Laws in Special Education Answer Key
advertisement
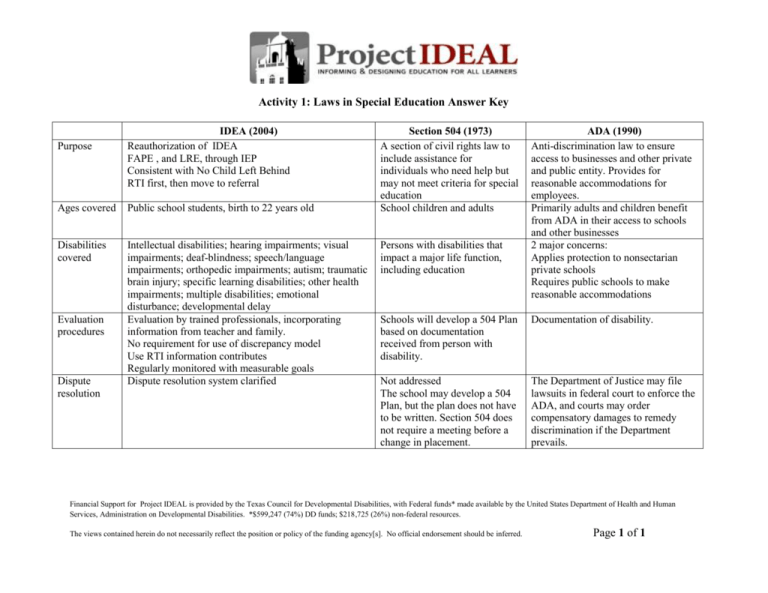
Activity 1: Laws in Special Education Answer Key Purpose IDEA (2004) Reauthorization of IDEA FAPE , and LRE, through IEP Consistent with No Child Left Behind RTI first, then move to referral Ages covered Public school students, birth to 22 years old Disabilities covered Intellectual disabilities; hearing impairments; visual impairments; deaf-blindness; speech/language impairments; orthopedic impairments; autism; traumatic brain injury; specific learning disabilities; other health impairments; multiple disabilities; emotional disturbance; developmental delay Evaluation by trained professionals, incorporating information from teacher and family. No requirement for use of discrepancy model Use RTI information contributes Regularly monitored with measurable goals Dispute resolution system clarified Evaluation procedures Dispute resolution Section 504 (1973) A section of civil rights law to include assistance for individuals who need help but may not meet criteria for special education School children and adults Persons with disabilities that impact a major life function, including education ADA (1990) Anti-discrimination law to ensure access to businesses and other private and public entity. Provides for reasonable accommodations for employees. Primarily adults and children benefit from ADA in their access to schools and other businesses 2 major concerns: Applies protection to nonsectarian private schools Requires public schools to make reasonable accommodations Schools will develop a 504 Plan based on documentation received from person with disability. Documentation of disability. Not addressed The school may develop a 504 Plan, but the plan does not have to be written. Section 504 does not require a meeting before a change in placement. The Department of Justice may file lawsuits in federal court to enforce the ADA, and courts may order compensatory damages to remedy discrimination if the Department prevails. Financial Support for Project IDEAL is provided by the Texas Council for Developmental Disabilities, with Federal funds* made available by the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Administration on Developmental Disabilities. *$599,247 (74%) DD funds; $218,725 (26%) non-federal resources. The views contained herein do not necessarily reflect the position or policy of the funding agency[s]. No official endorsement should be inferred. Page 1 of 1