Staining and Drying Acrylamide Gels
advertisement

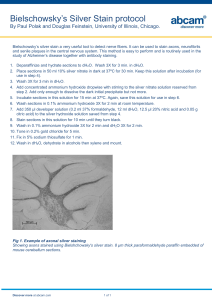
Staining and Drying Acrylamide Gels - Standard Coomassie stain procedures detect as little as 100ng, whereas silver stain can detect down to 2ng of protein in a single band (Bollag et al., 1996). - The most likely cause of high background staining are dirty glass plates, contaminated acrylamide solution or dirty water. - To increase staining, can combine Coomassie and silver stains. - Shrinking of the gel traps proteins within the gel and reflects a decrease in its hydration. Alcohols, usually methanol but sometimes ethanol, are used dehydrate the gel. Coomassie Blue Stain: (2hrs-O/N) - Coomassie stain was first used to stain proteins in 1962 (Fazekas de St.Groth et al., 1963) and on PAGE in 1965 (Meyer and Lamberts, 1965). - Acids are used to increase Coomassie binding, Coomassie binds preferentially Coomassie Solutions to positively charged amino acids (Tal et al., 1985). 1.0g Coomassie Blue R-250 - Steps: 0.1% Coomassie 300ml dH2O Fix & 45% MeOH Transfer gel from cassette directly to ~40ml of Fix & Stain solution 450ml methanol Stain 45% dH2O 100ml acetic acid Cover and rock for at least 1hr 10% Acetic acid dH2O to 1L Remove excess stain with several changes of Destain & Storage Destain 450ml methanol 45% MeOH solution (include a rolled up Kimwipe to soak up stain) & 45% dH2O 100ml acetic acid Storage Store at 4˚C in Destain & Storage solution, storage in water or other 10% Acetic acid dH2O to 1L solutions with little or no alcohols will swell the gel and potentially lead to loss of protein. Silver Stain: (<2hours) - Silver stain of PAGE was developed by Merill et al (Merril et al., 1979;Merril et al., 1981a;Merril et al., 1981b) - Can make solutions as you go, in a single 250ml cylinder that is rinsed out each time with dH2O. - Steps: Prepare Fix Incubate in Fix for 15min, meanwhile prepare Transition solution Incubate in Transition solution for 15min, meanwhile prepare Reduction solution Wash 2x 5min with dH2O Incubate for 15minutes in DTT/ dH2O, meanwhile prepare Silver Stain solution: Incubate in Silver Stain solution for 20minutes, meanwhile, prepare Developer solution: Set aside 5g of citric acid (Acros, #12491-0010) in a weigh boat Pour off Silver Stain solution Rinse once rapidly with ddH2O Rinse once rapidly with 100ml of Developer solution Incubate with the other 100ml of Developer solution When appropriate staining, add the 5g of citric acid directly to developer bath Wash the gel several time with dH2O Silver Stain Solutions Fix Transition Reduction Silver Stain 50% MeOH 10% acetic acid 5% MeOH 7% acetic acid Developer 100ml of methanol 80ml of dH2O 20ml acetic acid 176ml of ddH2O 14ml of acetic acid 10ml of methanol 100ml of dH2O 32μl of 0.1M DTT 0.10g of silver nitrate (Fischer, #S181-100) 100ml of dH2O 200ml ddH2O 6g of Na2CO3 (Sodium Carbonate, NOT sodium bicarbonate) 100μl of formaldehyde solution (Fischer, #F79500) Gel Drying: (~1hour) Optional: to obtain a more flexible gel, incubate in 10% glycine for 10min Carefully place gel on Whatmann paper Cover with plastic wrap Place on bed with cover Turn pump on Set temperature to 60°C Set timer for 1hour Form a seal by engaging pump and pushing out any remaining bubbles References: Bollag DM, Rozycki MD, Edelstein SJ (1996) Protein methods. New York: Wiley-Liss. Candiano G, Bruschi M, Musante L, Santucci L, Ghiggeri GM, Carnemolla B, Orecchia P, Zardi L, Righetti PG (2004) Blue silver: a very sensitive colloidal Coomassie G-250 staining for proteome analysis. Electrophoresis 25: 1327-1333. Fazekas de St.Groth S, Webster RG, Datyner A (1963) Two New Staining Procedures for Quantitative Estimation of Proteins on Electrophoretic Strips. Biochim Biophys Acta 71: 377-391. Merril CR, Dunau ML, Goldman D (1981a) A rapid sensitive silver stain for polypeptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 110: 201-207. Merril CR, Goldman D, Sedman SA, Ebert MH (1981b) Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science 211: 14371438. Merril CR, Switzer RC, Van Keuren ML (1979) Trace polypeptides in cellular extracts and human body fluids detected by two-dimensional electrophoresis and a highly sensitive silver stain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 76: 4335-4339. Meyer TS, Lamberts BL (1965) Use of coomassie brilliant blue R250 for the electrophoresis of microgram quantities of parotid saliva proteins on acrylamide-gel strips. Biochim Biophys Acta 107: 144-145. Tal M, Silberstein A, Nusser E (1985) Why does Coomassie Brilliant Blue R interact differently with different proteins? A partial answer. J Biol Chem 260: 9976-9980. http://www.geocities.com/simonwaynemoore/protocols.htm Page 1 of 1