הודעה על החמרה (מידע בטיחות) בעלון לרופא תאריך 27/08/2015 שם התכשיר
advertisement

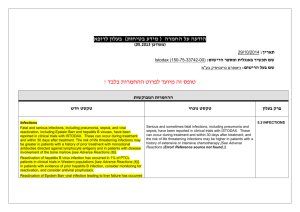
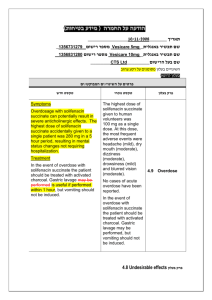
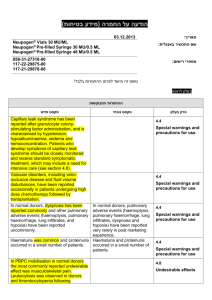
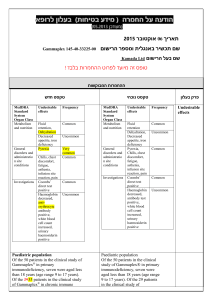
הודעה על החמרה (מידע בטיחות) בעלון לרופא 27/08/2015 תאריך Giroflox (133 31 30984) שם התכשיר באנגלית ומספר הרישום BioAvenir Ltd. שם בעל הרישום !טופס זה מיועד לפרוט ההחמרות בלבד ההחמרות המבוקשות טקסט חדש Severe infections and mixed infections with Gram-positive and anaerobic pathogens Ciprofloxacin monotherapy is not suited for treatment of severe infections and infections that might be due to Grampositive or anaerobic pathogens. In such infections ciprofloxacin must be coadministered with other appropriate antibacterial agents. Streptococcal Infections (including Streptococcus pneumoniae) Ciprofloxacin is not recommended for the treatment of streptococcal infections due to inadequate efficacy. Genital tract infections Epididymo-orchitis and pelvic inflammatory diseases may be caused by fluoroquinolone-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Ciprofloxacin should be coadministered with another appropriate antibacterial agent unless ciprofloxacinresistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae can be excluded. If clinical improvement is not achieved after 3 days of treatment, the therapy should be reconsidered. Intra-abdominal infections There are limited data on the efficacy of ciprofloxacin in the treatment of postsurgical intra-abdominal infections. Travellers’ diarrhoea The choice of ciprofloxacin should take into account information on resistance to ciprofloxacin in relevant pathogens in the countries visited. Infections of the bones and joints Ciprofloxacin should be used in combination with other antimicrobial agents depending on the results of the microbiological documentation. Inhalational anthrax Use in humans is based on in-vitro susceptibility data and on animal experimental data together with limited human data. Treating physicians should refer to national and /or international consensus documents regarding the treatment of anthrax. טקסט נוכחי … … Children and adolescents: 4 מתוך1 עמוד BPS-Safety update form SPC-01 פרק בעלון Special warnings and precautions for use Ciprofloxacin treatment should be initiated only by physicians who are experienced in the treatment of cystic fibrosis and/or severe infections in children and adolescents. … Musculoskeletal system: … The risk of tendinopathy may be increased in elderly patients or in patients concomitantly treated with corticosteroids (see section 4.8). … Central nervous system: … Cases of polyneuropathy (based on neurological symptoms such as pain, burning, sensory disturbances or muscle weakness, alone or in combination) have been reported in patients receiving ciprofloxacin. Ciprofloxacin should be discontinued in patients experiencing symptoms of neuropathy, including pain, burning, tingling, numbness, and/or weakness in order to prevent the development of an irreversible condition (see section 4.8). … QT interval prolongation Caution should be taken when using fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin, in patients with known risk factors for prolongation of the QT interval such as, for example: congenital long QT syndrome concomitant use of drugs that are known to prolong the QT interval (e.g. Class IA and III antiarrhythmics, tricyclic antidepressants, macrolides, antipsychotics) uncorrected electrolyte imbalance (e.g. hypokalaemia, hypomagnesaemia) cardiac disease (e.g. heart failure, myocardial infarction, bradycardia) Elderly patients and women may be more sensitive to QTc-prolonging medications. Therefore, caution should be taken when using fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin, in these populations. (See section 4.2 Elderly, section 4.5, section 4.8, section 4.9). … Methotrexate The concomitant use of ciprofloxacin with methotrexate is not recommended (see section 4.5). … … … Methotrexate … The concomitant use is not recommended (see section 4.4). 4 מתוך2 עמוד BPS-Safety update form SPC-01 Interactios with other medicinal products and … other forms of interaction Ropinirole … Monitoring of ropinirole-related side effects and dose adjustment as appropriate is recommended during and shortly after co-administration with ciprofloxacin (see section 4.4). Clozapine … Clinical surveillance and appropriate adjustment of clozapine dosage during and shortly after coadministration with ciprofloxacin are advised (see section 4.4). Ciprofloxacin, like other fluoroquinolones, should be used with caution in patients receiving drugs known to prolong the QT interval (e.g. Class IA and III antiarrhythmics, tricyclic antidepressants, macrolides, antipsychotics) (see section 4.4). The most commonly reported adverse drug reactions (ADRs) are nausea, diarrhoea, vomiting, transient increase in transaminases, rash, and injection and infusion site reactions. … Infections and infestations Rare: Antibiotic associated colitis (very rarely with possible fatal outcome) (see section 4.4) Blood and the lymphatic system disorders: Rare: Neutropenia Very rare: Bone marrow depression (lifethreatening) Psychiatric disorders: Uncommon: Psychomotor hyperactivity / agitation Rare: Confusion and disorientation Nervous system disorders: Rare: Par- and Dysaesthesia, Hypoaesthesia, Vertigo Frequency not known: Peripheral neuropathy (see section 4.4) Ear and labyrinth disorders: Rare: hearing loss hearing impaired Vascular disorders: Rare: Hypotension Hepato-biliary disorders: Rare: Hepatitis Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Very rare: Petechiae Stevens-Johnson syndrome (potentially life-threatening), Toxic epidermal necrolysis (potentially life-threatening) Musculoskeletal, connective tissueand bone disorders: Uncommon: Musculoskeletal pain (e.g. extremity pain, back pain, chest pain) Adverse reactions have been reported in 5-14% of patients receiving ciprofloxacin. The most frequent adverse effects involve the gastro-intestinal tract and the central nervous system. … Nervous system disorders: Rare: Paraesthesia Ear and labyrinth disorders: Rare: Transient hearing loss Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Very rare: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, epidermal necrolysis (Lyell Syndrome) 4 מתוך3 עמוד BPS-Safety update form SPC-01 Undesirable effects Rare: Increased muscle tone and cramping Very rare: Muscular weakness, Exacerbation of symptoms of myasthenia gravis (see section 4.4) General disorders and administration site conditions: Common: Injection and infusion site reactions (only intravenous administration) Rare: Sweating Investigations: Rare: increased amylase The following undesirable effects have a higher frequency category in the subgroups of patients receiving intravenous or sequential (intravenous to oral) treatment: Common Uncommon Rare Vomiting, Transient increase in transaminases, Rash Thrombocytopenia, Thrombocytaemia, Confusion and disorientation, Hallucinations, Parand dysaesthesia, Seizures, Vertigo, Visual disturbances, Hearing loss, Tachycardia, Vasodilatation, Hypotension, Transient hepatic impairment, Cholestatic icterus, Renal failure, Oedema Pancytopenia, Bone marrow depression, Anaphylactic shock, Psychotic reactions, Migraine, Olfactory nerve disorders, Hearing impaired, Vasculitis, Pancreatitis, Liver necrosis, Petechiae, Tendon rupture Reversible renal toxicity has been reported Overdose .מצ"ב העלון שבו מסומנים ההחמרות המבוקשות על רקע צהוב יש לסמן רק תוכן מהותי.)שינויים שאינם בגדר החמרות סומנו (בעלון) בצבע שונה (טקסט ירוק .ולא שינויים במיקום הטקסט 27/08/2015 הועבר בדואר אלקטרוני בתאריך 4 מתוך4 עמוד BPS-Safety update form SPC-01