How can we describe the position of celestial objects?
advertisement
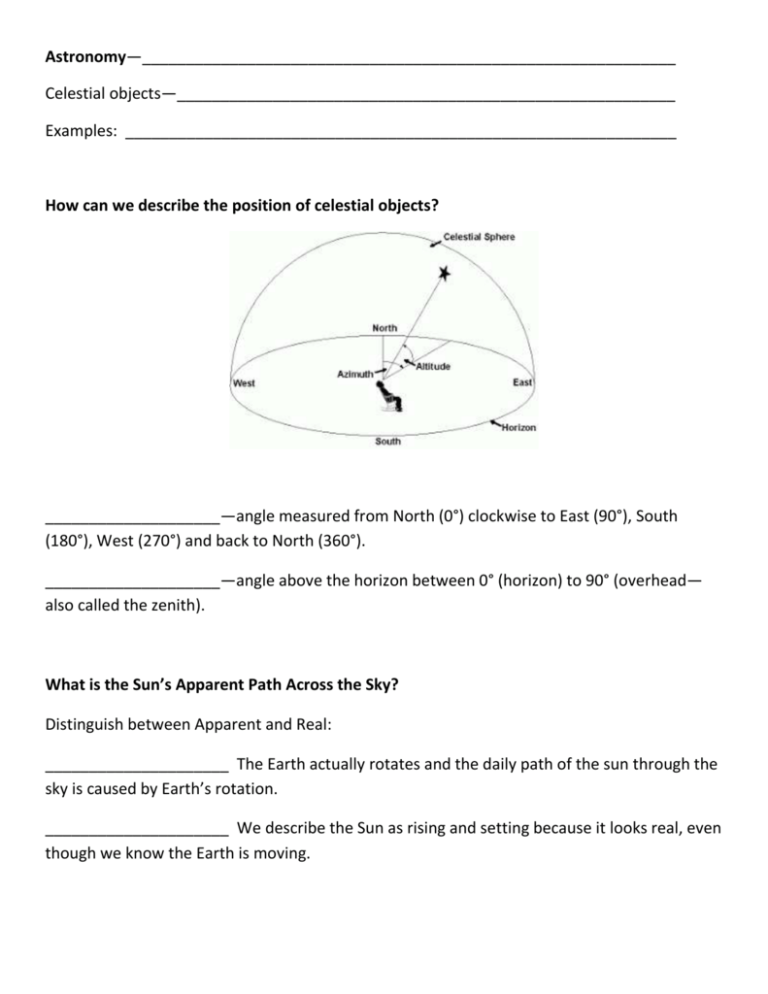
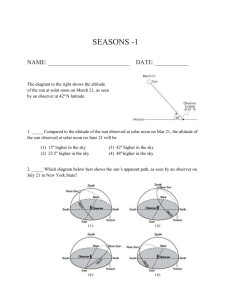
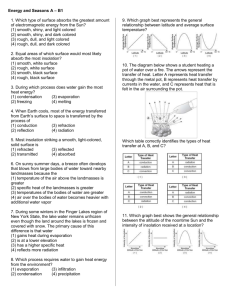
Astronomy—_____________________________________________________________ Celestial objects—_________________________________________________________ Examples: _______________________________________________________________ How can we describe the position of celestial objects? ____________________—angle measured from North (0°) clockwise to East (90°), South (180°), West (270°) and back to North (360°). ____________________—angle above the horizon between 0° (horizon) to 90° (overhead— also called the zenith). What is the Sun’s Apparent Path Across the Sky? Distinguish between Apparent and Real: _____________________ The Earth actually rotates and the daily path of the sun through the sky is caused by Earth’s rotation. _____________________ We describe the Sun as rising and setting because it looks real, even though we know the Earth is moving. Does the Sun’s Path Depend on the Observer’s Location? The path of the sun through the sky changes with ________________________. Since the earth is a sphere, the cycle of day and night changes most at the poles and is most constant at the equator. People at the equator experience approximately __________ hours of daylight every day and the noon sun is high in the sky and directly overhead for half of the year. Changes from season to season are hardly noticeable. As you move _____________ or _____________ of the tropics (23.5°N and 23.5°S), the noon sun is never directly overhead. You also notice distinct _____________________ and changes in the length of __________________________. How Does the Sun’s Apparent Path Change with the Seasons ___________________________________—in New York State the sun rises due ___________ at about 6am and sets due _____________ at about 6pm, giving _________ hours of daylight. The sun reaches its highest point at solar noon when it is in the southern sky at an altitude of 48°. _______________________________________—in New York State the sun rises in the _____________________________at 4:30 am and sets in the _______________________ at 7:30pm providing _________hours of daylight. The sun reaches its highest point at noon when it is near 72° altitude. _________________________________________—in New York State the sun rises in the __________________________at about 7:30 am and sets in the _____________________ at about 4:30 pm providing just _________ hours of daylight. The sun reaches its highest point at noon in the southern sky near an altitude of 24°. Variation in Intensity and Angle of Insolation When sunlight strikes the surface at an angle of 90° or ____________________________, it has _____________________________ intensity (heat) because the insolation is concentrated in the smallest possible area. As the angle __________________________ from 90° to 0°, the amount of insolation is spread over a greater and greater area and the intensity ____________________________. The intensity of insolation is greatest at the _______________________ and _________________________________with increasing latitude. The intensity of insolation also varies with the ____________________________. Since the maximum intensity corresponds to the angle of incidence (90°), during the solstices, the maximum intensity shifts from the Equator to the Tropic of Cancer (23.5°N) on June 21 and to the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5°S) on December 21. 24.5° Dec 21 48° Mar 21/Sep 23 71.5° Jun 21 Maximum angles of incidence at 42°N in different seasons. On any given day, the maximum intensity occurs at ___________________when the sun is highest in the sky. Note the changes in the direction and the length of the shadows. Relationship of Surface Temperature to Insolation/Seasonal and Daily Maximum Temperatures The hottest month of the year is August, not June and the hottest time of day is 3 pm not noon due to heat build-up. In the summer, due to the higher angle/higher intensity of the sun, we receive more insolation than we radiate so the earth heats up over the summer. The same thing happens each day; during the afternoon, we receive more insolation than we radiate. The opposite happens in the winter and at night. Variation in the Duration of Insolation Duration-- _______________________________________________________. Duration of insolation varies with ____________________ and ______________________. Only the Equator has _______ hours of daylight all year. At the Equinoxes, _______________________________ on Earth experiences _________hours of daylight. Variation in Insolation by Season Latitude Duration of Insolation Summer Solstice --June 21 Duration of Insolation Equinoxes—March 21/September 23 Duration of Insolation Winter Solstice—December 21 90°N 24 hrs 12 hrs 0 hrs 40°N 15 hrs 12 hrs 9 hrs 0° 12 hrs 12 hrs 12 hrs 90°S 0 hrs 12 hrs 24 hrs The Seasons Are Caused by Earth’s Motion Seasons are caused by: 1. ________________________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________________________ 3. ____________________________________________________________________ The Vertical Ray The vertical ray migrates between 23°N (Tropic of Cancer) and 23°S (Tropic of Capricorn). How Do Earth’s Motions Affect the Appearance of Other Celestial Objects? Constellations—__________________________________________________________ For example: The Big Dipper is called The Plow in Britain and the Great Bear (Ursa Major) in ancient Greece. Modern astronomers use the constellations to designate 88 regions of the night sky. This is a convenient way to map the stars in our sky. This star map shows constellations visible at about 40° N in March and April. If you find the Big Dipper high in the sky, you can use it to locate other stars and constellations as shown by the arrows on the chart. Why Do Stars Seem To Change Their Positions? Earth’s rotation makes stars appear to move through the sky just as the sun appears to move. In New York State, stars rise in the East and set in the West. Yearly Apparent Motions In addition to the apparent daily cycle of motion of stars through the sky, the stars positions appear to change in a yearly cycle as the earth revolves around the sun.