החמרה לעלון
advertisement

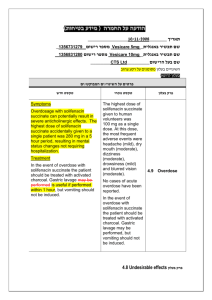
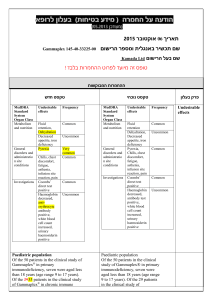
בטיחות) מידע בטיחות) החמרה (( מידע על החמרה הודעה על הודעה תאריך _______________12.90.22 שם תכשיר באנגלית______0.5mg, _caps מספר רישום: Agrylin 1117529454 שם בעל הרישום___Medison Pharma Ltd השינויים בעלון מסומנים ברקע צהוב עלון לצרכן פרטים על השינוי/ים המבוקש/ים פרק בעלון טקסט נוכחי טקסט חדש חומרים -אנטינאופלסטים קבוצה תרפויטית חומרים תרומבוליטים תגובות בין- תרופתיות: עליך להודיע לרופא המטפל אם הינך נוטל אחת מהתרופות הבאות: פלווקסמין (לטיפול בדכאון); אומפרזול (לטיפול בבעיות מערכת העיכול כגון רפלוקס או אולקוס); תיאופילין( באסתמה או בעיות נשימה חריפות);תכשירים לטיפול בהפרעות לב כגון מילרינון,אנוקסימון,אמרינון, אולפירון וסילוסטזול; אספירין ותכשירים אחרים המשפיעים על התסיות בדם. תופעות לוואי בנוסף לפעילות הרצויה של התרופה ,בזמן השימוש בה עלולות להופיע תופעות לוואי, כגון :שלשול, בחילה/הקאות,שלשול כאב ראש ,סחרחורת ,כאב בטן, חולשה ,חום ,כאבים ,גזים, חוסר תיאבון ,דלקת גרון, פעימות לב מואצות בנוסף לפעילות הרצויה של התרופה ,בזמן השימוש בה עלולות להופיע תופעות לוואי ,כגון :שלשול, בחילה/הקאות,שלשול כאב ראש(מיגרנה) ,סחרחורת ,כאב בטן, חולשה ,חום ,כאבים ,גזים ,חוסר תיאבון, דלקת גרון, פעימות לב מואצות,הפרעות בעין (ראיה מעוותת,כפל ראיה) ,הפרעות באוזן(טיניטוס תופעות לוואי הדורשות התייחסות מיוחדת גירוי או פריחה בעור ,בצקת, דפיקות לב מואצות ,כאב בחזה, קשיי נשימה ,צואה דמית או שחורה ,עור או עיניים צהובים, עייפות או חולשה מוגברת – אם הינך מזהה אחת מהתופעות האלה פנה לרופא מיד. בכל מקרה שבו הינך מרגיש/ה גירוי או פריחה בעור ,בצקת ,דפיקות לב מואצות הקשורות לחולשה ,התעלפות ,כאב בחזה חמור, קשיי נשימה ,צואה דמית או שחורה ,עור או עיניים צהובים ,עייפות או חולשה מוגברת ,קוצר נשימה ,במיוחד כאשר צבע השפתיים או העור הופך לכחלחל ,כאב בטן חמור או הפרעות במערכת העיכול ,הקאת דם. – אם הינך מזהה אחת מהתופעות האלה פנה עליך להודיע לרופא המטפל אם הינך נוטל אחת מהתרופות הבאות: פלווקסמין (לטיפול בדכאון); אומפרזול (לטיפול בבעיות מערכת העיכול כגון רפלוקס או אולקוס); תיאופילין( באסתמה או בעיות נשימה חריפות);תכשירים לטיפול בהפרעות לב כגון מילרינון,אנוקסימון,אמרינון ,אולפירון וסילוסטזול; אספירין ותכשירים אחרים המשפיעים על הטסיות בדם .בשילוב עם אספירין ,ישנה אפשרות של עליה בסיכון לשטפי דם(דימומים) .לרופא מיד ה תופעות לוואי/בכל מקרה שבו הינך מרגיש או עם חל שינוי,שלא צוינו בעלון זה ,בהרגשתך הכללית .עלייך להתייעץ עם הרופא מיד תופעות לוואי שלא צוינו בעלון או עם חל שינוי בהרגשתך,זה ,הכללית .עלייך להתייעץ עם הרופא מיד עלון לרופא ים/ים המבוקש/פרטים על השינוי טקסט חדש At the doses recommended for use in the treatment of essential thrombocythaemia, anagrelide may - potentiate the effects of other medicinal products that inhibit or modify platelet function e.g. acetylsalicylic acid. In two clinical interaction studies in healthy subjects, coadministration of singledose anagrelide 1mg and acetylsalicylic acid 900mg or repeat-dose anagrelide 1mg once daily and acetylsalicylic acid 75mg once daily showed greater anti-platelet aggregation effects than administration of acetylsalicylic acid alone. In the repeat-dose study, there was a shortlived decrease in ex vivo collagen-induced platelet aggregation beyond the effects of acetylsalicylic acid alone for the first 2 hours after administration. טקסט נוכחי פרק בעלון At the doses recommended for use in the treatment of essential thrombocythaemia, anagrelide may theoretically potentiate the effects of other medicinal products that inhibit or modify platelet function e.g. acetylsalicylic acid. In two clinical interaction studies in healthy subjects, co- Interaction with other medicinal administration of single-dose anagrelide 1mg and acetylsalicylic acid 900mg or repeat-dose anagrelide 1mg once daily and acetylsalicylic acid 75mg once daily showed greater anti-platelet aggregation effects than administration of acetylsalicylic acid alone. In products Co-administered anagrelide 1mg and acetylsalicylic acid 900mg single-doses had no effect on bleeding time, prothrombin time (PT) or activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). In some ET patients concomitantly treated by anagrelide and acetylsalicylic acid, major haemorrhages occurred. Therefore, the potential risks and benefits of the concomitant use of anagrelide with acetylsalicylic acid should be assessed, particularly in patients with a high risk profile for haemorrhage, before treatment is commenced. Anagrelide may cause intestinal disturbance in some patients and compromise the absorption of hormonal oral contraceptives. - the repeat-dose study, there was a short-lived decrease in ex vivo collagen-induced platelet aggregation beyond the effects of acetylsalicylic acid alone for the first 2 hours after administration. Coadministered anagrelide 1mg and acetylsalicylic acid 900mg single-doses had no effect on bleeding time, prothrombin time (PT) or activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). The clinical relevance of this interaction in ET patients is unknown • Anagrelide may cause intestinal disturbance in some patients and compromise the absorption of hormonal oral contraceptives. • A preclinical in vivo pharmacokinetic interaction study in the dog investigating the potential effects of anagrelide and hydroxyurea when given in combination demonstrated no adverse effects on the kinetics of either medicinal product. The following convention was used for frequency of adverse drug reactions: very common (≥1/10); common (≥1/100, The following convention was used for frequency of adverse Undesirable effects <1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000, <1/100); rare (≥1/10,000, <1/1,000). drug reactions: very common (>1/10); common (>1/100, <1/10); uncommon (>1/1,000, Blood and lymphatic system disorders Common: Anaemia Uncommon: Thrombocytopaenia, pancytopaenia, ecchymosis, haemorrhage Metabolism and nutrition disorders Common: Fluid retention Uncommon: Oedema, weight loss Rare: Weight gain <1/100); rare (>1/10,000, <1/1,000). Blood and lymphatic system disorders Common: Anaemia Uncommon: Thrombocytopaenia, pancytopaenia, ecchymosis, haemorrhage Metabolism and nutrition Nervous system disorders Very common: Headache Common: Dizziness Uncommon: Paraesthesia, insomnia, depression, confusion, hypoaesthesia, nervousness, dry mouth, amnesia Rare: Somnolence, abnormal coordination, dysarthria, migraine disorders Common: Fluid retention Uncommon: Oedema, weight loss Rare: Weight gain Nervous system disorders Very common: Headache Common: Dizziness - Uncommon: Paraesthesia, Eye disorders Rare: Vision abnormal, diplopia insomnia, depression, Ear and labyrinth disorders Rare: Tinnitus nervousness, dry mouth, Cardiac disorders Common: Palpitations, tachycardia Uncommon: Congestive heart failure, hypertension, arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, syncope Rare: Angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, Rare: Somnolence, abnormal confusion, hypoaesthesia, amnesia coordination, dysarthria Special senses Rare: Vision abnormal, tinnitus, diplopia Cardiac disorders Common: Palpitations, cardiomegaly, cardiomyopathy, pericardial effusion, vasodilatation, - postural hypotension - Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders Uncommon: Dyspnoea, epistaxis, pleural effusion, pneumonia Rare: Pulmonary hypertension, Pulmonary infiltrates Not known: Allergic alveolitis Gastrointestinal disorders Common: Nausea, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, flatulence, vomiting Uncommon: Dyspepsia, anorexia, pancreatitis, constipation, gastrointestinal haemorrhage, gastrointestinal disorder Rare: Colitis, gastritis, gingival bleeding, Hepatobiliary disorders Uncommon : Hepatic enzymes increased Not known : Hepatitis tachycardia Uncommon: Congestive heart failure, hypertension, arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, syncope Rare: Angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, cardiomegaly, pericardial effusion, vasodilatation, migraine, postural hypotension Respiratory and thoracic disorders Uncommon: Dyspnoea, epistaxis, pleural effusion, pneumonia Rare: Pulmonary infiltrates Gastrointestinal disorders Common: Nausea, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, flatulence, Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Common: Rash Uncommon: Alopecia, skin discolouration, pruritus Rare: Dry skin vomiting Uncommon: Dyspepsia, anorexia, pancreatitis, constipation, gastrointestinal haemorrhage, gastrointestinal Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders disorder Uncommon: Myalgia, Rare: Colitis, gastritis, gingival arthralgia, back pain bleeding, Renal and urinary disorders Hepatobiliary disorders Uncommon: Impotence Rare: Nocturia, renal failure Uncommon : Hepatic enzymes Not Known : Tubulointerstitial increased nephritis Not known : Hepatitis - Skin and subcutaneous tissue General disorders and administration site conditions Common: Fatigue Uncommon: Chest pain, weakness, chills, malaise, fever Rare: Asthenia, pain, flu-like syndrome Common: Rash Uncommon: Alopecia, skin discolouration, pruritus Rare: Dry skin Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Investigations Rare: Blood creatinine increased Uncommon: Myalgia, arthralgia, back pain Renal and urinary disorders Uncommon: Impotence Rare: Nocturia, renal failure Not Known : Tubulointerstitial nephritis Investigations Rare: Blood creatinine increased General disorders and administration site conditions Common: Fatigue Uncommon: Chest pain, weakness, chills, malaise, fever Rare: Asthenia, pain, flu-like syndrome Pharmacotherapeutic group: Other antineoplastic agents - ATC Code: L01XX35 Paediatric patients An open label clinical study with a 3 month treatment period did not raise any safety concerns for anagrelide in 17 children/adolescent patients with ET (age range 7-14 years) compared to 18 adult patients . -Earlier during clinical development a limited number Pharmacotherapeutic group: Proposed ATC Code: L01XX35(Other Antineoplastic Agents) Paediatric patients An open label clinical study with a 3 month treatment period did not raise any safety Pharmacodynamic properties (12) of children (age range 5-17 concerns for anagrelide in 17 years) with essential children/adolescent patients thrombocythaemia were treated with anagrelide. with ET (age range 7-14 years) - compared to 18 adult patients . earlier during clinical development a limited number (12) of children (age range 517 years) with essential thrombocythaemia were treated with anagrelide. This medicine has been authorized under "Exceptional Circumstances". This means that because of the rarity of this disease it has been impossible to get complete information on this medicine. The European Medicines Agency (EMEA) will review any new information which may become available every year and this Prescribing Information will be updated as necessary. Anagrelide is primarily metabolised by CYP1A2; less than 1% is recovered in the urine as anagrelide. Two major urinary metabolites, 2-amino-5, 6-dichloro-3, 4dihydroquinazoline and - 3hydroxy anagrelide have been identified. The mean recovery of 2-amino-5, 6-dichloro-3, 4dihydroquinazoline in urine is approximately 18-35% of the administered dose. Anagrelide is primarily metabolised by CYP1A2; less than 1% is recovered in the urine as anagrelide. Two major Pharmacokinetic urinary metabolites, 2-amino-5, properties 6-dichloro-3, 4dihydroquinazoline and N(5,6-dichloro-3,4- dihydroquinazalin-2-yl)-2Pharmacokinetic data from healthy subjects established that food decreases the Cmax of anagrelide by 14% but increases the AUC by 20%. Food had a more significant effect on the active metabolite and decreased the Cmax by 29% although it had no effect on the AUC. As expected from its half-life, there is no evidence for anagrelide accumulation in the plasma. Additionally these results show no evidence of auto-induction of the anagrelide clearance. Special populations oxoacetamide have been identified. The mean recovery of 2-amino-5, 6-dichloro-3, 4dihydroquinazoline in urine is approximately 18-35% of the administered dose. Pharmacokinetic data from healthy subjects established that food decreases the Cmax of anagrelide by 14% but increases the AUC by 20%. Food had a more significant effect on the active metabolite and decreased the Cmax by Paediatric patients Pharmacokinetic data from fasting children and adolescents (age range 7 – 14 years) with essential thrombocythaemia indicate that dose and body weight normalised exposure, Cmax and AUC, of anagrelide were lower in children/adolescents compared to adults. There was also a trend to lower exposure to the active metabolite. These observations may be a reflection of more efficient metabolic clearance in younger subjects. 29% although it had no effect on the AUC. As expected from its half-life, there is no evidence for anagrelide accumulation in the plasma. Additionally these results show no evidence of auto-induction of the anagrelide clearance. Special populationsPaediatric patients Pharmacokinetic data from Elderly Pharmacokinetic data from fasting elderly patients with ET (age range 65-75 years) compared to fasting adult patients (age range 22-50 years) indicate that the Cmax and AUC of anagrelide were 36% and 61% higher respectively in elderly patients, but that the fasting children and adolescents (age range 7 – 14 years) with essential thrombocythaemia indicate that dose and body weight normalised exposure, Cmax Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite, —-, 3-hydroxy anagrelide were 42% and 37% lower respectively in the elderly patients. These differences were likely to be caused by lower presystemic metabolism of anagrelide to —3-hydroxy anagrelide in the elderly patients. and AUC, of anagrelide were lower in children/adolescents compared to adults. There was also a trend to lower exposure to the active metabolite. These observations may be a reflection of more efficient metabolic clearance in younger subjects. Elderly Pharmacokinetic data from fasting elderly patients with ET (age range 65-75 years) compared to fasting adult patients (age range 22-50 years) indicate that the Cmax and AUC of anagrelide were 36% and 61% higher respectively in elderly patients, but that the Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite, 2-amino5, 6-dichloro-3, 4dihydroquinazoline, were 42% and 37% lower respectively in the elderly patients. These differences were likely to be caused by lower presystemic metabolism of anagrelide to 2amino-5, 6-dichloro-3, 4dihydroquinazoline in the elderly patients.