Chapter One Summary Gina Nash - special education is the
advertisement

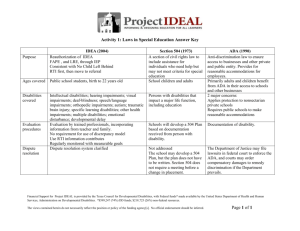
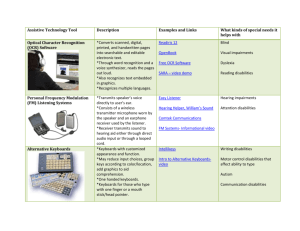
Chapter One Summary Gina Nash - special education is the specifically designed instruction for a student with disabilities provided by the school district. -Related services are different forms of assistances provided to meet the needs of each individual student. EX: speech/language therapy, transportation, and physical therapy. - Children with disabilities are entitled to supplementary aids and services. Although the rest of the students do not receive the priviledege, these students need preferential seating, access to computer technology, more time to complete tests, and simplified assignments. -Provisions include a LRE (Least Restrictive Environment) in which the student can have the most normal environment in a setting with their peers, but one in which they will be successful due to accommodations. - Inclusion Practices: 1. Physical Integration- actually being in the same classroom with their peers is important for the student. Removal from the classroom environment would not benefit the child. Seeing how their peers behavior and classroom reactions is a good way for the student to learn from example. 2. Social Integration: Relationships should be established between the student receiving special education and the class. The classmates would develop empathetic characteristics along with feelings of equality while the disabled student would be able to live a lifestyle without exclusion. 3. Instructional integration: being taught the same curriculum is a positive for integration, this way the student is able to stay as close as possible to the class academic level. -special education services were not always mild in the form of treatment. -children with disabilities did not receive an appropriate education until the 20th century. The Brown vs. Board of education and civil rights movement, and section 504 changed education policies. -Americans with Disabilities Act: an act made in 2008 to protect all children with disabilities from discriminations *outside source: http://www.businessinsurance.com/article/20110821/NEWS07/308219994?tags=|309|70|75|339|303 -Individuals with disabilities education improvement act: special education teachers must be highly certified. School districts encouraged to use money provided to find strategies for prevention for special education. -elementary and secondary education act of 1965: NO CHILD LEFT BEHIND: Outside source* http://www.journalgazette.net/article/20110830/LOCAL04/308309939/1002/LOCAL The importance of collaboration for meeting student needs is one of the keys to successful inclusion practices. Like the following: -meeting with special education teachers -co teaching -working with paraprofessionals -meeting on teams -interacting with parents - who receives special education and other special services? 1. learning disabilities 2.speech of language impairments 3. mental retardation 4. emotional disturbances Outside source* http://www.education.com/reference/article/emotional-disturbance/ 5. autism 6. hearing impairments 7. visual impairments 8. deaf-blindness 9. orthopedic impairments 10. tramatic brain injury 11. multiple disabilities 12. developmental delays