Midterm Science study guide answers
advertisement

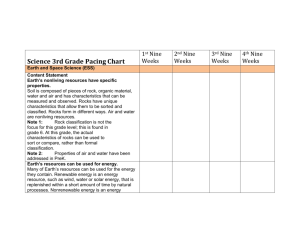
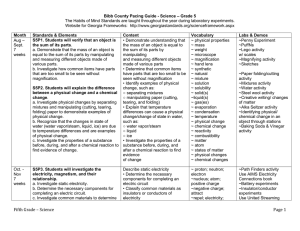
Name ____________________________________ Midterm Study Guide Answers Test Friday., Jan. 16 Be able to: S5L3. Students will diagram and label parts of various cells (plant, animal, single-celled, multi-celled). a. Use magnifiers such as microscopes or hand lenses to observe cells and their structure. How can you identify a plant cell? Plant cells take the shape of the cell wall which gives them rectangular shape. Plant cells also have chloroplasts and one large vacuole. How can you identify an animal cell? Animal cells can be any irregular shape and have many small vacuoles. Why are microscopes necessary? When would you need to use a microscope? Microscopes are necessary if what needs to be observed is too small to be seen with the naked eye or a hand lens. It is microscopic, like a germ. When would you need to use a hand lens (magnifying lens)? A hand lens is used to magnify an object. It is used to get a closer look at small features or objects; for example, the veins on a leaf or the parts of an insect. b. Identify parts of a plant cell (membrane, wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts) and of an animal cell (membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus) and determine the function of the parts. Explain the function of the following cell parts: Cell membrane – A covering that holds the cell together and controls what materials move into and out of the cell Cell wall - A rigid layer that supports and protects the plant cell Cytoplasm A jellylike substance containing many chemicals to keep the cell functioning Nucleus The organelle that controls all of the cell’s activities Mitochondria Organelles that break down food and release energy for the cell to use Vacuole Organelles that store food, water, and waste Chloroplast Organelles that make food for the plant cell and contains the green coloration for plants What makes a plant cell different from an animal cell? (structures and shape) Plant and animal cells differ in that plant cells have a rigid structure from the cell wall that causes them to have a rectangular shape where an animal is more rounded. Plant cells also have different organelles like one large vacuole and chloroplasts that help them make food. Animal cells have many small vacuoles and do not make their own food. Label the following cell diagrams: _Animal________ Cell ____Plant___ Cell c. Explain how cells in multi-celled organisms are similar and different in structure and function to single-celled organisms. How are multi celled organisms similar to single celled organisms? The organelles are very closely related in multi-celled and single celled organisms in terms of having cell membrane, nucleus, etc. How are multi-celled organisms different from single-celled organisms? (How are they both organized?) The single cell organism can carry out every function needed for the life process. In multi-celled organisms – every cell has a different function and cannot work alone to sustain life. Multi-celled organisms are organized by cell, a group of similar cells with the same function is tissue, many layers of tissue is an organ and a group of organs working together to complete a process is an organ system. Think pyramid – and the circulatory system. S5L4. Students will relate how microorganisms benefit or harm larger organisms. a. Identify beneficial microorganisms and explain why they are beneficial. How is bacteria helpful? bacteria is helpful because it helps aid digestion, make certain foods like cheeses and yogurt and break down organic matter. b. Identify harmful microorganisms and explain why they are harmful. Name 3 microorganisms and explain how they are harmful. 1. streptococcus – causes strep 2. Bacilli are responsible for a number of much more serious diseases, most notably tuberculosis 3. Spirilla-type microorganisms can cause other serious diseases, including syphilis S5L1. Classify organisms into groups and relate how they determined the groups with how and why scientists use classification. a. Demonstrate how animals are sorted into groups (vertebrate and invertebrate) and how vertebrates are sorted into groups (fish, amphibian, reptile, bird, and mammal). Name and define the two groups scientists use to classify organisms in the animal kingdom. 1. Vertebrates Definition: organisms with a backbone 2. invertebrates Definition: organisms without a backbone List 3 examples of invertebrates. mollusks, cnidarians, echinoderms, arthropods, Name the five classes of vertebrates. 1. mammal 2. bird 3. reptile 4. fish 5. amphibian Using the list from above, give the characteristics of each class and an example of each class. 1. bird Characteristics: lays eggs, lungs, feathers, warm-blooded, land Example: eagle, robin, hummingbird 2. mammal Characteristics: live birth, lungs, skin or fur, warm-blooded, land Example: human, bear, tiger 3. reptile Characteristics: lay eggs, lungs, roughy-scaly skin, cold-blooded, land Example: lizard, snake, turtle 4. amphibian Characteristics: lay eggs, lungs & gills, moist skin, cold-blooded, land & water Example: frog toad salamander 5. fish Characteristics: lay eggs, gills, scales, cold-blooded, water Example: shark, catfish, bass b. Demonstrate how plants are sorted into groups. Name the two groups scientists use to classify plants. Then give a definition and example of each. 1. vascular Definition: plant tissue through which water and food move (tubes) Example: trees, shrubs, grass, etc. 2. non-vascular Definition: containing no plant tissue through which water and food move Example: moss and algae S5L2. Recognize that offspring can resemble parents in inherited traits and learned behaviors. a. Compare and contrast the characteristics of learned behaviors and of inherited traits. Explain the difference between a learned behavior and an inherited trait. Learned behaviors are learned from parents and environment. Inherited traits are passed down from parents to offspring in genes. List 3 examples of inherited traits. eye color, hair color, rolling tongue, hairline, hitchhiker thumb, List 3 examples of learned behaviors. speaking, reading, sports, walking What is an instinct? A way of acting or behaving that an animal is born with and does not have to learn. Give 2 examples of an instinct. spinning a web, breathing, building a nest b. Discuss what a gene is and the role genes play in the transfer of traits. Explain what genes are and why they are important. Genes are the menu or directions to show your traits. It shows eye color, hair color, etc. Explain the meaning of heredity. Heredity is an explanation of how species are born with certain similar traits to the parent.