NOTES CHAPTER 6
advertisement

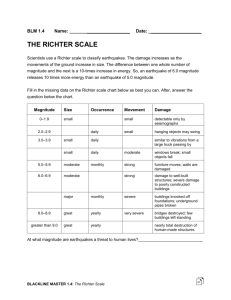
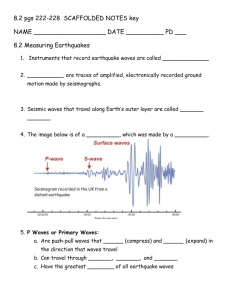
Earthquakes 2 Notes Elastic Rebound Theory Rocks on each side of the fault are moving slowly •____________________________________________________________________________________ •____________________________________________________________________________________ •Rocks along the fault release energy as ____________________________________________________ •Focus: __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ •Epicenter: __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Focus Depths Shallow-Focus Earthquakes –__________________________________________________________________ –__________________________________________________________________ Intermediate Focus Earthquakes –__________________________________________________________________ Deep-Focus Earthquakes –__________________________________________________________________ –__________________________________________________________________ –Occur farther inland 3 Major Earthquake Zones 1.__________________________________________________________________ 2. __________________________________________________________________ 3. __________________________________________________________________ •Fault Zones: –_________________________________________________________________________________________ –Form at plate boundaries ____________________________________________________________________ •Example: ________________________________________________________________________________ 3 Types of Seismic Waves P waves Primary waves –________________________________________________________________________________________ –________________________________________________________________________________________ –Travel through solids and liquids –Faster through more rigid material –________________________________________________________________________________________ •Cause rock particles to move together and apart along the direction of the waves S waves •Secondary Waves –________________________________________________________________________________________ –________________________________________________________________________________________ –________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ –Shear waves •Cause rock particles to move at right angles to the direction in which the waves are traveling Surface Waves •________________________________________________________________________________________ •________________________________________________________________________________________ •________________________________________________________________________________________ •Cause the surface to rise and fall •Very destructive: ________________________________________________________________________ Finding the Epicenter of an Earthquake •Analyze difference in arrival times between P waves and S waves. •_______________________________________________________________________________________ Measuring Earthquakes also called a Seismic Event • Three standard measures of the "size" of the earthquake are commonly used: –_______________________________________________________________________________________ –_______________________________________________________________________________________ –_______________________________________________________________________________________ Magnitude •_______________________________________________________________________________________ •The amount of ground motion •Higher the magnitude the larger the seismic event. Moment Magnitude Scale •Introduced 1979 to replace Richter Scale. •_______________________________________________________________________________________ –A 4 is 10000 times a 3 –A 3 is 1000 times a 2 –A 2 is 100X a 1. Moment Magnitude Scale •_________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ –For example: with Richter Scale a major EQ lasting 1 minute could be a 9, while the same EQ lasting 5 min is still a 9, in fact still a 9 if it lasted 10 minutes. •_________________________________________________________________________________________ •The USGS uses Richter for EQs smaller than 3.5. Modified Mercalli Scale •Modified Mercalli (MM) Scale based on 1909 model of volcano damage. •_________________________________________________________________________________________ •_________________________________________________________________________________________ Modified Mercalli Scale •I. _______________________________________________________________________________________ •II. A few people might notice movement if they are at rest and/or on the upper floors of tall buildings. •III. _____________________________________________________________________________________. Hanging objects swing back and forth. People outdoors might not realize that an earthquake is occurring. •IV. _____________________________________________________________________________________. Hanging objects swing. Dishes, windows, and doors rattle. The earthquake feels like a heavy truck hitting the walls. A few people outdoors may feel movement. Parked cars rock. •V. ______________________________________________________________________________________. Sleeping people are awakened. Doors swing open or close. Dishes are broken. Pictures on the wall move. Small objects move or are turned over. Trees might shake. Liquids might spill out of open containers. •VI. _____________________________________________________________________________________. People have trouble walking. Objects fall from shelves. Pictures fall off walls. Furniture moves. Plaster in walls might crack. Trees and bushes shake. Damage is slight in poorly built buildings. No structural damage. Modified Mercalli Scale •VII. ____________________________________________________________________________________ Drivers feel their cars shaking. Some furniture breaks. Loose bricks fall from buildings. Damage is slight to moderate in well-built buildings; considerable in poorly built buildings. •VIII. ____________________________________________________________________________________. Houses that are not bolted down might shift on their foundations. Tall structures such as towers and chimneys might twist and fall. Well-built buildings suffer slight damage. Poorly built structures suffer severe damage. Tree branches break. Hillsides might crack if the ground is wet. Water levels in wells might change. •IX. _____________________________________________________________________________________. Houses that are not bolted down move off their foundations. Some underground pipes are broken. The ground cracks. Reservoirs suffer serious damage. •X. ______________________________________________________________________________________. Some bridges are destroyed. Dams are seriously damaged. Large landslides occur. Water is thrown on the banks of canals, rivers, lakes. The ground cracks in large areas. Railroad tracks are bent slightly. •XI. Most buildings collapse. Some bridges are destroyed. Large cracks appear in the ground. Underground pipelines are destroyed. Railroad tracks are badly bent. •XII. ____________________________________________________________________________________. Objects are thrown into the air. The ground moves in waves or ripples. Large amounts of rock may move. Magnitude Scales •Richter Scale Destruction to Buildings and Property •1. ______________________________________________________________________________________ •2. ______________________________________________________________________________________ •3. Buildings on loose soil and rock, much more likely to be damaged. •4. Buildings on firm soil or bedrock are much more likely to survive. Tsunamis Form in one of two ways 1. _____________________________________________________________________, causes a sudden drop or rise in ocean floor, displaces a large volume of sea water. This volume of water churns up and down as it adjusts to the change. This sets into motion a series of low, long waves that develop into tsunamis. 2. _____________________________________________________________________ causes tons of debris to drop down to sea floor, which causes water to be displaced, then this sets into motion a series of low, long waves that develop into tsunamis. Earthquake Warnings and Predictions Smiley face denotes success of research. 1. Animal research continues to determine if they can tell us something. 2. Using past EQ dates scientists approximate future dates. 3. Sensors placed at faults help to measure strain on rocks. 4. SEISMIC GAPS_ a place where fault is locked & does not move lets strain build up surrounding it. These are believed to be future EQ 5. Slight tilting of ground before EQ. 6. Magnetic & electrical properties of rocks change 7. Increase in natural gas seepage from rocks 8. Decrease in P wave speed, longer the decrease stronger the EQ