printer-friendly sample test questions
advertisement

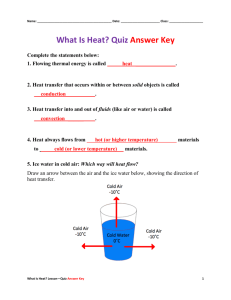
Content Benchmark P.8.C.5 Students know heat energy flows from warmer materials or regions to cooler ones through conduction, convections, and radiation. E/S Sample Test Questions 1st Item Specification: Explain convection, conduction, and radiation using terms of heat transfer. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 1. When heat is transferred to an object, the particles in the object A. slow down. B. stop moving. C. speed up. D. are unaffected. 2. The idea that matter is made up of small particles that are in constant motion is called the A. Law of Conservation of Matter B. Kinetic Theory of Matter C. Thermal Energy D. Transfer of Heat 3. The total energy of the particles in an object is often called A. temperature. B. thermal energy. C. kinetic energy. D. heat transfer. 4. When thermal energy changes in two objects of different temperature that are touching each other, this is called A. heat transfer. B. temperature. C. particle motion. D. momentum. 5. If one part of a solid object is at a higher temperature and another part of the same object is at a lower temperature, the heat is transferred within the object through the process of A. conduction. B. convection. C. insulation. D. radiation. 6. Warm air moves from vents located near the floor to the rest of the room in a process called A. conduction. B. convection. C. insulation. D. radiation. Depth Of Knowledge Level 2 7. If you place three ice cubes in a glass of water at room temperature, which of the following will occur? A. Energy from the water will transfer to the ice cubes, causing the ice to melt. B. Cold from the ice cubes will transfer to the water, causing the water to freeze. C. Energy will transfer equally between the ice cubes and the water, causing no change. D. Cold is transferred from the ice/water mixture to the air, causing the air to cool. 8. When a bar of steel at 90 deg C is placed in a basin of water at 20 deg C, A. the temperature of the steel increases and the temperature of the water decreases. B. the temperature of the steel increases and the temperature of the water increases. C. the temperature of the steel decreases and the temperature of the water increases. D. the temperature of the steel decreases and the temperature of the water decreases. 2nd Item Specification: Given a scenario involving heat transfer, recognize convection, conduction, and radiation. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 9. When you use a microwave oven to increase the temperature of a cup of hot chocolate, which type of heat transfer is taking place? A. conduction B. convection C. insulation D. radiation 10. Earth is comfortably warm because energy travels through space from the Sun by A. conduction. B. convection. C. insulation. D. radiation. Depth Of Knowledge Level 2 11. A shiny metal pot filled with water is sitting on an electric stove that is turned to high. Explain how heat is being transferred in the stove-pot-water system. A. Heat is being transferred from the stove to the pot through convection and from the pot to the water through conduction. B. Heat is being transferred from the stove to the pot through conduction and from the pot to the water through radiation. C. Heat is being transferred from the stove to the pot through radiation and from the pot to the water through radiation. D. Heat is being transferred from the stove to the pot through conduction and from the pot to the water through conduction. 12. In a small refrigerator, the ice-box is suspended from the top so that A. warm air from the rest of the refrigerator will rise to the ice-box. B. cold air from the rest of the refrigerator will rise to the ice-box. C. cold air from the ice-box will sink to rest of the refrigerator. D. warm air from the ice-box will sink to the rest of the refrigerator. 3rd Item Specification: Compare different materials and their ability to transfer heat. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 13. When heated, most matter A. condenses. B. contracts. C. expands. D. solidifies. 14. A measure of the average kinetic energy of the individual particles in an object is called A. heat. B. thermal energy. C. heat transfer. D. temperature. 15. Heat transfer occurs A. in many directions at the same time regardless of the temperature difference between objects. B. at the same time from both warm objects to colder ones and from cold objects to warmer ones. C. between objects of different temperatures and goes only from warm objects to colder ones. D. between objects of different temperatures and goes only from cold objects to warmer ones. Depth Of Knowledge Level 2 16. In an experiment, you were instructed to heat a sample of soil and a sample of water with heat lamps and then measure the temperature of each sample once a minute, for eight minutes. Suppose that the experiment yielded the results shown in the table below. Time (min) Soil Temp (C) Water Temp (C) 0 20 1 21 2 22.5 3 24 4 26 5 27.5 6 29.5 7 30.5 8 32 20 21.5 23 23.5 24 25.5 26 27.5 28.5 Which of the following predictions is best supported by the data? A. The temperatures of the soil and the water would rise at the same average rate. B. The temperature of the soil would not rise at all over the next time period. C. The temperature of the water would rise at a faster average rate than the average rate that the temperature of the soil would rise. D. The temperature of the soil would rise at a faster average rate than the average rate that the temperature of the water would rise. 17. Which of the following is the best explanation for why metal handles of pans are often colored black? A. Black handles increase the amount of heat transferred from the handle to the air through radiation, causing the handles to remain cooler. B. Black handles decrease the amount of heat transferred from the pan to the handle through conduction, causing the handles to remain cooler. C. Black handles increase the convective currents throughout the pan, causing more heat to be transferred to the food that is at a lower temperature. D. Black handles increase the amount of heat transferred from the handle of the pan to the food that is at a lower temperature. 4th Item Specification: Understand the properties of conductors and insulators. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 18. Which of the following is the best conductor of heat? A. steel B. copper C. lead D. zinc 19. Fiberglass is a good heat insulator because it A. contains a lot of air. B. cannot burn easily. C. radiates energy easily. D. has little heat energy. Depth Of Knowledge Level 2 20. A house has many windows that are single paned (a single sheet of glass). During the winter, a large amount of heat is transferred from the inside of a house to the outside environment through these windows. Of the following, which would be the best way to decrease the amount of heat transferred through the windows? A. Decrease the thickness of the glass in the window because glass is such a good conductor of heat. B. Increase the amount of fiberglass insulation in the walls to reduce heat transfer through all surfaces. C. Install double paned windows because the dead air trapped in between the window panes is an excellent heat insulator. D. Place fans behind the windows because moving air around the windows is an excellent heat insulator. 21. A pot is made out of aluminum, but the pots handles are plastic. Why are these materials used in this way? A. Aluminum is a conductor of heat, which allows the pot’s temperature to increase rapidly, while plastic is a heat insulator, preventing rapid heat transfer and keeping the handles cool. B. Plastic is a heat conductor, which allows heat to move quickly out of the handles, keeping the handles cool, while aluminum is a heat insulator that holds the heat within the pot. C. Both aluminum and plastic are heat conductors that allow heat to be transferred throughout the pot. D. Both aluminum and plastic are heat insulators that keep the heat contained within the pot. Constructed Response P.8.C.5 1. You put a glass of cold lemonade on an unshaded picnic table and then went for a bike ride. When you returned 20 minutes later, you noticed the outside of the glass had water on it. A. In terms of heat transfer, explain what happened to the glass of lemonade. B. Explain why the glass would have had more water on the outside or less water on the outside, if the picnic table would have been shaded. Content Benchmark P.8.C.5 Students know heat energy flows from warmer materials or regions to cooler ones through conduction, convections, and radiation. E/S Answers to Sample Test Questions 1. C, DOK level 1 2. B, DOK level 1 3. B, DOK level 1 4. A, DOK level 1 5. A, DOK level 1 6. B, DOK level 1 7. A, DOK level 2 8. C, DOK level 2 9. D, DOK level 1 10. D, DOK level 1 11. D, DOK level 2 12. C, DOK level 2 13. C, DOK level 1 14. D, DOK level 1 15. C, DOK level 1 16. D, DOK level 2 17. A, DOK level 2 18. B, DOK level 1 19. A, DOK level 1 20. C, DOK level 2 21. A, DOK level 2 Constructed Response 3-point Answer and Score Rubric: 3 points Response addresses all parts of the question clearly and correctly. A temperature difference exists between the lemonade, the glass, and the surrounding air. Convection transfers energy from the air to the glass at the same time that radiation transfers energy from the Sun to the air, glass, and lemonade. Conduction transfers energy from the glass to the lemonade, and to a much lesser degree, from the air to the glass. As the air near the glass cools down, water from the air condenses onto the glass. If the picnic table were shaded, the radiation effect would be significantly reduced and a smaller temperature difference would be present. This would result in less energy transfer from the air to the glass, and therefore, less condensation of water vapor from the air onto the glass. 2 points Response addresses all parts of the question and includes only minor errors. 1 point Response does not address all parts of the question. 0 points Response is totally incorrect or no response provided.