beam under different loading conditions. Define shear force (SF) and bending moment (BM). 49 9.6 9.7 9.8 9.9 10. Differentiate shear force (SF) and bending moment (BM). Explain the sign convention and characteristics of S.F and B.M diagram. Draw S.F and B.M diagram of simple supported beams with point load and distributed load. Draw S.F and B.M diagram of cantilever beams with point load and distributed load. Understand the aspects of work, power and energy. 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.7 Define work, power and energy. Explain the work done in rotation. Mention the types of engine power. State the meaning of the engine efficiency. Mention the types of energy. Express the derivation of the equation of kinetic energy. Solve problems related to work, power and energy. SIMPLE LIFTING MACHINES 11. 12. Understand the principles of simple machines. 11.1 State the meaning of simple machine, compound machine and ideal machine. 11.2 Define the terms velocity ratio, mechanical advantage and efficiency of a machine. 11.3 Relate between efficiency, mechanical advantage and velocity ratio of lifting machine. 11.4 State the law of the machine. 11.5 Explain the reversibility of a machine and self locking machine. 11.6 Solve problems involving velocity ratio, mechanical advantage and efficiency of simple lifting machines. Understand the various aspects of gear trains. 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.6 12.7 12.8 12.9 Practical : State what is meant by gear. Identify the types of gears. Identify the simple gear drive. Express the derivation of the equation of velocity ratio of simple gear drive. Identify the compound gear drive and gear train. Identify the equation of power transmitted by simple and compound train. Identify the epicyclic gear train. Express the derivation of the velocity ratio of an epicylic gear train. Solve problems related to gear trains. 50 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Verify the triangle law of forces. Verify the polygon law of forces. Show the resultant of forces by using the force board. Proof Lami’s theorem by using the force board. Determine the coefficient of friction of timber, concrete and mild steel. Determine the tensile stress-strain by testing a mild steel specimen (also draw stress-strain diagram). Determine the compressive stress of a timber specimen. Determine the mechanical advantage of a screw jack. Determine the center of gravity of a wooden block. Determine the reaction of beam by using spring balance. REFERENCE BOOKS 1 Structural Mechanics 2 Structure Mechanics 3 Applied Mechanics 4 Mechanics of Materials 5 6 7 7144 W. Morgan and D.T Williams Singer/Popov R. S. Khurmi Philip Guatave Laurson Williams Junkin Cox. Analytical Mechanics Virgil Moring Faires Vector mechanics for engineers Beer and Johnston. Engineering mechanics - P. L. Ballaney. AUTOMOTIVE SUSPENSION, BRAKE & TRANSMISSION SYSTEM T P 2 C 6 4 AIMS To provide the students with an opportunity to acquire knowledge, skill and attitude of automotive suspension, brake and power transmission system with special emphasis on : 51 suspension systems manual and automatic transmission systems drive shafts & universal joints differentials & drive axles steering systems brake systems SHORT DESCRIPTION Suspension systems; Clutches; power transmission system Manual transmissions; Automatic transmissions; Gear boxes; Fluid coupling & Torque converter Drive axles; Universal joints & slip joints; Differentials: Steering systems & Brake systems. DETAIL DESCRIPTION Theory : SUSPENSION SYSTEMS 1 Understand the features of suspension systems. 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 Define suspension. State the purpose of suspension systems. Identify the components of suspension systems. Mention the classification of the various suspension systems. Describe the construction of various suspension systems. Describe the operation of various suspension systems. Describe the construction of shock absorber and springs used in automobile suspension systems. Describe the operation of shock absorber and springs used in automobile suspension systems. Explain the terms sprung and unsprung weight. Describe the basic suspension movements, viz. bouncing, pitching, rolling, etc. 52 AUTOMOTIVE DRIVE TRAINS 2 Understand the features of power transmission system. 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 3 Understand the features of automotive clutches. 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 4 Define power transmission system. Classify power transmission system List the components of power transmission system Draw & describe the power flow system of front engine front wheel drive (including trans axle system), front engine rear wheel drive, rear engine rear wheel drive, four wheel drive system. Draw & describe the operation of different types of power flow system of two & three wheelers. State the purpose of a clutch. Mention the classification of the automotive clutches. Describe the construction of a coil spring & diaphragm spring clutch. Describe the operation of clutch coil spring & diaphragm spring clutch Explain the operating principle of multi plate clutch, multi plate wet clutch and multi plate dry clutches. Explain the operating principle of centrifugal clutch, semi-centrifugal clutch and crown spring type clutch. Explain the operating principle of hydraulic clutch and electromagnetic clutch. Understand the features of gear boxes. 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 State the necessity of a gear box. Mention the principle of gearing. List different types of gear boxes. Describe the construction of sliding mesh & constant mesh (dog clutch type & synchromesh type) gear boxes. Describe the operation of sliding & constant mesh (dog clutch type & synchromesh type) gear boxes. Describe the power flow system in gear box at different gear position. 53 4.7 4.8 4.9 4.10 5 Compare the sliding mesh, constant mesh and synchromesh gear boxes. List the advantages and disadvantages of sliding mesh gear box, constant mesh gear box and synchromesh gear box. Mention the difference among three speed, four speed and five speed gear box. State the importance of over drive in power transmission system. Understand the features of automatic transmissions. 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 Define fluid coupling. Describe the construction and operation of fluid coupling. Define torque converter Describe construction & operation of torque converter. Mention the difference between the fluid coupling & torque converter Describe the operation of planetary gear system. Describe the construction of automatic transmissions. Describe the operation of automatic transmissions Explain the automatic transmission control system. DRIVE SHAFTS AND UNIVERSAL JOINTS 6 Understand the features of drive shafts and universal joints. 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 Explain the drive lines. Mention the function of propeller shaft. Mention the classification of the propeller shafts. Describe the function of universal joints, slip joints and CV joints. Mention the construction of universal joints, slip joints and CV joints. Describe the operation of universal joints, slip joints and CV joints. Explain the hotchkiss drive and torque tube drive. DIFFERENTIALS AND DRIVE AXLES 7 Understand the features of differential. 7.1 7.2 7.3 State the function of differential. Mention the type of differential. Explain the differential action on turns. 54 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 8 Describe the construction of conventional differential. Describe the operation of conventional differential. Describe the construction & operation of limited slip differentials. Describe the construction & operation of double reduction differential. Understand the features of drive axles. 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 State the function of axles. Mention the classification of axles. Mention the function of different types of drive axles. Describe the construction of different types of drive axles. Describe the operation of different types of drive axles. Mention the causes of axle failure. STEERING SYSTEMS 9 Understand the features of automotive steering systems. 9.1 State the purpose of steering system. 9.2 Mention the types of steering system. 9.3 Describe the operation of typical manual steering system. 9.4 Mention the function of each component of steering system. 9.5 Describe the operation of different type of steering gear box. 9.6 Describe the operation of integral & linkage booster type hydraulic power steering system. 9.7 Describe the operation of electrical power steering system. 9.8 Define front end geometry. 9.9 define camber angle, caster angle, toe-in, toe-out on turn and king pin inclination. 9.10 Mention the advantage of camber angle, caster angle, toe-in, toe-out on turn and king pin inclination. AUTOMOTIVE BRAKES 10 Understand the features of automotive brakes. 10.1 10.2 10.3 State the purpose of brake systems used in automobile. Mention the classification of the brake systems. Describe the construction & operation of mechanical brake systems used in automobile. 55 10.4 Describe the construction and operation of hydraulic brake systems used in automobile. 10.5 Describe the construction and operation of conventional master cylinder, tandem master cylinder & wheel cylinder. 10.6 State the functions of disc brake and drum brake. 10.7 Describe the construction and operation of vacuum servo brake system. 10.8 Describe the construction and operation of air brake system. 10.9 Describe the construction and operation of electrical brake system. 10.10 List the advantages and disadvantages of different brakes. 10.11 Explain the different brake adjustments. 11 Understand the aspects of brake fluid. 11.1 11.2 11.3 Mention the types of brake fluid. Mention the characteristics of brake fluid. Describe the process of brake bleeding. Practical : 1 Study the automotive suspension systems. 1.1 1.2 1.3 2 Service the automotive suspension system components. 2.1 2.2 2.3 3 Remove, inspect and install struts and shock absorbers. Remove, inspect and install wheel hubs. Install and adjust wheel bearings. Study the automotive clutches. 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 4 Identify the components of suspension systems. Remove, inspect and install the components of suspension system. Diagnose and correct troubles of suspension systems. Remove, inspect and install a clutch. Identify the components of clutch assembly. Diagnose and correct clutch troubles. Service the clutch and perform clutch adjustments. Study the automotive gear boxes. 56 4.1 4.2 4.3 Disassemble, inspect and reassemble the automotive gear boxes. Identify the components of gear boxes. Diagnose and correct gear box troubles. 5 Study the automotive drive lines. 5.1 Identify the components of drive lines. 5.2 Diagnose, service and replace universal joints. 5.3 Diagnose, service and replace CV joints. 6 Study the automotive differential unit. 6.1 Remove, inspect and install a differential. 6.2 Identify the components of differential. 6.3 Diagnose and service an open differential and a limited slip differential. 7 Study the automotive drive axle. 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Disassemble, inspect and reassemble a drive axle. Identify the components of drive axle. Replace bearing and seals of drive axle. Diagnose and rectify drive axle troubles. 8 Study the automatic transmission systems. 8.1 Identify the components of automatic transmission systems. 8.2 Inspect and service automatic transmission. 8.3 Diagnose and correct automatic transmission troubles. 9 Study the automotive steering system. 9.1 9.2 9.3 10 Identify the components of steering system. Check steering system performance. Diagnose and rectify steering system troubles. Service the automotive steering system components. 57 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 11 Study the wheel alignment. 11.1 11.2 11.3 12 Perform pre-alignment inspection. Check front wheel alignment angles. Perform caster, camber and toe adjustments. Study the disc and drum brakes. 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 13 Remove, inspect, install and adjust tie rods. Remove, inspect, install and adjust steering linkage parts. Remove, inspect and install steering gears. Remove, inspect and install ball joint and control arms. Identify disc brake components. Identify drum brake components. Remove, inspect and install disc brake components. Remove, inspect, install and adjust drum brake system. Service the hydraulic drum brakes. 13.1 Repair, replace the master cylinder or wheel cylinder. 13.2 Replace brake linings. 13.3 Refinish the drums. 13.4 Repair or replace the power booster unit. 13.5 Flush the hydraulic brake system and add brake fluid. 13.6 Bleed the hydraulic system to remove air. REFERENCE BOOKS 10 11 12 13 14 15 Automotive Fundamentals Fredric C. Nash Vehicle and Engine Technology Heinz Heisler Automotive Mechanics Crouse-Anglin Automobile Engineering Dr. Kirpal Singh The Automobile Harbans Singh Reyat Auto Mechanics 58 7042 Mitchell MACHINE SHOP PRACTICE T 1 P C 6 3 OBJECTIVES To enable recognize commonly used machine tools. To provide understanding the functions of commonly used machine tools. To develop skills in setting up and operating of machine tools. To provide concept of using Coolant in machining. To provide ability to set and operate commonly used allied tools and accessories. To provide understanding the operation of Milling Machine. SHORT DESCRIPTION Machine tools: Lathe machine; Drilling machine; Shaper; Grinding machine; Milling Machine; Measuring techniques. DETAIL DESCRIPTION Theory : 1 Understand the concept of machine tools. 1.1 State what is meant by machine tools. 1.2 Classify commonly used machine tools. 59 1.3 State general safety precautions to be observed in machine shop. 2 Understand the application of Lathe machine. 2.1 Identify different types of lathe machines. 2.2 Identify major components of lathe machine. 2.3 Explain the function of different parts and attachments of lathe machine. 2.4 Carry out basic calculations for speed and feed for lathe works. 2.5 State safety precautions during working on a lathe. 2.6 Identify single point cutting tools, tool materials, cutting angles and their relevant functions. 3. Understand the application of Coolant in machining operation. 3.1 Explain the nacessity of coolant in machining. 3.2 Indentify different types of coolant. 3.3 Describe the use of various types of coolant. 4. Understand the application of drilling machine. 4.1 Identify different types of drilling machine. 4.2 Explain the function of different drilling machines. 4.3 Identify major components of drilling machine. 4.4 Illustrate workholding methods. 4.5 Carry out basic calculations for speed and feed. 4.6 State safety precautions during working on a drilling machine. 4.7 Identify different types of twist drill, tool materials, cutting angles and their relevant functions. 5. Understand the application of shaper. 5.1 Identify the shaping machines. 5.2 Identify major components of shaping machine. 5.3 Describe the quick return mechanism and ram adjustments. 5.4 Explain how to set a workpiece on the machine table of shaper. 5.5 Identify typical operations for shaper. 5.6 State safety precautions during working on the shaper. 6 Understand the application of grinding machine. 6.1 Identify different types of grinding machines. 6.2 Distinguish surface grinder, cylindrical grinder and pedestal/bench grinder. 6.3 Explain the need for grinding wheel balancing. 6.4 Identify typical operations for the pedestal and surface grinder. 6.5 State safety precautions during working on grinding machine. 6.6 Identify grinding wheel types, bonds and uses. 60 7 Understand the features of milling machine. 7.1 State the meaning of Milling. 7.2 Identify different types of milling machine. 7.3 Indentify the principal parts of a milling machine. 7.4 Distinguish among plain, universal, and vertical milling machine. 7.5 Identify the verious kinds of milling cutter. 7.6 Mention the use of various milling cutter. 7.7 State safety precautions during working on milling machine. 7.8 Mention the care and maintenance of milling cutters. Practical : 1 Demonstrate the setting and operating of lathe machine. 1.1 Perform simple setting up of machine, workpiece, tool bit and setting machine speed and feed. 1.2 Carry out machining operations for facing, parallel turning, center drilling. 1.3 Produce a job to an engineering drawing specification. 1.4 Carry out additional machining operations of knurling, taper turning, drilling, parting off, simple screw cutting and boring. 1.5 Sharpen a number of commonly used single point cutting tools using pedestal grinder. 1.6 Observe workshop safety precautions. 2 Demonstrate the setting and operating of shaping machine. 2.1 Perform simple setting up of machine, workpiece, tool bit, speed and feeds, ram position and stroke. 2.2 Carry out machining operation for parallel shaping and vertical face shaping. 2.3 Produce a simple job to an engineering drawing specification. 2.4 Observe workshop safety precautions. 3 Demonstrate the setting and operating of a drilling machine. 3.1 Perform simple setting up of machine, workpiece, drill bit, speeds and feeds. 3.2 Sharpen a twist drill on the pedestal grinder. 3.3 Drill a number of holes with appropriate drill bit. 3.4 Observe workshop safety precautions. 4 Demonstrate the setting and operating of a grinding machine. 4.1 Determine type of wheel, grit, bond, balance and soundness by ringing. 4.2 Mount grinding wheel on machine spindle. 61 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 Use the pedestal grinder to grind single point tools and drill bits. Perform simple setting up of surface grinding machine workpiece, magnetic chuck, hydraulic system of machine feed. Produce a job to an engineering drawing specification. Observe ground surface finish, grain direction, bouncing of wheel. Carry out wheel dressing exercise on both pedestal grinder and surface grinder. Observe workshop safety precautions. 5 Demonstrate workshop maintenance practice. 5.1 Produce a maintenance schedule common used in machine shop. 5.2 Carry out simple maintenance procedures, including lubrication. 5.3 Observe workshop safety precautions. 6 Milling machine setting and operation. 6.1 Set up the machine vice and hold workpiece to produce a flat surface using a milling cutter. 6.2 Prodece the parallel and slotted workpiece using appropriate cutter. REFERENCE BOOKS 1 2 3 4 5 Basic Machine Shop Practice I & II V. K. Tejwani Workshop Technology I & II W. A. J Chapman Machine Shop Practice I & II Berghardt Machine Shop Practice Somenath De Machine tool operation Anderson. 62 6744 ELECTRICAL MACHINES T 2 P C 3 3 OBJECTIVES To develop understanding and skill on DC generator. To develop understanding and skill on DC motor. To familiarize with the construction and operation of transformer. To develop understanding on the principles of operation on 3-phase and 1phase induction motor. To develop understanding on the principle of synchronous motor and alternator. SHORT DESCRIPTION DC generator; DC motor; Transformer; Induction motor; 3-phase induction motor; 1phase induction motor; Synchronous motor; Alternator. DETAIL DESCRIPTION Theory : DC GENERATOR 1 Understand the principles of operation of DC generator. 1.1 Explain the working principle of DC generator. 1.2 Describe the constructional features of DC generator. 1.3 Explain the function of commutator. 1.4 Describe the factors determining induced emf. 1.5 Develop the emf equation of a DC generator. 1.6 Describe different types of excitation. 1.7 Identify different types of DC generator. 1.8 Explain losses and efficiency of DC generator. 2 Understand the principle of operation of DC motor. 2.1 Explain the working principle of DC motor. 2.2 Explain the factors determining torque of a DC motor. 2.3 Identify different types of DC motor. 2.4 Describe starting process and speed control of DC motor. 2.5 Explain losses and efficiency of DC motor. 63 TRANSFORMER 3 Understand the working principle and construction of transformer. 3.1 Define transformer. 3.2 Explain the working principle of transformer. 3.3 List of uses of transformer. 3.4 Describe the constructional details of transformer. 3.5 List different types of transformer. 3.6 Distinguish between core type and shell type transformer. 4 Understand emf equation and transformation ratio of transformer. 4.1 Explain the emf equation of a transformer. 4.2 Solve problems on emf equation of transformer. 4.3 Explain transformation ratio (voltage, current and turns). 4.4 Solve problems on transformation ratio. 5 Understand losses, efficiency and voltage regulation of transformer. 5.1 Explain different losses in transformer. 5.2 Explain the factors affecting core loss and copper loss. 5.3 Explain the equation for maximum efficiency. 5.4 Solve problems on efficiency and maximum efficiency. 5.5 Explain the equation for voltage regulation of transformer. 5.6 Solve problems on voltage regulation of transformer. 6 Apply the principle of impedance transformation and equivalent circuit of transformer. 6.1 Explain equivalent resistance of transformer in terms of primary and in terms of secondary. 6.2 Explain equivalent reactance of transformer in terms of primary and in terms of secondary. 6.3 Solve problems on impedance transformation. 6.4 Explain the equivalent circuit of transformer. INDUCTION MOTOR 7 Understand the principle of induction motor. 7.1 Explain the general principle of induction motor. 7.2 Distinguish between the principles of induction motor and conduction motor. 7.3 Define slip and slip speed. 7.4 List the types of induction motor. 7.5 List the uses of induction motor. THREE-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR 8 Understand the working principle of 3-phase induction motor. 64 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 8.7 Describe the construction of 3-phase induction motor. Explain the construction of squirrel cage induction motor. Explain the construction of wound rotor induction motor. Explain the production of rotating magnetic field in a 3-phase induction motor. Describe double squirrel cage induction motor. Explain the methods of starting of 3-phase induction motor. Explain the principles of speed control of 3-phase induction motor. SINGLE-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR 9 Understand the working principle of 1-phase induction motor. 9.1 Explain single phase motor is not self starting. 9.2 List the methods of making single phase motor self starting. 9.3 Describe standard split phase motor. 9.4 Describe capacitor motor. 9.5 Describe shaded pole motor and repulsion motor. 9.6 Describe hysteresis motor, universal motor, reluctance motor and AC series motor. 9.7 Describe the methods of speed control of single phase induction motor. SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR 10 Understand synchronous motor. 10.1 Explain the principle of operation of synchronous motor. 10.2 Describe the constructional features of synchronous motor. 10.3 Describe the starting methods of synchronous motor. 10.4 Explain the characteristics of synchronous motor. 10.5 Describe the application of synchronous motor. 10.6 Explain V-Curves. ALTERNATOR 11 Understand the concept of alternator. 11.1 Explain the principle of alternator. 11.2 List the parts of an alternator. 11.3 Explain the emf equation of an alternator. 11.4 Discuss the effect of load on alternator. 11.5 Explain the losses and efficiency of an alternator. 11.6 Describe voltage regulation of an alternator. 11.7 Define the term synchronizing. 11.8 Describe the process of synchronizing alternators. 11.9 List the conditions for synchronizing. Practical : 65 1 Show skill in studying of a DC generator. 1.1 Prepare a list of the parts of a DC generator. 1.2 Dismantle the components/parts of the DC generator. 1.3 Develop sketches of each parts. 1.4 Sketch the developed diagram of the winding of the generator. 1.5 Assemble the dismantled parts. 1.6 Start the generator. 2 Show skill in constructing load versus speed characteristic curve of DC shunt motor. 2.1 Sketch the required circuit diagram for the experiment. 2.2 List the instrument and materials required for the experiment. 2.3 Connect all the instruments and equipment according to circuit diagram. 2.4 Take the necessary data from the connected instruments. 2.5 Draw the required curve. 3 Show skill in determining the transformation ratio of a transformer. 3.1 Develop a circuit to perform the experiment. 3.2 Collect required equipment and materials. 3.3 Connect the components according to the circuit diagram. 3.4 Check the connections. 3.5 Record the primary (EP) and secondary (ES) voltages. 3.6 Calculate the transformation ratio using the relation ES NS EP = NP = K 4 Show skill in performing open circuit test of a single phase transformer. 4.1 Select the circuit diagram for the experiment. 4.2 Collect required tools, equipment and materials. 4.3 Connect all the equipment according to the circuit diagram. 4.4 Connect the low side to its rated voltage to the power supply keeping high side open. 4.5 Record instrument readings. 4.6 Calculate required data. 4.7 Draw no load vector diagram with the data obtained. 5 Show skill in performing short circuit test of a single phase transformer. 5.1 Select the required circuit diagram for the experiment. 5.2 Collect required tools, equipment and materials. 5.3 Connect the equipment according to the circuit diagram. 5.4 Energize the circuit by applying reduced voltage. 5.5 Record copper loss and calculate Re , Xe and Ze. 66 6 Show skill in determining the equivalent circuit of a transformer. 6.1 Select required tools, equipment and materials. 6.2 Perform open circuit and short circuit tests for the transformer. 6.3 Calculate required data for the equivalent circuit. 6.4 Draw the equivalent circuit. 7 Show skill in winding of a small transformer. 7.1 Develop the design of a small transformer. 7.2 Select the transformer core. 7.3 Select super enamel copper wire for both high voltage winding and low voltage winding. 7.4 Select other necessary materials eg. leatheroid paper, ampere cloth, ampere tube, soldering material, varnish etc. 7.5 Perform the windings. 7.6 Test the windings. 7.7 Connect power supply. 8 Show skill in studying the components/parts of a 3-phase induction motor. 8.1 Prepare a list of the different parts of a 3-phase induction motor. 8.2 Dismantle the components/parts of the motor. 8.3 Develop sketches of each part. 8.4 Sketch the developed diagram of the windings of the motor. 8.5 Assemble the dismantled parts. 9 Show skill in operating a 3-phase induction motor. 9.1 Sketch the circuit diagram. 9.2 List tools, equipment required for the experiment. 9.3 Connect starter with motor. 9.4 Connect power supply to the circuit. 9.5 Observe the operation. 9.6 Measure the speed of the rotor. 10 Show skill in winding of a 3-phase induction motor. 10.1 Develop the winding diagram of a 3-phase induction motor. 10.2 Select the proper size of copper wire. 10.3 Place the required coils in proper space and turns. 10.4 Place the coils in proper ways into slots. 10.5 Connect the coils in proper sequence. 10.6 Test the winding and connections. 10.7 Connect 3-phase supply with the motor stator. 11 Show skill in starting a capacitor type motor/ceiling fan with regulator. 11.1 List the tools and equipment required for the experiment. 11.2 Sketch a working diagram. 67 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.6 11.7 Identify two sets of coils. Connect the capacitor with the proper set of coil. Connect a regulator with the fan. Connect power supply to the fan. Test the rotation of fan in opposite direction by changing the capacitor connection. 12 Show skill in winding of a single phase capacitor motor. 12.1 Develop the winding diagram of a single phase capacitor motor. 12.2 Select correct size of super enamel copper wire for starting and running windings. 12.3 Prepare coils in proper space and turns. 12.4 Place the coils in slots. 12.5 Connect the coils. 12.6 Select the correct size of capacitor for motor. 12.7 Test the capacitor. 12.8 Connect the capacitor with the starting winding. 12.9 Connect proper supply and observe operation of motor. 13 Show skill in operating a synchronous motor by changing field excitation. 13.1 Select required tools, equipment, machine and materials. 13.2 Sketch the circuit diagram. 13.3 Connect the instrument according to the diagram. 13.4 Check the circuit. 13.5 Change the field excitation. 13.6 Record armature and field current. 13.7 Draw the ‘V’ curve. 14 Show skill in operation of an alternator. 14.1 List the required tools, equipment and machine for the experiment. 14.2 Sketch the circuit diagram. 14.3 Connect the equipment according to circuit diagram. 14.4 Start the alternator. 14.5 Develop the voltage. 14.6 Record the data. REFERENCE BOOKS 1. 2. A Text Book of Electrical Technology B. L. Theraja Electrical Machines Siskind 68 6811 BASIC ELECTRICITY T 3 P 3 C 4 OBJECTIVES To familiarize the basic electrical quantities & laws and to apply them in solving problems of electrical circuits. To acquaint with electro-chemistry, electro-magnetism, electro-magnetic induction and electrostatic. To develop skill in electrical wiring. To appreciate the safety measures to be taken for electrical wiring. SHORT DESCRIPTION Electric current and ohm's law; Conductors and insulators; Basic electrical circuits; Power and energy; Basic electro-chemistry; Electro-magnetism; Electro-magnetic induction; Electrostatics; Wires and cables; Hand tools used in wiring; House wiring; Controlling devices; Protective devices; Earthing. DETAIL DESCRIPTION Theory : ELECTRIC CURRENT 1 Understand electricity and its nature. 69 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 State the meaning of electricity. Describe the structure of atom. Define current, voltage and resistance. State the units of current, voltage and resistance. CONDUCTOR & INSULATOR 2 Understand conductor and insulator. 2.1 Define conductor and insulator. 2.2 Explain the conductor and insulator according to electron theory . 2.3 List at least 5 conductors and 5 insulators. 2.4 Describe the factors upon which the resistance of a conductor depends. 2.5 State laws of resistance. 2.6 Prove the relation R= L A 2.7 Explain the meaning of resistivity and name the unit of resistivity. 2.8 Solve problems relating to laws of resistance. OHM'S LAW 3 Understand Ohm's Law 3.1 State Ohm's law. 3.2 Deduce the relation between current, voltage and resistance. 3.3 Solve problems relating to Ohm's law. BASIC ELECTRIC CIRCUITS 4 Understand electric circuit. 4.1 Define electric circuit. 4.2 Name the different types of electric circuits. 4.3 Define series circuit, parallel circuit and mixed ckt. 4.4 Describe the characteristic of series circuit and parallel circuit. 4.5 Calculate the equivalent resistance of series circuit, parallel circuit and Mixed circuit. 4.6 Solve problems relating to series circuit, parallel circuit and mixed ckt . POWER AND ENERGY 5 Apply the concept of electrical power and energy. 5.1 Define electrical power and energy. 5.2 State the unit of electrical power and energy. 5.3 Show the relation between electrical power and energy. 5.4 List the name of instruments for measuring of electrical power and energy. 5.5 Draw the connection diagram of wattmeter and energy meter in an electrical circuit. 5.6 Solve problems relating to electrical power and energy Calculation. 6 Understand the principles of Joule's law. 70 6.1 Describe the heating effect of electricity when current flows through a conductor. 6.1 Explain Joule's law regarding the development of heat in electrical circuit. 6.2 Describe meaning of "J". 6.3 Solve problems relating to Joule’s law. 6.4 Solve problems relating to Joule’s law. BASIC ELECTRO-CHEMISTRY 7 Understand the concept of cells. 7.1 Describe the meaning of potential difference. 7.2 Define the meaning of cell. 7.3 Classify the Cell 7.4 Define Primary Cell 7.5 List the different types of primary Cell 7.6 Describe the construction and principle of action of a simple Voltaic cell. 7.7 List the defects of a simple Voltaic cell. 7.8 Describe the causes of defects of a simple Voltaic cell. 7.9 Describe the methods of removing the defects of a simple Voltaic cell. 8. Understand the construction and principle of action of secondary cell. 8.1 Define secondary cell. 8.2 Describe the construction and principle of action of a lead acid cell. 8.3 List the uses of lead acid cell. 8.4 List the advantages of secondary cell. 8.5 Distinguish between a cell and a battery. 8.6 Describe the series and parallel grouping of cells. 8.7 Distinguish between Primary & Secondary Cell 9 Understand the concept of capacitors and capacitance. 9.1 Define capacitor and capacitance. 9.2 Name the unit of capacitance. 9.3 Name the different types of capacitor. 9.4 Write the uses of capacitor. 9.5 Determine the equivalent capacitance of a number of capacitors connected in series. 9.6 Determine the equivalent capacitance of a number capacitors connected in parallel. 9.7 Explain the energy stored in a capacitor. 9.8 Solve problems relating to capacitor connected in series and in parallel. ELECTRO - MAGNETISM 10 Understand Electro - magnetism. 10.1 Describe magnetic field, magnetic lines of force and its properties. 10.2 Describe field intensity and magnetic flux density. 71 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.7 10.8 10.9 Distinguish between absolute permeability and relative permeability. Describe the concept of magnetic effect of electrical current. States Maxwell's cork screw rule and Fleming's right hand rule for determining the direction of magnetic field and current. Explain the force experienced in a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field. State Fleming's left hand rule. Explain the work done by a moving conductor in a magnetic field. Explain the force between two parallel current carrying conductor. 11 Understand magnetic circuit. 11.1 Define a magnetic circuit. 11.2 Define the terms magnetizing force, magnetomotive force, ampere – turns, reluctance, permeance, permeability, magnetic linkage and leakage. 11.3 Show the relation between magnetomotive force, reluctance and magnetic field intensity or magnetizing force. 11.4 Compare a magnetic circuit with an electrical circuit. ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION 12 Understand electro- magnetic induction. 12.1 Define Faraday's laws of electro-magnetic induction. 12.2 Describe the magnitude of dynamically induced emf and statically induced emf 12.3 Solve problems relating to emf generation. 12.4 Define Lenz's law and Fleming's right hand rule for determining the direction of induced emf and current. 12.5 Define self induced emf and self inductance. 12.6 Explain inductance of a iron cored inductor. 12.7 Define mutual inductance and co-efficient of coupling. WIRES AND CABLES 13 Understand the uses of wires and cables. 13.1 Define electrical wires and cables. 13.2 Distinguish between wires and cables. 13.3 Describe the construction and uses of PVC, VIR, TRS or CTS and flexible wires 13.4 Describe the procedure of measuring the size of wires and cables by wire gauge. 13.5 Describe the current carrying capacity of a wire. JOINTS AND SPLICES 14 Understand the usefulness of joints and splices. 14.1 Define the meaning of joints and splices. 72 14.2 14.3 14.4 State the five steps of making a joint. Describe the procedure to make a pig tail joint, western union joint, Britannia joint, duplex joint, tap joint, simple splice. Give example of uses of above mentioned joints. HOUSE WIRING 15 Understand the different methods of house wiring. 15.1 State the meaning of wiring. 15.2 List the types of wiring. 15.3 State the procedure for Channel wiring, surface conduit wring and concealed wiring. 15.4 State the types of wiring used in : a) Residential building. b) Workshop c) Cinema hall/Auditorium d) Temporary shed 15.5 List the name of fittings used in different types of electrical wiring. CONTROLLING DEVICES 16 Understand the construction and uses of controlling devices. 16.1 Define controlling device. 16.2 Name the different types of controlling devices. 16.3 Describe the constructional features and uses of tumbler switch, iron switch, push button switch and gang switch. PROTECTIVE DEVICES 17 Understand the construction and uses of protective devices. 17.1 Define protective devices. 17.2 Name the different types of protective devices. 17.3 Name the different types of fuses used in house wiring. 17.4 Describe the construction and uses of renewable fuse. 17.5 Name the different types of circuit breaker used in house wiring. EARTHING 18 Understand the necessity of ear thing. 18.1 Define earthing 18.2 Explain necessity of earthing 18.3 Name different types of ear thing WIRING CIRCUITS 19 Apply the principle of controlling electrical circuit by switch. clad 73 19.1 19.2 19.3 19.4 19.5 Sketch the wiring diagram of one lamp controlled by one SPST switch and describe its uses. Sketch the wiring diagram of one lamp controlled by two SPDT switch and describe its uses. Draw the wiring diagram of one calling bell with a lamp controlled from one point. Draw the wiring diagram of a fluorescent tube light circuit. Describe the working principle of fluorescent tube light. ELECTRICITY ACT 20 Understand electricity act/rule of Bangladesh and safety practices. 20.1 State electricity act/rule of Bangladesh to be followed in electrical wiring. 20.2 Describe the importance of electricity act/rule. 20.3 Describe safety procedure against electrical hazards. 20.4 List the performance of safety practices for electrical equipment, machines and accessories. 74 Practical : 1 Identify and use electrical measuring instruments. 1.1 Identify Voltmeters, Ammeters, Ohm Meter, Wattmeter, Energy meter and AVO meter. 1.2 Select & read the scale of given meters. 1.3 Connect correctly voltmeter, ammeter, wattmeter and energy meter to a given circuit.. 2 Show skill in verification of Ohm’s Law. 2.1 Sketch the circuit diagram for the verification of Ohm’s Law. 2.2 List tools, equipment and material required for the experiment . 2.3 Prepare the circuit according to the circuit diagram using proper equipment. 2.4 Check all connections before the circuit is energized. 2.5 Verify the law by collecting relevant data. 3 Verify the characteristics of series and parallel circuits. 3.1 Draw the working circuit diagram. 3.2 List tools, equipment and materials required for the experiment . 3.3 Prepare the circuit according to the circuit diagram using proper equipment. 3.4 Check all connections before the circuit is energized. 3.5 Record data and verify that in a series circuit total voltage and resistance is equal to the summation of individual voltage and resistance respectively but total current is equal to the individual current. 3.6 Record data and verify that for a parallel circuit supply voltage is equal to the branch voltage, supply current is equal to summation of branch currents and total conductance is equal to the summation of branch conductance. 4 Show skill in measuring the power of an electric circuit. 4.1 Sketch the necessary circuit diagram of an electrical circuit w electrical load, ammeter, voltmeter and wattmeter. 4.2 Prepare the circuit according to the circuit diagram using ammeter, voltmeter and wattmeter. 4.3 Record the power, measured by the wattmeter and verify t reading with that of calculated from ammeter and voltmeter. 4.4 Compare the measured data with that of calculated and rat power. 5 Show skill in measuring the energy consumed in an electrical circuit. 5.1 Sketch the necessary diagram of an electric circuit wattmeter, energy meter and electrical load. 5.2 Prepare the circuit according to the circuit diagram user wattmeter and energy meter. 5.3 Record the energy measured by the energy meter and verify with that of calculated from wattmeter for a fixed time. 75 6 Show skill in grouping a number of cell to form a battery . 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Sketch the connection diagram of 4 cells (1.5 V each) in series. List the materials and equipment required for the experiment. Connect the terminals of the cells according to the diagram. Determine the terminal voltage of the group and verify it with the calculated result. 7 Make a simple Cell. 7.1 List the materials for constructing a simple cell. 7.2 Prepare electrolyte by diluting H2SO4 with distilled water on proper ratio. 7.3 Assemble the cell using required electrolyte and electrodes along with necessary materials. 7.4 Measure the emf of the cell. 8 Show skill in making artificial magnets. 8.1 Make an artificial magnet by rubbing method (Single touch) 8.2 Make an artificial magnet by divided touch method. 8.3 Make an artificial magnet by passing electrical current. 8.4 Detect the polarity of the produced artificial magnet with the help of a compass needle. 9. Show skill in uses of hand tools, wires and cables. 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 10. Show skill in 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 11 List the hand tools used in electrical wiring. Identify the hand tools used in electrical wiring. Draw neat sketches of hand tools used in electrical wiring. Identify different types of wires and cables. Measure the diameter of the identified wire and cables using standard wire gauge. making a duplex joint and a T-joint . Sketch a duplex joint and a T-joint Perform skinning and scraping of two pieces of PVC duplex cal and two pieces of simplex PVC cables. Make the joints according to sketches. Write a report. Show skill in preparing wring circuit of two lamps controlled from the points separately. 11.1 11.2 11.3 Sketch a working circuit of two lamps controlled from two poin separately. Make the wiring circuit using required materials and equipment a wiring board. Test the connection of circuit by providing proper supply. 76 12 Show skill in preparing wiring circuit of one lamp controlled from the points. 12.1 Sketch a working diagram of one lamp controlled by two SPD tumbler switches. 12.2 Complete the wiring circuit using required materials and equipment on wiring board. 12.3 Test the connection of circuit by providing proper supply. 13 Show skill in preparing wiring circuit of one bell with two indicating lamp controlled from two points. 13.1 Sketch a working diagram of one bell with two indicating lamps controlled by two push button switch. 13.2 Make the wiring circuit using required materials and equipment in wiring board. 13.3 Test the connection of circuit by providing proper supply. 14 Show skill in preparing wiring circuit of a fluorescent tube light. 14.1 Sketch a working diagram of a fluorescent tube light circuit. 14.2 Make the connection of a fluorescent tube light circuit using required materials and equipment. 14.3 Test the connection of the circuit by providing supply. REFERENCE BOOKS 1 2 3 A text book of Electrical Technology B. L. Theraja Basic Electricity Charles W Ryan Basic Electrical theory and Practice E. B. Babler SOCIAL SCIENCE – II (BANGLADESH : HISTORY & CULTURE) 5821 D‡Ïk¨ T 2 P C 0 2 cÙv-†gNbv-hgybv eØxc Aayy¨wlZ †fŠ‡MvwjK A‡j ev½vjx mgvR MVb Ges bvbv HwZnvwmK weeZ©‡bi ch©vq †cwi‡q MwVZ AvaywbK evsjv‡`k m¤ú‡K© wk¶v_©x‡`i h_v_© AeMZ Kiv‡bv Ges Zv‡`i mwVK †eva m„wóKiY| cÖvK…wZK I A_©‰bwZK KvVv‡gvi cwigÛ‡j evsjv‡`‡ki mvs¯‹…wZK weKv‡ki mv‡_ wk¶v_©x‡`i D¾xweZ K‡i evsjv‡`‡ki †hvM¨ I cwikxwjZ bvMwiK wnmv‡e h_v_© weKwkZKiY| msw¶ß weeiYx 77 BwZnvm BwZnv‡mi msÁv| evsjv‡`‡ki AvenvIqv I Awaevmx| cÖv‰MwZnvwmK I cÖvPxbKv‡j evsjv‡`k | evsjvq gymjgvb‡`i AvMgb, cÖwZôvjvf I kvmb LjRx I ZzK©x kvm‡b evsjvq ¯^vaxb myjZvbx cÖwZôv; evsjv‡`‡k kvnx Avgj, AvdMvb I †gvNj Avg‡j evsjvi kvmb| evsjvq BD‡ivcxq ewYK‡`i AvMgb; bevex Avg‡j evsjvi kvmb e¨e¯’v; evsjvq Bs‡iR kvmb ¶gZv jvf I cÖwZôv| weªwUk we‡ivax mk¯¿ cÖwZ‡iva Av‡›`vjb; ms¯‹vi Av‡›`vjb I RvZxqZvev‡`i weKvk Ges evsjvi beRvMiY; e½f½ I e½f½ DËiKv‡j evsjvi ivRbxwZ I †`k wefvM| cvwK¯Ívb Avg‡j evsjv‡`k Ges evsjv‡`‡ki gyw³ msMÖvg I hy×| ms¯‹…wZ ms¯‹…wZi msÁv, Avw`hy‡M evsjvi mgvR-ms¯‹…wZi iƒc‡iLv, myjZvbx, †gvNj I bevex Avg‡ji evsjvi mgvR ms¯‹…wZ; Bs‡iR Avg‡j evsjvi mgvR I ms¯‹…wZ| iex›`ª I bRi“j hyM Ges iex›`ª I bRi“j DËi evsjvi mgvR I ms¯‹…wZ; cvwK¯Ívb Avg‡j evsjv‡`‡ki mvs¯‹…wZK iƒc‡iLv; ¯^vaxbZvDËi evsjv‡`‡ki ms¯‹…wZ| wek` weeiYx BwZnvm 1. BwZnv‡mi msÁv, cÖv‰MwZnvwmK Avg‡ji evsjv‡`k Ges evsjv‡`‡ki AvenvIqv I Awaevmx m¤ú‡K© AeMZ nIqv| 1.1 BwZnv‡mi msÁv cÖ`vb| 1.2 evsjv‡`‡ki cÖvPxb Rbc` D‡j­L Kiv| 1.3 e½ ev evsjv bv‡gi DrcwË e¨vL¨v Kiv| 1.4 e‡½i mxgv‡iLv wPwýZ Kiv| 1.5 evsjvi AvenvIqv I Gi Awaevmx‡`i Pwi‡Î AvenvIqvi cÖfve wee„Z Kiv| 1.6 cÖv‰MwZnvwmK I cÖvPxb evsjvi Av_©mvgvwRK e¨e¯’v eY©bv Kiv| 2. evsjv‡`‡k ¸ß, ivRv kkv¼, cvj I gymwjg kvmb m¤ú‡K© AeMZ nIqv| 2.1 ¸ß kvmb Avg‡j evsjvi kvmbe¨e¯’v eY©bv Kiv| 2.2 ivRv kkv‡¼i ivR¨ weRq I kvmb eY©bv Kiv| 2.3 evsjvi AivRKZv I wnD‡qbmvs Gi Avg‡j evsjvi Ae¯’v eY©bv Kiv| 2.4 †Mvcvj KZ©„K AivRKZvi Aemvb NUv‡bvi K…wZ‡Z¡i eY©bv Kiv| 2.5 evsjv‡`‡k gymjgvb‡`i AvMgb I eLwZqvi LjRxi evsjv weRq eY©bv Kiv| 2.6 evsjv‡`‡k ¯^vaxb myjZvbx kvmb cÖwZôvq kvgQywÏb Bwjqvk kvTxi K…wZZ¡ eY©bv Kiv| 2.7 evsjvq †gvNj kvm‡bi BwZe„Ë e¨vL¨v Kiv| 2.8 1757 mv‡ji cjvkxi hy‡×i KviY, NUbv I djvdj eY©bv Kiv| 3. cjvkxhy× cieZ©x Ae¯’vq B÷ BwÛqv †Kv¤úvbxi AvwacZ¨ we¯Ívi m¤ú‡K© © ÁvZ nIqv| 3.1 †`Iqvbx, ‰ØZkvmb I evsjvi `ywf©¶ eY©bv Kiv| 3.2 Bs‡iR‡`i wPi¯’vqx e‡›`ve¯Í Ges Gi djvdj eY©bv Kiv| 78 3.3 3.4 3.5 evsjv‡`‡k Rwg`vi, cÖRve¨e¯’v cÖwZôv Ges Av_©-mvgvwRK e¨e¯’vq Rwg`vi‡`i f‚wgKv I cÖRvKz‡ji mvwe©K Ae¯’v D‡j­L Kiv| 1905 mv‡ji e½f½ Av‡›`vjb I djvdj e¨L¨v Kiv| nvRx kixqZ Dj­vni div‡qRx Av‡›`vjb I Gi djvdj e¨L¨v Kiv| 4. e½f½DËi ivRbxwZ I †`k wefvM m¤ú‡K© © AewnZ nIqv| 4.1 1937 Gi wbe©vPb I Gi ˆewkó¨ D‡j­L Kiv| 4.2 jv‡nvi cÖ¯Íve e¨³ Kiv| 4.3 1943 Gi evsjvi `ywf©‡¶i KviY I Gi c~e©vci Ae¯’v D‡j­L Kiv| 4.4 cvwK¯Ív‡bi c~e©vÂj wnmv‡e 1947 mv‡j c~e© cvwK¯Ív‡bi cÖwZôv e¨vL¨v Kiv| 5. cvwK¯Ívb Avg‡j evsjv‡`‡ki (ZrKvjxb c~e© cvwK¯Ívb) ivRbxwZ, A_©bxwZ I mvgvwRK Ae¯’v m¤ú‡K© AeMZ nIqv| 5.1 fvlv Av‡›`vjb I mgKvjxb ivR‰bwZK I mvgvwRK †cÖw¶Z e¨³ Kiv| 5.2 AvIqvgxjxM cÖwZôv, hy³d«›U I 21 `dv `vexi wfwˇZ wbe©vPb Abyôvb Ges hy³d«‡›Ui gwš¿mfv MVb I evwZj Av‡jvPbv Kiv| 5.3 cvwK¯Ív‡bi mvgwiK Afz¨Ìvb, AvBqye we‡ivax Av‡›`vjb I 6 `dv `vex, AvMiZjv lohš¿ gvgjvi BwZe„Ë eY©bv Kiv Ges c~e©-cwðg cvwK¯Ív‡bi A_©‰bwZK ˆel‡g¨i LwZqvb D‡j­L Kiv| 5.4 1969 mv‡ji MYAfz¨Ìvb Ges Gi avivevwnKZvq evsjv‡`‡ki gyw³hy× I ¯^vaxb mve©‡fŠg evsjv‡`k cÖwZôv Kivi cUf~wg I NUbv cÖevn eY©bv Kiv| 5.5 1971 mv‡ji HwZnvwmK gyw³hy× Ges ¯^vaxb mve©‡fŠg evsjv‡`‡ki Afz¨`q eY©bv Kiv| 6. ¯^vaxb mve©‡fŠg evsjv‡`‡ki ivRbxwZ I Av_©-mvgvwRK Ae¯’v m¤ú‡K© AeMZ nIqv| 6.1 hy‡×vËi ¯^vaxb mve©‡fŠg evsjv‡`‡ki Av_©-mvgvwRK cybM©Vb Kg©ZrciZv eY©bv Kiv| 6.2 1973 mv‡ji wbe©vPb Ges 1974 mv‡j msweav‡bi 4_© ms‡kvabxi gva¨‡g miKvi c×wZi cwieZ©b e¨³ Kiv| 6.3 1975 mv‡ji 15 AvM÷ RvwZi RbK e½eÜz †kL gywReyi ingvb -Gi kvnv`vZ eiY Ges ivR‰bwZK cUcwieZ©b| 6.4 1981 mv‡j ivóªcwZ wRqvDi ingv‡bi kvnv`vZ eiY, 1982 mv‡ji mvgwiK Afz¨Ìvb Ges ivR‰bwZK cUf‚wg cwieZ©b| 6.5 1990 mv‡j Gikv` miKv‡ii cZb Ges ZË¡veavqK miKvi c×wZ Abyms‡M 1991 m‡bi wbe©vPb Ges MYZvwš¿K Abykxj‡bi m~Pbv| ms¯‹…wZ 7. ms¯‹…wZi msÁv Ges cÖvPxb I ga¨hyMxq evsjvi ms¯‹…wZ I mvwnZ¨ PP©v m¤ú‡K© AeMZ nIqv| 7.1 ms¯‹…wZi msÁv `vb| 7.2 cÖvPxb evsjvi fvlv mvwnZ¨ I ms¯‹…wZi iƒc‡iLv eY©bv Kiv| 7.3 ev½vjx ms¯‹…wZ wbg©v‡Y gwm©qv I cyuw_ mvwn‡Z¨i cÖfve eY©bv Kiv| 8. AvaywbK hy‡M evsjv‡`‡ki ms¯‹…wZ I evsjvfvlvi AvaywbK iƒcjvf m¤ú‡K© AeMZ nIqv| 8.1 Bs‡iR kvmb Avg‡j mvgvwRK Kzms¯‹vi `~ixKi‡Y (m¨vi ˆmq` Avng`, ˆmq` Avgxi Avjx I ivRv ivg‡gvnb ivq) Gi Avwef©ve Ges Zv‡`i Kg©ZrciZv e¨vL¨v Kiv| 79 8.2 8.3 8.4 9. K¨vwi mv‡ne Ges †dvU© DBwjqvg K‡jR/ms¯‹…Z K‡jR ¯’vc‡bi gva¨‡g evsjvi bZzb ms¯‹…wZi iƒcjvf eY©bv Kiv| Bs‡iR‡`i wk¶vbxwZ cÖeZ©b e¨vL¨v Kiv Ges KwjKvZv wek¦we`¨vjq I Bmjvwgqv gv`ªvmv ¯’vc‡bi gva¨‡g evsjvi ms¯‹…wZi weKvk e¨³ Kiv | XvKv wek¦we`¨vjq cÖwZôvi BwZe„Ë e¨vL¨v Kiv| 1947 Gi †`k wefvM I mvs¯‹…wZK Ae¯’vi cwieZ©b m¤ú‡K© AeMZ nIqv| 9.1 ZrKvjxb c~e© cvwK¯Ív‡bi ZgyÏyb gRwj‡mi f‚wgKv D‡j­L Kiv| 9.2 1952 mv‡ji fvlv Av‡›`vj‡bi mvs¯‹…wZK ¸i“Z¡ D‡j­L Kiv| 9.3 XvKv †Kw›`ªK wkíx-mvwnwZ¨K‡`i evsMvjx ms¯‹…wZ wewbg©v‡Yi f‚wgKv cvjb D‡j­L Kiv| 9.4 Õ69 Gi MY Av‡›`vj‡b mvs¯‹…wZK Kg©x‡`i f‚wgKv D‡j­L Kiv| 9.5 evOjv GKv‡Wgxi cÖwZôv Ges evsjv fvlv I mvwn‡Z¨ Gi f~wgKv D‡j­L Kiv| 9.6 9.7 AvšÍR©vwZK gvZ…fvlv w`em wn‡m‡e 21 †deª“qvwii Zvrch© e¨³ Kiv| fvlv, wkí mvwnZ¨ PP©vq msev`cÎ I B‡jKUªwbK wgwWqvi f‚wgKv D‡j­L Kiv| 10. ms¯‹…wZi Dci MÖvgxY A_©bxwZi cÖfve AeMZ nIqv| 10.1 ZuvZ wkí I gmwjb Drcv`‡bi BwZe„Ë e¨vL¨v Kiv| 10.2 cvU Pv‡li A_©‰bwZK cÖfve e¨³ Kiv| 10.3 ev½vjx ms¯‹…wZi Ask wn‡m‡e `y»RvZ wgóvbœ mvgMÖxi (wgwó, gvLb, `wa, wcVv-cywj cÖf…wZ) cÖfve e¨³ Kiv| 10.4 †`kxq †gjv I cve©‡bi mvs¯‹…wZK ¸i“Z¡ e¨vL¨v Kiv| 10.5 MÖvgxY †ckvRxwe‡`i (Kvgvi, Kzgvi, ZuvZx, †R‡j, QyZvi, BZ¨vw`) mvs¯‹…wZK ¸i“Z¡ e¨vL¨v Kiv| 11. evsjv‡`‡ki ms¯‹…wZ‡Z Avw`evmx ms¯‹…wZ I cÖZœ ZvwË¡K wb`k©‡bi Ae`vb m¤ú‡K© AeMZ nIqv| 11.1 evsjv‡`‡ki Avw`evmx m¤ú‡K© D‡j­L Kiv| 11.2 evsjv‡`‡ki ms¯‹…wZ‡Z Mv‡ov, ivLvBb, mvIZvj, PvKgv Avw`evmx‡`i ms¯‹…wZK Ae`vb e¨L¨v Kiv| 11.3 evsjv‡`‡ki cÖvPxb ms¯‹…wZi HwZn¨ wnmv‡e gnv¯’vbMo, gqbvgwZ I cvnvocy‡ii cÖZœZvwË¡K wb`k©‡bi eY©bv `vb| mnvqK cy¯ÍK iwng, †PŠayix, gvngy` I Bmjvg, Òevsjv‡`‡ki BwZnvm (cwiewa©Z I cwigvwR©Z)Ó ; bI‡ivR wKZvwe¯Ívb, AvM÷, 1999| †K, Avjx Òevsjv‡`‡ki BwZnvmÓ; AvwRwRqv eyK wW‡cv, 2001| wmivRyj Bmjvg, Òevsjv‡`‡ki BwZnvm-1704-1971Ó; 1g, 2q I 3q LÛ; 80 evsjv‡`k GwkqvwUK †mvmvBwU, †deª“qvwi 2000| †Kv-Av‡šÍvbfv, wcÖ, K‡Zvfw®‹, ÒfviZe‡l©i BwZnvmÓ; cÖMwZ cÖKvkb, 1988| †Mvcvj nvj`vi; Òms¯‹…wZi iƒcvšÍiÓ; gy³aviv, †g 1984| †gvZv‡ni †nv‡mb †PŠayix, Òms¯‹…wZ K_vÓ; bI‡ivR wKZvwe¯Ívb, Rvbyqvwi 1998| †Mvcvj nvj`vi, Òevsjv mvwn‡Z¨i iƒc‡iLv-1g I 2q LÛÓ; gy³aviv, RyjvB 1978|