Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Booklet
advertisement

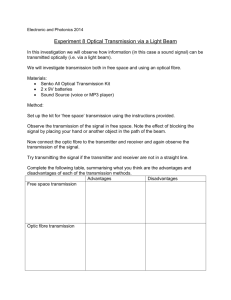
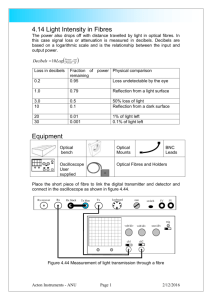
Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Booklet. Telecommunications Telecommunications is the name given to the process of sending information over a large distance. All telecommunications systems send information from a transmitter to a receiver. A common method of sending information is by using a radio. Radios are useful because they do not need wires to connect the transmitter and receiver. A radio signal is sent from the transmitter to the receiver as a wave. The radio wave carries energy. Radio waves travel very quickly through the air, in fact they travel at 300 000 000 metres per second. This means that they could go more than six times around the Earth in one second. For most of us a radio is used to listen to music, but there are many other applications. The emergency services use radios to keep in touch with their bases. Taxi drivers use radios to get information about pick-ups. Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft All radio receivers are made up from the same basic parts. A diagram showing these parts in order is shown below. Aerial Tuner Decoder Amplifier Loudspeaker What do the parts do? Aerial-this part picks up all the radio signals that are present. This will normally be hundreds of radio signals from many different sources. Tuner-this part selects one signal from the hundreds that are there. It has nothing to do with fish. Decoder-this part takes away the high frequency part of the radio signal,[the carrier wave],leaving the audio[sound] part. Amplifier- this part increases the energy of the audio signal that comes from the decoder. Loudspeaker-this part changes electrical energy into sound energy. Radio stations have to distinguish themselves from each other so that their listeners can choose the correct station to listen to. Radio stations have different frequencies for their radio signals. The frequency of a radio signal is the number of radio waves produced each second. There is a word we can use instead of saying ‘the number of radio waves produced each second’, it is hertz. Hertz is called the unit of frequency. It can be written as an abbreviation, Hz. Radio stations have high frequencies, Real Radio is 101 000 000 Hz. Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft Television Television is very similar to radio in many ways. The main difference is that televisions produce a picture as well as sound. Because of this the diagram of the parts of the television is different. Aerial Tuner Vision decoder Audio decoder Vision amplifier Audio amplifier Tube Speaker The Aerial, Tuner, Decoder, Amplifier and Loudspeaker do exactly the same job in the television as they do in the radio. The Tube changes electrical energy into light energy. The tube has three types of special paint that gives off light of a particular colour. The three colours of light produced are RED, BLUE and GREEN. Mixing these three colours produces all other colours that you see on a TV screen. RED + BLUE RED + GREEN BLUE + GREEN RED + BLUE + GREEN = MAGENTA = YELLOW = CYAN = WHITE Varying the strength of the three original colours can produce other colours. Example extra RED + normal GREEN = ORANGE. Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft Satellites Satellites have changed communication around the world dramatically. Now it is possible to use satellites to send signals from one part of the Earth to another thousands of miles away. The satellites used in this type of communication are called GEOSTATIONARY satellites. They are special because they stay above the same point on the Earth’s surface at all times. The satellite transmitter and receiver have a particular shape. You may have noticed this common shape from the satellite dishes on the sides of people’s houses. The dishes have a curved shape to increase the strength of the signal falling on the aerial. The diagram below shows what happens to the signal from the satellite when it reaches the dish. The dish picks up the signal over its curved surface and reflects all of the signal to the aerial that is placed at the focus point. Curved Dish Aerial Incoming Signal Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft Optical Fibres When light strikes an object it will be reflected. We are able to see objects because they either produce light, like a lamp or the sun, or they reflect light into our eyes, which is practically everything we see. Usually we will use mirrors when we want to cause light to reflect. If the mirror is plane[flat] then the light reflects in a specific way. angle of incidence i r angle of reflection normal The angle that the light strikes the barrier is the same as the angle that the light reflects from the barrier. This fact is used in a type of signal transfer, the transfer of information using optical fibres. An optical fibre is a thin glass thread that will carry light signals. A signal is converted into light and passed along the fibre. Each time the signal meets the surface of the fibre it is reflected back inside and will go from one end to the other of the fibre. The signal passes along the fibre at a speed of almost 200 000 000 m/s. This is slower than the speed that radio waves travel through air. Although the light signal does not travel as quickly it can carry much more information and is less likely to have interference. Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft Optical fibres are used in many modern applications in the home. Telephone services: 1471 and 1571 Cable television Home banking Internet Optical fibres have meant that these services can now be accessed in many homes, that is a great advantage of this type of system. There are disadvantages though; not all homes are connected to the optical fibre system. The roads and pavements have to be dug up to lay the cables containing the fibres. Telephone The telephone has been used as a method of communication since 14 February 1876 when Alexander Graham Bell registered his invention. The modern telephone is very similar to his original invention. Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft Telephones are like all other forms of communication, a signal is sent from a transmitter to a receiver. The signal can be sent by using metal wires, optical fibres or radio waves between the transmitter and the receiver. Wire carries signals to and from the telephone Earpiece Loudspeaker Electrical to sound Mouthpiece Microphone Sound to electrical The names of the parts of the telephone handset, the devices contained in them and the energy change that takes place in them are shown on the diagram above. If the signal is sent along a wire it travels at almost 300 000 000 m/s. A mobile phone uses radio waves to transfer the signal. The mobile phone acts as both transmitter and receiver for radio waves. Radio waves also travel very quickly at a speed of 300 000 000 m/s. Many people have mobile phones these days. They have the advantage of not needing wires so they can be used almost anywhere. A disadvantage is that mobile telephone calls are more expensive than ordinary home phones. A useful application of the telephone lines is to send facsimile messages, more commonly known as FAX. This allows pictures and diagrams to be sent. Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft In all telephone systems we need to change an electrical signal into sound so that we can hear the message sent to us. The electrical signal can be examined using a device called an oscilloscope. The pattern on the oscilloscope screen can give an indication of what the signal would sound like when it is changed to sound by the loudspeaker. telephone handset oscilloscope wire carrying signal from telephone If we know what a particular signal looks like on the screen, we can compare the sound produced with any other signal pattern given. This is the original pattern. If the sound gets louder the height of the pattern gets bigger [diagram A] If the sound gets higher pitch the number of waves on the screen increases [diagram B] diagram A diagram B Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft Telecommunications Learning Outcomes • Radio » » » » » » » » Radio communication does not require wires between transmitter and receiver. Radio signals are waves that transfer energy. Radio signals travel at 300 000 000 m/s How to complete a block diagram of a radio receiver. Describe what the following parts of a radio receiver do: The aerial , tuner , decoder , amplifier and loudspeaker. The number of of waves produced in one second is the frequency of a signal. The frequency of a signal is measured in Hertz. Radio stations can be identified by the frequency of their signal. • Television » » » » » Television signals have a higher frequency than radio signals Just like a radio station TV stations are identified by the signal frequency. How to complete a TV block diagram Describe what the following parts of a TV receiver do: The aerial , tuner , amplifiers, tube and loudspeaker. All colours on a TV screen are produced from RED, BLUE and GREEN light. • Satellites » » » » How satellites are used. A geostationary satellite remains above the same point on the Earth’s surface. Curved reflectors on an aerial make the signals stronger Explain why curved reflectors on an aerial make the signals stronger. Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft • Optical Fibres » » » » » » » » » Light can be reflected The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection An optical fibre is a thin glass thread which can carry signals. Optical fibres are used in telecommunication. Information passes along optical fibres as light signals The signals travel along the optical fibre at a speed of 200 000 000 m/s [slower than in air] The light signal reflects from the inside surface of the fibre to pass along it. Optical fibres have allowed more information to be sent into homes i.e.cable TV,digital phones,internet access etc. Advantages and disadvantages of optical fibre technology. • Telephone » » » » » » » » » » » » » » Signals are sent out by a transmitter and picked up by a receiver Telephone systems may use metal wires, optical fibres or radio waves to carry the signal A mobile phone acts as both transmitter and receiver Advantages and disadvantages of mobile phones The mouthpiece of a phone contains a microphone The mouthpiece of a phone is the transmitter The earpiece of a phone contains a loudspeaker The earpiece of a phone is the receiver The microphone changes sound to electrical energy The loudspeaker changes electrical to sound energy The signal in a metal telephone wire travels at a speed of 300 000 000 m/s. Fax is the process of sending documents and pictures using the telephone system Advantage of using fax. Draw and recognise the effect of the signal pattern on an oscilloscope due to a change in; » Loudness of sound » Frequency of sound Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft Revision Questions Radio 1. Why is radio a useful method of communication? 2. At what speed do radio waves travel through air? 3. Copy and complete the following sentence Radio signals are sent from the _______________ and are picked up by the _______________. 4. What is carried by radio waves? 5. Copy and complete the block diagram of the radio receiver below. Aerial Decoder 6. Give a brief description of the function of the five parts of the radio receiver. 7. What is different about the radio signals from Beat 106 and Real Radio. 8. What is meant by the frequency of a radio signal? 9. What is the unit of frequency? Television 10. The table below contains information on two sets of signals that are broadcast in Scotland. Set Frequency (hertz) A 1 215 000 B 628 000 000 One set of signals is for a radio station and the other is for a TV station. a) Which set of signals could be the TV signals? b) Explain your answer to part a). 11. Draw a block diagram for a television in the same style as Q5. 12. Describe the function of any part of the above diagram that does not appear on the radio block diagram. Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft 13. What are the three colours of light produced by the paint on a TV screen? 14. Copy and complete the table below showing the colour produced on a TV screen when different paints are lit. Colour lit Colour seen on screen Red Blue Red + Blue Blue + Red + Cyan Yellow + 15. Explain how colours other than those in the table above can be produced. Satellites 16. Give a brief description how satellites are used to send signals from Australia to Scotland. 17. Communications satellites are geostationary satellites. What is meant by geostationary? 18. Copy and complete the diagram below showing a satellite TV receiving dish. Curved Dish Incoming Signal 19. Explain why the set up above can make the signal stronger. Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft Optical fibres 20. Copy and complete the diagram showing two rays of light striking a mirror below. B normal A 21. What is an optical fibre? 22. Copy and complete the diagram showing a ray of light passing through an optical fibre. 23. Which telecommunications systems use optical fibres. You should be able to give at least three examples. 24. Copy and complete the table below Type of signal Radio signal through air Light signal through optical fibre Phone signal through metal wire Approximate speed of signal(m/s) 300 000 000 25. Write a short note on the advantages and disadvantages on the use of optical fibres to send signals into the home. Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft Telephone 26. Copy and complete the following passage. A telephone like all telecommunication systems sends signals from a __________ to a ____________. These signals may be sent along metal ________, __________ fibres or through the air as _________ waves. 27. Give advantages and disadvantages of a mobile phone. Present your answer in a table with appropriate headings. 28. Look at the diagram of a telephone handset below. Name the parts labelled X and Y. For each part give the name of the electrical component used and give the energy change that takes place. X Y 29. What device could be used to send a document by telephone transmission. 30. What is the advantage of using this system? Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft 31. The trace on an oscilloscope showing the signal pattern for a signal that is sent to a loudspeaker is shown below. Give the change that you would hear in the sound from the loudspeaker for each of the other four patterns shown below A, B, C and D. A B C D Dick Orr 2002 Intermediate 1 Physics Revision Book Draft