Name: Date: Period: ____ Evidence of Evolution Part A: FOSSILS
advertisement
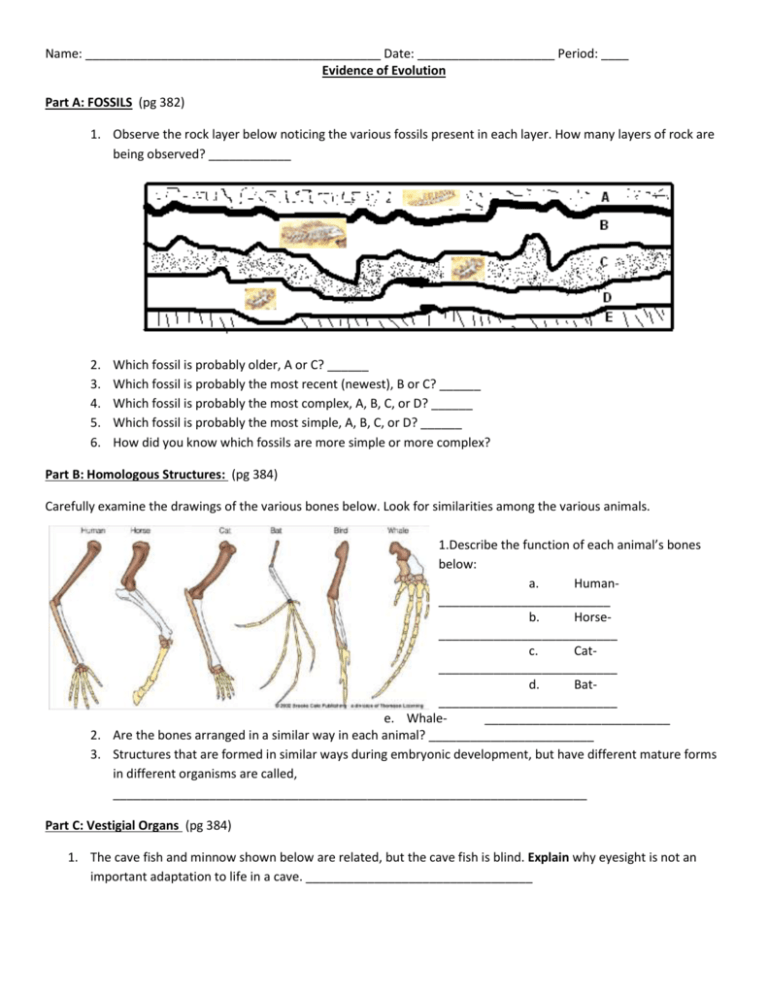
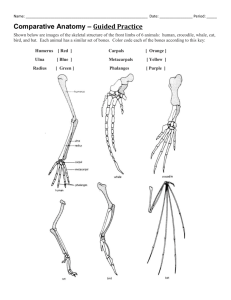
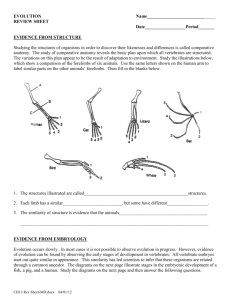
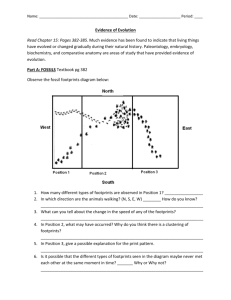
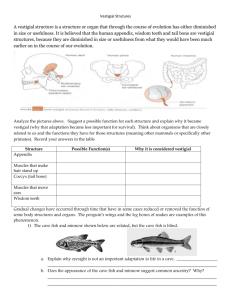
Name: ___________________________________________ Date: ____________________ Period: ____ Evidence of Evolution Part A: FOSSILS (pg 382) 1. Observe the rock layer below noticing the various fossils present in each layer. How many layers of rock are being observed? ____________ 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Which fossil is probably older, A or C? ______ Which fossil is probably the most recent (newest), B or C? ______ Which fossil is probably the most complex, A, B, C, or D? ______ Which fossil is probably the most simple, A, B, C, or D? ______ How did you know which fossils are more simple or more complex? Part B: Homologous Structures: (pg 384) Carefully examine the drawings of the various bones below. Look for similarities among the various animals. 1.Describe the function of each animal’s bones below: a. Human_________________________ b. Horse__________________________ c. Cat__________________________ d. Bat__________________________ e. Whale___________________________ 2. Are the bones arranged in a similar way in each animal? ________________________ 3. Structures that are formed in similar ways during embryonic development, but have different mature forms in different organisms are called, _____________________________________________________________________ Part C: Vestigial Organs (pg 384) 1. The cave fish and minnow shown below are related, but the cave fish is blind. Explain why eyesight is not an important adaptation to life in a cave. _________________________________ Name: ___________________________________________ Date: ____________________ Period: ____ 2. Does the appearance of the cave fish and minnow suggest common ancestry? ______ Why? ______________________________________ 3. Do vestigial organs serve a useful purpose or function? ______ 4. Name two human vesitigial organs. _______________________ and ________________ Part F: Biochemical Similarities Compare the Cytochrome C amino acid sequence in humans to each of the organisms listed below. You will find amino acid data on the “Amino Acids in the Protein Cytochrome C” table. For each organism, circle each amino acid that differs from the human sequence. Note: Letters in boldface represent amino acids that are identical in all species. indicates an amino acid that is missing in some species. In places where one species has and the other has a letter, count that as a difference. 1. Write down the number of differences between a human and a: Tuna Gray Whale Rhesus Monkey Chicken/Turkey Baker’s Yeast Silkworm Moth 2. Based on the amino acid sequence data you collected, which organism are humans most closely related to? _____________________ Most distantly related to? _____________________ Explain your reasoning. _____________________________________________________________ 1. If the amino acid sequences in the proteins of two organisms are similar, why will their DNA also be similar? _______________________________________________________________________