Bio 34 Breakdowns - Plain Local Schools
advertisement

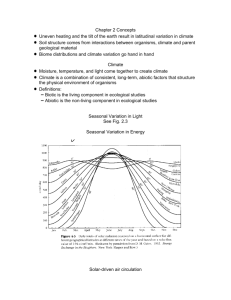
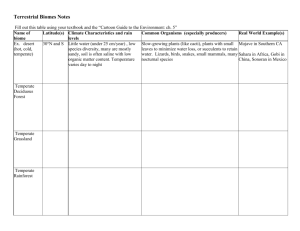
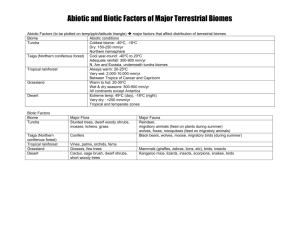
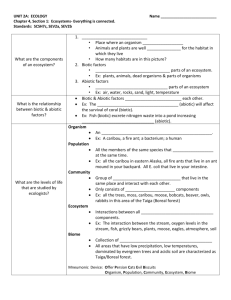
Integrated Biology 34.1 Name: Learning Objectives: After reading section 34.1 you should be able to… Define: Ecology – biotic factor – abiotic factor – population – community – ecosystem – biosphere - habitat Describe the five levels of ecological study Explain how the patchiness of the biosphere creates different habitats Identify key abiotic factors Complete the learning objectives and vocabulary in the space below: Reflection: Think about and describe your favorite outdoor spot. List all of the living things that are there. List all of the nonliving things that are there. Formative assessment: 1. Describe what is meant by the “patchiness” of the environment. 2. Explain the importance of sunlight as an abiotic factor in terrestrial ecosystems. 3. List one ecosystem and describe three biotic and three abiotic factors that we would find there. Use your technology! What are the two most venomous spiders found in Ohio? Integrated Biology Section 34.2 Name: Learning Objectives: After reading section 34.2 you should be able to… Define: tropics – polar zones – temperate zones – current – microclimate Explain how the sun heats the earth unevenly Describe global patterns of wind, precipitation, and ocean currents Distinguish between local climates and microclimates Complete the learning objectives and vocabulary in the space below: Reflection/Reaction: Think about a rotating storm like a hurricane or tornado. Which direction does the air rotate in the US? Why do you think this is? Formative assessment: 1. Explain how the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface creates different temperature zones. 2. How do surface currents affect climate patterns? 3. Give one example of a microclimate Use your technology! Who is Gustave-Gaspard Coriolis? Why is he famous? Integrated Biology 34.3 Name: Learning Objectives: After reading section 34.3 you should be able to… Define: biome – tropical rain forest – savanna – desert – chaparral – temperate grassland – temperate deciduous forest – coniferous forest – tundra - permafrost Describe what defines a biome List and describe eight major terrestrial biomes Complete the learning objectives and vocabulary in the space below: Reflection: Which of the biomes that you learned about today is under the greatest threat from human activity? What are humans doing that is threatening the biome? Formative assessment: 1. What factors determine the type of biome in an area? 2. Compare and contrast tropical rain forests , temperate deciduous forests, and coniferous forests. 3. Give an example of a desert organism. List three ways that your organism is adapted to life in the desert. Use your technology! What are the two most venomous spiders in Ohio? Integrated Biology 34.4 Name: Learning Objectives: After reading section 34.4 you should be able to… Define: photic zone – phytoplankton – aphotic zone – benthic zone – estuary – pelagic zone – intertidal zone – neritic zone – oceanic zone – zooplankton – hydrothermal vent Compare and contrast ponds, streams, and estuaries Compare conditions and typical organisms in the intertidal, neritic, and oceanic zones Describe the abiotic and biotic factors that characterize coral reefs and hydrothermal vent communities Complete the learning objectives and vocabulary in the space below: Reflection: In which of the biomes that we learned about today did Disney’s “Finding Nemo” occur. What are some human activities (shown in the movie) that put this biome at risk? Formative assessment: 1. Describe the abiotic factors that affect organisms in ponds, streams, and estuaries. 2. Compare and contrast the intertidal zone, neritic zone, and oceanic zone. 3. Discuss sunlight as an abiotic factor in coral reefs and deep-sea vent communities. Use your technology! What kind of luminescent fish chased nemo in the deepest part of the ocean where there was no sunlight.