Lab: bio 135 evolution unit
advertisement

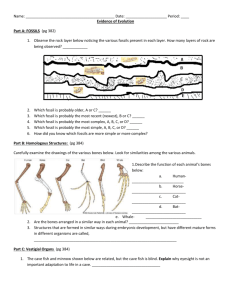
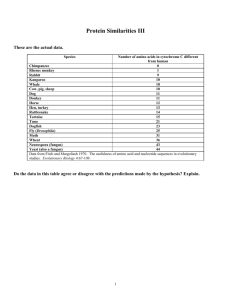
Round robin Evolution Lab. Use Ch. 15/16 as reference when necessary. Lab table 1: Law of Superposition and index fossils. Look at the fossils in the “paper sedimentary layers” provided. Based on the law of superposition, the oldest fossils will be on the bottom layer and the youngest at the top. Determine the sequence of rock layers by looking for organisms that transition to the next layer but may vanish (become extinct) in the layer above. 1a. Write the letters of the sequence here: Top layer Bottom layer 1b. An index fossil is animal/plant that had a brief existence on Earth. They may be found in only one layer of sedimentary rock and therefore can be used to age that layer of rock when they are found. 1b. List 2 index fossils: Lab table 2: Body structures – 2a..View the video on whale evolution : linked on my website-pbs whale. 2b. Answer question 33 on page 390. . Refer to the 3 appendages in figure 1. 2c. Are the functions these 3 limbs the same? Or different? 2d. What similarities do you observe in these 3 limbs? 2e. Would these limbs be “homologous” or “analogous” to each other? Explain your answer. 2f. How does a similarity in structure indicate a common ancestry? Lab table 3: Mutations & Predicting evolutionary relationships Molecular Biology Cytochrome c is a protein found in mitochondria. It is used in the study of evolutionary relationships because most animals have this protein. Cytochrome c is made of 104 amino acids joined together. Below is a list of the amino acids in part of a cytochrome protein molecule for 9 different animals. Any sequences exactly the same for all animals have been skipped. Compare the cytochrome C amino acid sequence in humans to a tuna fish. Write down the amino acid position number(s) where the tuna amino acid differs from the human. Write down the number of differences below. Do the same for the same for the horse. The first amino acid difference has been done for you. 3a. Tuna positions that differ from human: 12, Total number of differences between a Tuna compared to human: ____________ 3b. Horse positions that differ from human: Total number of differences between a horse compared to human: ______ According to evolutionary theory, species that shared a common ancestor have more DNA similarities . 3c. Using evidence from the data of the amino acid sequences of cytochrome c, explain which animal (tuna, or horse) is most closely related to a human. Refer to p. 394: 3d. List 3 ways a mutation might occur. 3e. List 2 ways genes are “shuffled” in offspring. Lab table 4: Hardy Weinberg problems Questions: Show all work. 4a. If there are 12 pocket mice with dark fur and 4 with light fur in a population, what is the value of q? Remember that light fur is recessive. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4b If the frequency of p in a population is 60% (0.6), what is the frequency of q? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4c In a population of 1,000 rock pocket mice, 360 have dark fur. The others have light fur. How many of the mice with dark fur would you expect to be homozygous dominant? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4d.. Refer to p 402 and list the 5 conditions that MUST be met to prevent a population from evolving, to remain at equilibrium. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Lab table 5: There are also many examples of body structures in animals that are very similar in function and superficially similar in form and but develop very different and have very different internal structures and embryonic development. These structures are called analogous structures. Analogous structures mean that the animals do not share a recent common ancestor. Analogous structures have the same function (job) but not the same structure. 5a. What function do the butterfly wing and bird wing share? 5b. In what ways do the 2 wings differ? 5c. Explain why these wings are considered analogous structures. Lab table 6: Embryology 6a. Go to the embryology link on my website and LAUNCH the interactive. http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/evolution/guess-embryo.html Embryo 1 is ________________________ Embryo 2 is ______________________ Embryo 3 is _______________________ Embryo 4 is ________________________ 6 b. Using the images of embryos provided, hypothesize which embryo is from which species. Lab table 5: Types of selection. Refer to p. 398 -399 to answer the question after graphing. One person should do the graph for 1976 and the partner should do the graph for 1978. 1. Create a histogram (bar graph) using this data. Then identify the mean (average), median (middle) and mode (most repeating). Mean: Median: Mode: 2. Refer to your text and compare the changes in the “mean” size of beaks over the 2 year period. What type of selection is resulting from environmental pressures? a. disruptive b. stabilizing c. directional 3. Explain how your graphs support your answer.