Intro to Genetics
advertisement

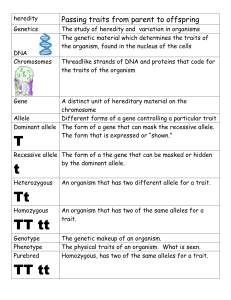
TEKS 7.14A define heredity as the passage of genetic instructions from one generation to the next TEKS 7.14C recognize that inherited traits of individuals are governed in the genetic material found in the genes within chromosomes in the nucleus Introduction to Genetics Gregor Mendel is often called the “Father of Genetics”. He identified dominant and recessive traits by studying the heredity of pea plants. The process by which characteristics or traits are passed from parents to offspring is called heredity. The scientific study of heredity, or how genes pass to offspring, is called genetics. Traits are an organism’s physical characteristics (phenotype), like nose shape, eye color, blood type or eyelash length. These traits are controlled by genes that are passed to us from our parents. Human cells contain rod-shaped structures called chromosomes. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of a cell and are made up of long strands of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). DNA is made up of genes that carry the genetic information that controls our traits. Chromosomes exist in pairs, each chromosome having the same genes; therefore genes also exist in pairs (genotype). Offspring receive one set from the mother and one from the father. Each offspring will receive a different combination of genes from its parents. Sexual reproduction results in more diversity due to the large number of gene combinations that may occur. Each member of a gene pair is called an allele. Alleles are different forms of the same gene, for example one allele may be for dimples and the other allele for no dimples. Alleles may be dominant or recessive. A dominant allele is a strong form of a gene whose traits always show up in the organism. The recessive allele on the other hand is a weak form of a gene that can be hidden or covered up if the dominant allele is present. TEKS 7.14A define heredity as the passage of genetic instructions from one generation to the next TEKS 7.14C recognize that inherited traits of individuals are governed in the genetic material found in the genes within chromosomes in the nucleus Introduction to Genetics Gregor ______________ is often called the “Father of Genetics”. He identified __________________ and ________________ traits by studying the heredity of pea plants. The process by which characteristics or ______________ are passed from parents to offspring is called ______________. The scientific study of heredity, or how ______________ pass to offspring, is called ______________. ______________ are an organism’s ______________ characteristics (phenotype), like nose shape, eye color, blood type or eyelash length. These traits are controlled by ______________ that are passed to us from our ______________. Human cells contain rod-shaped structures called ___________________. Chromosomes are found in the ______________ of a cell and are made up of long strands of ______________ (deoxyribonucleic acid). DNA is made up of ______________ that carry the genetic information that controls our ______________. ___________________ exist in pairs, each chromosome having the same ______________; therefore genes also exist in ______________ (genotype). Offspring receive one set from the ______________ and one from the ______________. Each ___________________ will receive a different ___________________ of genes from its parents. Sexual ___________________ results in more ___________________ due to the large number of gene combinations that may occur. Each member of a gene pair is called an ______________. Alleles are different forms of the same ______________, for example one allele may be for dimples and the other allele for no dimples. Alleles may be ______________ or ______________. A ______________ allele is a ______________ form of a gene whose traits always show up in the organism. The ______________ allele on the other hand is a ______________ form of a gene that can be hidden or covered up if the dominant allele is present.