Name
advertisement

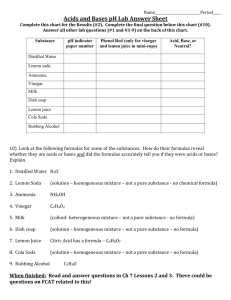
1 Name: ________________________________________ Homeroom: ____________ Chapter 13 - Matter and How it Changes Essential Question: What Are the Physical Properties of Matter? Physical Properties Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Matter is made up of atoms. A physical property is something that describes a property by itself and can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance. Three physical properties apply to all substances: mass, volume, and density. Mass, Volume, and Density Mass is the amount of matter something has. Mass can be measured in grams. Volume is the amount of space something takes up. It can be measured in liters (metric) or gallons(customary). Density is the amount of mass something has in relation to its volumne. Density = mass ÷ volumne. Can be measured in grams per liter. Any substance that floats on a liquid has a higher density than the liquid it is floating on. Physical Changes When a substance undergoes a physical change, one or more physical properties changes, but the substance does not become a different substance. When matter goes through a physical change its mass does not change. Dissolving, Melting, and Boiling 2 Dissolving, melting, and boiling are physical changes. The ability for a substance to dissolve is known as solubility. This property is the measure of how much a substance will dissolve in a liquid. We must keep in mind that even though a substance changes state the nature of the substance does not change. Essential Question: What Are Mixtures? Mixtures & Separating Mixtures A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that keep their original properties. Keep in mind that the amount of the substances in the mixture can change, but the properties of each substance remains the same. We can then separate the mixture into the original substances. This is not always an easy process depending on what physical changes have taken place. Solutions A solution is a mixture in which all the substances are evenly distributed. To be distributed evenly means to have the substances spread out evenly among each other. A solution occurs when a solute dissolves in a solvent. A solute is the substance that is dissolved. A solvent is the substance it’s dissolved in. Most often we think that solids dissolve in liquid, but there are other types of solutions. An example of a gas dissolved in a liquid is soda. Liquids can also be dissolved in liquids such as the mixture of gasoline and motor oil that often powers lawn mowers. Solids can even dissolve in solids. These mixtures are very common such as iron, manganese, and carbon making steel. Solutions that involve two or metals are 3 called alloys. Dissolving a solid in another solid is a more difficult process that often requires the solids to be melted, liquified, mixed together, and then allowed to return to the solid state. Other Types of Mixtures Suspension: do NOT stay mixed. A suspension is a uniform mixture that contains particles that are large enough to be seen. Colloid: stays mixed. A mixture that contains particles that are too small to be seen. Example: milk Emulsion: a mixture of two liquids that do not dissolve. Essential Question: What Are Chemical Properties of Matter? Chemical Properties and Changes A chemical change is one in which one or more new substances are formed. A chemical property is something that describes the ability of a substance to react with other materials and form new substances. Reactivity is the ability of a substance to go through a chemical change. While the opposite, stability is the ability of a substance to resist going through a chemical change. Types of Reactions Synthesis Reaction: putting together - two or more substances are put together to form a single substance. Decomposition Reaction: breaking up- a single substance breaks up, forming two or more different substances. 4 Single Replacement Reaction: one substance replaces another substance. Double Replacement Reaction: two substances switch places. Preventing Chemical Changes Heat starts or helps speed up a chemical reaction, therefore removing heat can slow or stop a chemical reaction. Food spoiling is a chemical reaction. In order to slow this reaction we put in the refrigerator, but to slow the reaction down even more we put food in the freezer. Essential Question: What Are Acids and Bases? Acids and Bases An acid is a substance that turn blue litmus paper red. Acids often taste sour. (NEVER taste anything in science) Many acids share certain physical properties. Examples of acids: lemon juice, vinegar, aspirin A base is a substance that turns red litmus paper blue. Many bases feel slippery. Many bases also share physical properties. Examples of bases: soap, ammonia, baking soda Indicators Indicators are thing such as litmus paper and wide range indicators because they indicate whether a substance is an acid or a base. The pH scale measures the strength or weakness of acids or bases. The pH scales ranges from 0 to 14. Neutral is right in the middle at 7. A neutral is neither an acid nor a base. The lower the pH value, the stronger the acid. THe higher the pH 5 value the stronger the base. In order to determine whether a substance is an acid or a base and find the pH value of the substance a wide-range indicator is used. How People Use Acids and Bases Hydrochloric acid: helps breaks down the food we eat. Cleaning metals. Bases: Water purification, hair dyes, most batteries.