CHEMISTRY 315: SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
advertisement
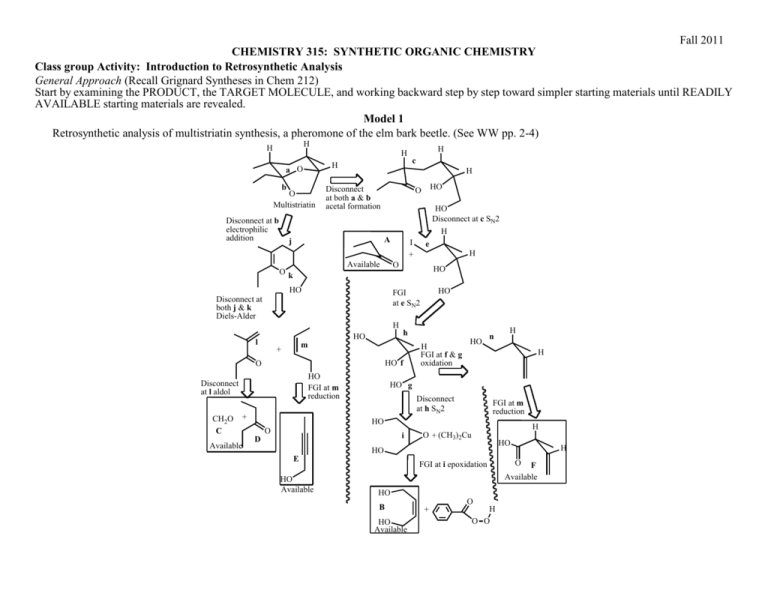
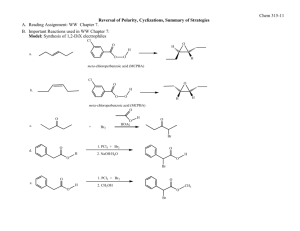
Fall 2011 CHEMISTRY 315: SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Class group Activity: Introduction to Retrosynthetic Analysis General Approach (Recall Grignard Syntheses in Chem 212) Start by examining the PRODUCT, the TARGET MOLECULE, and working backward step by step toward simpler starting materials until READILY AVAILABLE starting materials are revealed. Model 1 Retrosynthetic analysis of multistriatin synthesis, a pheromone of the elm bark beetle. (See WW pp. 2-4) H H H H a O b O Multistriatin Disconnect at b electrophilic addition H Disconnect at both a & b acetal formation HO Disconnect at c SN2 Available Ok H HO m + HO FGI at m reduction + Available H HO HO h HO f Disconnect at l aldol e FGI at e SN2 O CH2O C H I + O HO l HO O A j Disconnect at both j & k Diels-Alder H c H FGI at f & g oxidation HO n H H HO g Disconnect at h SN2 FGI at m reduction HO D O i E HO Available H O + (CH3)2Cu HO HO FGI at i epoxidation HO B HO Available + O H O O O F Available H Chem 315 2 Model 2 Multistriatin Synthesis developed from Model 1. H H HO H LiAlH4 HO H Intro to Retrosynthetic Analysis H TsCl TsO H O H H O O multistraitin H SnCl4 H H O H OO O base H H H H O O O 1. Which of the molecules in Model 2 have letter designations in Model 1? Place those letter designations on the structures in Model 2. How did you locate the structures in Model 1? 2. Trace the steps of the synthesis in Model 1 in the Retrosynthetic Analysis in Model 2. Provide your warrant. 3. How does the synthetic path (Model 2) relate to the retrosynthetic path (Model 1)? Provide your warrant. 4. Use Model 1 to develop a different synthetic path to multistriatin from available starting materials. You need not provide specific reagents for each step, but do provide your warrant for devising your synthesis including how you recognized “available starting materials” in Model 1. Chem 315 3 Intro to Retrosynthetic Analysis 5. Based on Models 1 & 2 and your experience with Retrosynthesis in Chem 212, describe the step-by-step process used to create a retrosynthetic analysis of a target molecule. Provide your warrant. 6. Based on your experience in steps 1-4, describe the step-by-step process used to convert a Retrosynthesis into a synthetic path. Provide your warrant. 7. Use the retrosynthetic approach to design a synthesis of the following cyclic alkyne. If you have difficulty with this problem, see below. target molecule 8. If you encountered problems in 7., what additional information would assist you in creating a synthetic path to the target molecule?