Bibb County Pacing Guide
advertisement

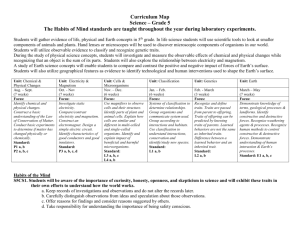
Bibb County Pacing Guide - Science – Grade 5 The Habits of Mind Standards are taught throughout the year during laboratory experiments. Website for Georgia Frameworks: http://www.georgiastandards.org/scienceframework.aspx Month Aug – Sept. 7 weeks Standards & Elements S5P1. Students will verify that an object is the sum of its parts. a. Demonstrate that the mass of an object is equal to the sum of its parts by manipulating and measuring different objects made of various parts. b. Investigate how common items have parts that are too small to be seen without magnification. S5P2. Students will explain the difference between a physical change and a chemical change. a. Investigate physical changes by separating mixtures and manipulating (cutting, tearing, folding) paper to demonstrate examples of physical change. b. Recognize that the changes in state of water (water vapor/steam, liquid, ice) are due to temperature differences and are examples of physical change. c. Investigate the properties of a substance before, during, and after a chemical reaction to find evidence of change. Oct. Nov 7 weeks S5P3. Students will investigate the electricity, magnetism, and their relationship. a. Investigate static electricity. b. Determine the necessary components for completing an electric circuit. c. Investigate common materials to determine Fifth Grade – Science Content • Demonstrate understanding that the mass of an object is equal to the sum of its parts by manipulating and measuring different objects made of various parts • Determine that common items have parts that are too small to be seen without magnification • Identify examples of physical change, such as: ○ separating mixtures ○ manipulating paper (cutting, tearing, and folding) • Explain that temperature differences can cause a physical change/change of state in water, such as: ○ water vapor/steam ○ liquid ○ ice • Investigate the properties of a substance before, during, and after a chemical reaction to find evidence of change Vocabulary ~ physical properties ~ mass ~ weight ~ microscope ~ magnification ~ hand lens ~ synthetic ~ natural ~ mixture ~ solution ~ solubility ~ solid(s) ~liquid(s) ~ gas(es) ~ evaporation ~ condensation ~ temperature ~ physical change ~ chemical change ~ reactivity ~ combustibility ~ matter ~ atom ~ states of matter ~ physical changes ~ chemical changes Labs & Demos ~Penny Experiment ~PuffNs ~Lego activity w/ scales ~Magnifying activity ~Sketches Describe static electricity • Determine the necessary components for completing an electric circuit • Classify common materials as insulators or conductors of electricity ~ proton; neutron; electron ~nucleus; atom; positive charge ~negative charge; attract ~repel; electricity; ~Path Finders activity Use AIMS Electricity Connections book ~Battery experiments ~Insulator/conductor experiments Use United Streaming ~Paper folding/cutting activity ~Mixtures activity ~Water activity ~Steel wool activity ~Creative writing/ changes of matter ~Alka Seltzer activity ~Identifying physical/ chemical change in an object through stations ~Baking Soda & Vinegar activity Page 1 Nov. – Dec. 6 weeks Jan. – Feb. 6 weeks if they are insulators or conductors of electricity. d. Compare a bar magnet to an electromagnet. • Compare a bar magnet to an electromagnet S5L3. Students will diagram and label parts of various cells (plant, animal, singlecelled, multi-celled). a. Use magnifiers such as microscopes or hand lenses to observe cells and their structure. b. Identify parts of a plant cell (membrane, wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts) and of an animal cell (membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus) and determine the function of the parts. c. Explain how cells in multi-celled organisms are similar and different in structure and function to single-celled organisms. plant cells ~animal cells ~multi/single celled organisms S5L4. Students will relate how microorganisms benefit or harm larger organisms. a. Identify beneficial microorganisms and explain why they are beneficial. b. Identify harmful microorganisms and explain why they are harmful. S5L1. Students will classify organisms into groups and relate how they determined the groups with how and why scientists use classification. Fifth Grade – Science current ~insulator; conductor ~magnetism; bar magnet ~electromagnet ~!magnetic field ~poles; battery; series ~parallel; open/closed ~static electricity ~circuits ~insulators/conductors ~bar magnet/ electromagnet ~membrane ~ cell wall ~ cytoplasm ~ nucleus ~ chloroplasts ~ cell ~organelles ~ mitochondria ~ cell membrane ~ chromosomes ~ vacuoles ~ microscope ~Tic-Tac-Toe activity ~Mostly Magnets Cell activities ~Magnificent Microworld Adventures AIMS book ~Build a model of cells ~Blue Cheese microscope activity ~Compare/ contrast ~Compost activity ~Magnificent Microworld Adventures AIMS book ~organism ~microorganism ~bacteria ~virus • Demonstrate how animals are sorted in the following groups: ○ fish ○ amphibian ~classification; kingdom; vertebrate ~invertebrate; moneran; protist Grouping activities ~United Streaming ~Animal Poster project ~Kinky Creatures Page 2 Feb. – March. 3 weeks a. Demonstrate how animals are sorted into groups (vertebrate and invertebrate) and how vertebrates are sorted into groups (fish, amphibian, reptile, bird, and mammal). b. Demonstrate how plants are sorted into groups. ○ reptile ○ bird ○ mammal • Explain how plants are sorted into groups • • Explain how magnifiers such as microscopes or hand lenses are used to observe cells and their structure • Recognize and determine the function of the parts of a plant cell, such as: ○ membrane ○ wall ○ cytoplasm ○ nucleus ○ chloroplasts • Recognize and determine the function of the parts of an animal cell, such as: ○ membrane ○ cytoplasm ○ nucleus • Distinguish between the structure and function of cells in multi-celled organisms and singlecelled organisms • Identify beneficial microorganisms and explain why they are beneficial • Identify harmful microorganisms and explain why they are harmful ~fungi; genus; species ~animal; mammal ~reptile ~amphibian ~fish ~birds ~plants ~vascular ~nonvascular ~spore ~gymnosperm ~pollen ~vertebrate ~invertebrate ~classification ~microorganisms S5L2. Students will recognize that offspring can resemble parents in inherited traits and learned behaviors. a. Compare and contrast the characteristics of Compare and contrast the characteristics of learned behaviors and inherited traits • Describe what a gene is and the ~heredity ~learned behavior ~traits ~offspring Fifth Grade – Science ~Kidspiration ~Cinquain Poems ~Graphing activity Page 3 March – May 7 weeks learned behaviors and of inherited traits. b. Discuss what a gene is and the role genes play in the transfer of traits. Teacher note: Be sensitive to this topic since biological parents may be unavailable. role genes play in the transfer of traits S5E1. Students will identify surface features of the Earth caused by constructive and destructive processes. a. Identify surface features caused by constructive processes. • Deposition (Deltas, sand dunes, etc.) • Earthquakes • Volcanoes • Faults b. Identify and find examples of surface features caused by destructive processes. • Erosion (water—rivers and oceans, wind) • Weathering • Impact of organisms • Earthquake • Volcano c. Relate the role of technology and human intervention in the control of constructive and destructive processes. Examples include, but are not limited to • Seismological studies, • Flood control, (dams, levees, storm drain management, etc.) • Beach reclamation (Georgia coastal islands) • Distinguish between surface features caused by constructive processes, such as: ○ deposition (deltas, sand dunes, etc.) ○ earthquakes ○ volcanoes ○ faults • Distinguish between surface features caused by destructive processes, such as: ○ erosion (water and wind) ○ weathering ○ impact of organisms ○ earthquakes ○ volcanoes • Determine and evaluate the role of technology and human intervention in the control of constructive and destructive processes, such as: ○ seismological studies ○ flood control (dams, levees, storm drain management, etc.) ○ beach reclamation (Georgia coastal islands) Fifth Grade – Science ~genetics ~ hybrid ~genes ~chromosomes ~traits ~dominant ~recessive fault ~volcano ~deposition ~erosion ~delta ~earthquake ~eruption ~lava ~magma ~weathering ~seismograph ~levees ~constructive force ~destructive force ~technology ~Punnet Square activity ~United Streaming activity ~Writing activities United Streaming ~Build models ~Read Out of the Dust w/ writing activity ~Read Call it Courage w/writing activity ~www.coreknowledge.com ~www.beaconlearning.com ~Cause & Effects activity See attached ~Research technology items on internet ~Creating landform map Page 4