WEATHER AND CLIMATE - High Point University
advertisement

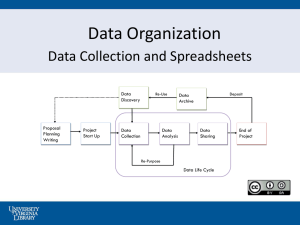
Hyperlink to observation/record 1daily weather Hyperlink to observation/record 2 climate zones WEATHER AND CLIMATE Lesson plan for a Weather/Climate Science Unit, grades 5 - 6 Students will learn what climate is and why it relates to weather. This lesson will center around seven different regional climate zones in the continental United States. While students learn the location and characteristics of each climate zone, they will record data on a spreadsheet. They will also record data from the weather observations that they make each day for about two weeks. By using a spreadsheet students will learn to incorporate technology into their research. OBJECTIVE/GOALS: 1. To teach about climate and how it relates to weather. 2. To teach about some of the different climate zones in the United States. 3. To have students practice dealing with recorded information. 4. To have students practice observational skills and recording data. 5. To have students practice being good communicators through writing and forming technology graphs. REVIEW AND FOCUS: 1. What is weather? 2. Does anyone know what climate means and how it is different from weather? 3. There are several climate regions in the US, how many do you think there are? 4. Spreadsheet review. TEACHER INPUT: 1. Climate is… 2. Weather is… 3. Explanation of the difference between weather and climate. Use chart paper of Venn-diagram as you discuss with the class as a whole. Have these items displayed in the classroom through out this unit. 4. List the seven regional climate zones, each on a separate piece of chart paper. Having students use their text and you using the text and other sources, explore each climate zone and identify the characteristics of each. 5. Use a US map to make identification more clear and to incorporate geography. GUIDED PRACTICE: 1. What is climate? 2. What is weather? 3. To day the weather is__________? 4. It rarely rains in the dessert, it has a _______ climate? 5. As I point to the climate zone, tell me it name and give me some characteristics. We will do this by a show of hand, EVERYONE be prepared to answer questions. INDEPENDENT PRACTICE: 1. Students divided into groups of 3 to 4 (depending on class size). Students may use those in their group to work with and find information. However, everyone Hyperlink to observation/record 1daily weather Hyperlink to observation/record 2 climate zones will record their data separately (first on paper and then into a computer spreadsheet on a separate visit to the computer lab). Everyone will do their quiz separately also. 2. Spreadsheet 1(dailweathobserv) – record daily weather in your local area. Look outside, list what weather conditions you can see (rain, sunny, cloudy, etc.) and record a temperature (degree Fahrenheit) based on the thermometer outside of your classroom at the beginning of the school day (am) and at the end (pm). Record the inches of rain at the end of the day or following precipitation (inches) based on the rain gauge outside of your classroom. Do this for about two school weeks, with Sat and Sun as optional extra credit. Follow the directions for graphing data. 3. Spreadsheet 2 (cliamtezoneres) – compare the differences between the different climate zones. With each climate zone put the normal weather conditions Jan July, the name for its climate description, and which states are included in its zone. Students may use sources such as their text book, chart paper notes, and the internet on classroom computer by going in groups (due to the small number of computers in the classroom). ASSESSMENT: Students will be assessed on their completion of their spreadsheets and also by a 14 question quiz that will be accessed through a website in which they may use information from their spreadsheets to answer questions. http://weathereye.kgan.com/cadet/climate/quiz.html