Care & Prevention Vocabulary

Care & Prevention Vocabulary
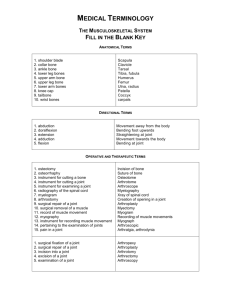
Abduction: movement of a body part away from the midline
Active Range of Motion: portion or total range of motion through which a joint can be moved by an active muscle contraction
Acute Injury: injury with sudden onset and short duration
Adduction: movement of a body part towards the midline
Ambulation: move or walk
Amnesia: loss of memory
Analgesia: pain inhibition
Anterior: before or in front of
Antipyretic: fever reducing agent
Apophysis: Natural outgrowth or projection
Atrophy: Wasting away of tissue or an organ
Avascular: Death of tissue resulting from a lack of blood supply
Avulsion: A tearing away
Bilateral: Pertaining to both sides
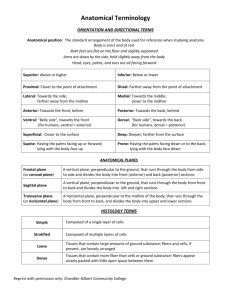
Bursa: Pieces of synovial membrane that contain a small amount of fluid
Capitation: Form of reimbursement
Catastrophic injury: Permanent injury to the spinal cord that leaves the athlete quadriplegic or paraplegic
Central Nervous System: Brain and spinal cord
Chondromalacia: Degeneration of a joint’s articular surface leading to softening
Chronic injury: Injury with long onset and long duration
Concussion: Agitation or shaking from being hit
Condyle: Rounded prominence at the end of a bone
Contusion: Bruise
Collagen: White fibrous substance composing connective tissue
Collision sport: Athletes use their bodies to deter or punish opponents
Concentric: muscle shortens while contracting against resistance
Cramp: painful, involuntary muscle contraction
Crepitus: crackling sound or feel
Cyanosis: slightly bluish discoloration of the skin due to reduced blood hemoglobin
Distal: farthest from the point of reference
Dorsiflexion: bending towards the rear
Dorsum: the back of a body part
Eccentric: muscle lengthens while contracting against resistance
Ecchymosis: black & blue skin discoloration
Edema: swelling as a result of the collection of fluid in connective tissue
Effusion: swelling or fluid within the joint
Epicondyle: rounded projection at the end of a bone, usually serving as a place of attachment for ligaments or tendons
Epiphysis: cartilaginous growth region of a bone
Eversion: to turn the foot outward
Fibrocartilage: type of cartilage in which the matrix contains thick bundles of cartilaginous fibers
Fracture: broken bone
Hematoma: blood tumor
Hemorrahage: discharge of blood
Hematuria: blood in the urine
Hemarthrosis: blood within the joint cavity
Hyaline cartilage: thin, smooth cartilaginous covering of bone
Hypertrophy: enlargement of a part caused by an increase in the size of its cells
Inferior: located beneath or directed downward
Inversion: to turn the foot inward
Ischemia: local anemia
Lateral: Pertaining to point of reference away from midline of the body
Ligament: connective tissue that attaches bone to bone
Luxation: total dislocation
Medial:
Pertaining to point of reference closest to the midline of the body
Meniscus:
Thick fibrocartilage
Myositis ossificans: Calcium deposits that result from repeated trauma
Necrosis: Death of tissue
Osteochondral: Refers to the relationship of bone and cartilage
Palpate/Palpation:
To use the hands to examine; feeling the injury with the fingers
Passive Range of Motion: Portion of the total ROM that a joint can be taken through passively
Pathology: Study of the nature and cause of disease
Paresthesia: Abnormal sensation such as numbness, pricking, and tingling
Paralysis:
Loss of voluntary movement
Periosteum: The fibrous covering of a bone
Physis: Growth plate
Posterior: Toward the rear or back
Proximal: Nearest to the point of reference
SAID principal: Specific adaptations to imposed demands
Sign:
Objective evidence of an abnormal situation within the body
Sprain: Injury to a ligament
Spasm: Sudden, involuntary muscle contraction
Strain: Injury to a muscle or tendon
Subluxation:
A bone is forced out but goes back into place
Superficial: Near the surface
Superior: Above or on top of
Syndrome: Group of typical symptoms that characterize an injury or disease
Symptom: Subjective evidence of an abnormal situation within the body
Tendon: Tough band of connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone
Valgus:
Bent outward
Varus: Bent inward
Vasoconstriction: Decrease in the diameter of a blood vessel
Volar: Referring to the palm or the sole