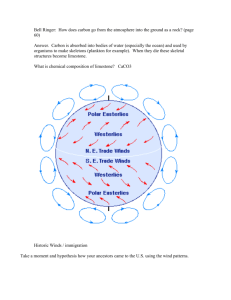
InSolAtion – INcoming SOLar radiATION, electromagnetic energy
advertisement

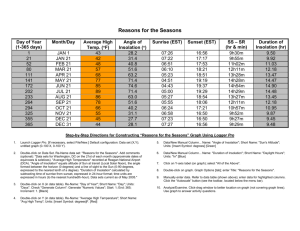
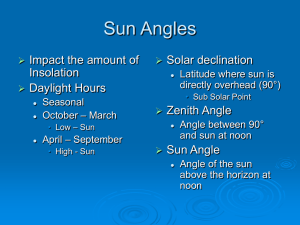
InSolAtion – INcoming SOLar radiATION, electromagnetic energy from the Sun, sunlight Angle of Insolation – the angle at which the sun’s energy reaches the Earth. When insolation is perpendicular to a surface its intensity is maximum (striking the surface at 90˚ angle) IT WILL NEVER BE 90˚ OVER N.Y.S. Therefore: higher angle of insolation = higher intensity = higher temperature (it is warmer) Time of Day – angle of insolation is the same as the altitude of the sun. Sun’s altitude varies from 0˚ at sunrise (East), increase all day to maximum at apparent solar noon (South)(when the sun is highest in the sky), then decrease back to 0˚ again at sunset (West). Duration – the length of time that insolation is received each day (# hours the sun is visible) Duration varies with latitude and the seasons (length of daylight changes) Seasons – 4 divisions of the year characterized by different types of weather conditions – major difference in seasons is the temperature Causes: o tilt of the Earth (23.5˚) o parallelism of axis o revolution of the Earth around the Sun ****From June 21st until December 21st the days are continuously getting shorter! ****From December 21st until June 21st the days are continuously getting longer! June 21st – first day of Summer (solstice) the Sun is perpendicular (90˚) at 23.5˚ North (Tropic of Cancer) longest day of the year 16 hours of daylight, 8 hours of darkness Sun will rise North of East, move across the Southern sky, and set North of West Northern Hemisphere tilted toward the Sun September 23rd – first day of fall/ autumn, (equinox) the Sun is perpendicular at 0˚ (Equator) 12 hours of daylight and darkness Sun will rise due East, move across the Southern sky, and set due West December 21st – first day of Winter (solstice) Sun is perpendicular at 23.5˚ South, (Tropic of Capricorn) Shortest day of the year 8 hours of daylight, 16 hours of darkness Sun will rise South of East, move across the Southern sky, and sets South of West Northern Hemisphere tilted away from the Sun March 21st – first day of Spring, (Vernal Equinox) Sun is perpendicular to 0˚ (Equator) 12 hours of daylight and darkness Sun will rise due East, move across the Southern sky, and set due West