Answers to Assignment #5
advertisement

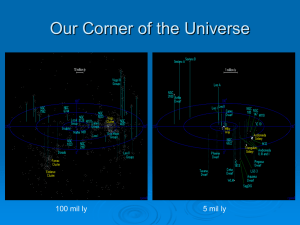
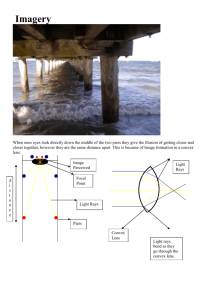
Answers to Assignment #5 1. The inner Terrestrial (rocky) planets are composed of ____ solid rock____and have ____ high ______ average density. 2. The outer Jovian (gaseous) planets are composed of ___ gas_______ and have ____ low _____ average density. 3. Stars like the Sun appear to move at __ 15° ____ per hour because the earth ____ rotates _____ 15 degrees per hour. 4. The only star that does not appear to move is _____ Polaris _______ because it is located directly above the Earth’s _ axis ______of____ rotation _______. 5. The earth _____ rotates _______ from west to east (24 hours) at a rate of _ 15° __ degrees per hour.“Right Hand Rule” 6. The earth ______ revolves ______ around the sun (365 1/4) days.) 7. All celestial objects appear to move from ___ east _____ to ___ west __. 8. The moon has phases because it ____ revolves___ around the __earth ___. 9. Eclipses only occur at the ____ new ______ and full moon phases. 10. A lunar eclipse is when the ____ full moon _____ is blocked out. 11. A solar eclipse is when the ____ sunlight______ is blocked out. 12. Earth’s seasons are caused by 1. ____ Earth’s revolution around sun____ 2.______ Tilt ___ of the Earth’s Axis 3._______ Parallelism ____________ of the Earth’s Axis 56. Evidence of Earth’s revolution around the Sun is the changing ____ seasons___ and _____ constellations _______ throughout the year, 57. Summer solstice is on ____ June 21______. The ___ northern ________ hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun. The direct (perpendicular) rays of the sun hit the Tropic of ___ Cancer______. Sun rise is __ north _____ of east, and sunset is ___ north _____ of the west. 58. Winter solstice is on __ December 21 ______. The _ southern ______ hemisphere is tilted towards the sun. The direct (perpendicular) rays of the sun hit the Tropic of ___Capricorn___. Sun rise is ___ south ____ of east, and sunset is ___ south _____ of west. 59. Equinoxes are ___ March 21 _____ and __ September 23 ______. The direct (perpendicular) rays hit the ______ equator_________. The sun rise_____ due east ____ and sets ___ due west_ on the equinoxes. 60. Duration of insulation = ___ 12 _____hours on the equinox. 61. The three important locations that receive the direct/perpendicular rays of the sun are: _____ Tropic of Cancer 23.5 N________,____ Equator 0° __,______ Tropic of Capricorn 23.5 S° ____ 62. Greatest angle of insolation/perpendicular/vertical rays of the Sun (overhead sun) can only occur between __ 23.5° _____°N & ___ 23.5° ____°S. 63. The maximum duration of insolation is __ 24 ____ hrs. 64. The greatest duration of insolation can only occur at __ 90 ___°N or ___ 90 __°S 65. The largest angle of insolation is __ 90 ____ degrees. 66. As the sun’s angle of insolation increases, the sun’s intensity ____ increases ______. 67. The equator always has __ 12 ____ hours of daylight. 68. The higher the altitude of the sun, the ______ shorter________ the shadow. 69. Shadows are the longest at ___sunrise/sunset _____ (time of day). And the shortest at ___ noon _______. 70. Noon shadows are the shortest in NY on ____ June 21 ____(date). Longest on __ December 21 _____(date) 71. In NY, an observer must always look ___ south_____ to see the sun at noon. 72. The sun is ____ never _____ at an observer’s zenith (90 degrees) in NY. 73. Winds, ocean currents and anything else moving across Earth are deflected (curve) because of the ___ Coriolis Effect. 74. Foucault’s pendulum and Coriolis effect is evidence that the Earth ____Rotates. 75. Changing Seasons and Constellations is evidence that the Earth _____Revolves. 76. The Earth is closer to the sun during the ____ winter ______ season. Perihelion – earth is ___ closest _______to the sun. Aphelion – earth is ____ farthest away ______ to the sun. The closer a planet is to the sun, the ______ faster____ its velocity as its orbits. The closer a planet is to the sun, the ______ stronger _______ the gravitational attraction. Gravity is greatest when the mass of objects are _____ large ____ and the distance between them is ____close______. 82. Tides are caused by the _____ moon’s _____ gravitational attraction. 83. There are ____ 2 ____ high tides, and ___ 2 ______ low tides per day (12.5 hours apart)- a cyclic pattern. 84. Our solar system is located ¾ the way down one of the spiral arms of our galaxy- the ____ Milky Way ____. 85. A _____ galaxy ______ is a cluster of 100-200 billion stars. 86. The following is in _____ decreasing _____ size and age order: Universe, Galaxy, Solar system, Earth. 87. _____ Geocentric _______ model is earth centered. Everything revolves around the earth. 88. ______ Heliocentric ______________ model is sun centered. Planets revolve around the sun. 89. All planets orbit in ______ elliptical__________ (shaped) orbits with the _____ sun ______ at one foci. 90. The farther from the Sun the _____ slower_______ the orbital path. 91. As the distance between foci increases, the eccentricity ______ increases (closer to 1)_____. 92. The more ___ circular _____ the orbit the less eccentric/elliptical it is. 93. The closer the eccentricity is to 0 the more ____ circular _______, the closer it is to 1 the more ___ eccentric________ the orbit is. 94. The earth’s orbit is extremely round, almost perfect, but it is slightly elliptical, see ESRT pg 15 77. 78. 79. 80. 81.