Chemistry 634: Advanced Organic Chemistry – Synthesis and Reactivity
advertisement

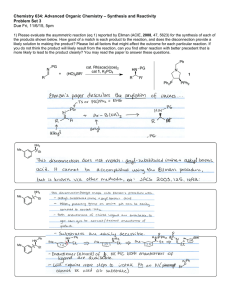
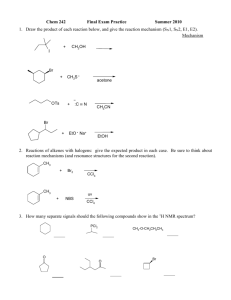
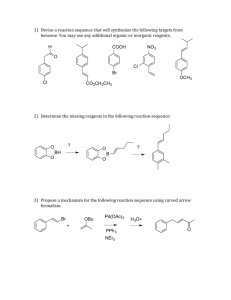
Chemistry 634: Advanced Organic Chemistry – Synthesis and Reactivity Problem Set 3 Due Fri, 11/6/15, 5pm 1) Please evaluate the asymmetric reaction (eq 1) reported by Ellman (ACIE, 2008, 47, 5623) for the synthesis of each of the products shown below. How good of a match is each product to the reaction, and does the disconnection provide a likely solution to making the product? Please list all factors that might affect the outcome for each particular reaction. If you do not think the product will likely result from the reaction, can you find other reaction with better precedent that is more likely to lead to the product cleanly? You may read the paper to answer these questions. Ph N PG + (HO)2BR' R cat. Rh(acac)(coe)2 cat 1, K3PO4 HN PG R N 1 R' Ph2P PPh2 NH2 Me Et NH2 Me Et HN NH2 Et Me Me Ph HN Et Me Me NH2 Me Et HN Me Ph Et HN Ts Me Me Ts 2) In metalloenamine alkylation, only the syn product (and not the anti) is observed, though in theory both should be possible. This likely results from the stability of the metalloenamines, as shown. Using FMO analysis, please explain this observation. Li N R N E-X R N Li E R E-X R observed, syn product N E not observed, anti product Explanation: 3) Provide the missing reagents and provide rationale for any stereoselective steps. Me Me Me Me O OBn OH O O OMe Me Me O OBn OH O Me Me O OMe Me Me Synthesis (Missing Reagents): Stereochemical Rationale: (3 – continued) O 5 steps TBSO OH TBSO H Me this enantiomer > 99% ee Synthesis (Missing Reagents): Stereochemical Rationale: 4) Enolate oxidation via heteroatom installation is also an important reaction, but was not discussed in class. Given the example below, provide a mechanistic rationale both for bond formation (arrow-pushing mechanism), as well as the observed stereochemistry. O Me O N O Bu2BOTf Et3N, then NBS O Me N Me Me Bn Arrow-Pushing Mechanism and Stereochemical Rationale: O Br Bn O 5) Camphor-derived chiral auxiliaries are also important in organic synthesis. Below such an auxiliary (developed by Helmchen) that is useful for ester synthesis. a) Build a model of the starting material and draw it in 3D. b) Using this model and your knowledge of enolate formation, rationalize the stereochemical outcome below. Me PhO2S N Me Me O Me O Me Me CyN(i-Pr)Li, THF/HMPA then I Me PhO2S N Me Me Me Me O Me Me O Me dr = 94:6 Stereochemical Rationale: Me Me 6) Predict the products from each of the following reactions. Me Me OMe OMe Br Br Br O Me OMe Me O Me O Me Me Me KOtBu KOtBu Me O O KOtBu N N O O Me O Me OMe Me N O O Me Me O Me Me Me Me O Me Me O O NaHMDS, MeI NaHMDS, MeI NaHMDS, MeI LiHMDS; EtI LiHMDS; EtI LiHMDS; EtI 7) For each of the following, predict the product of the reaction and provide a model to explain the expected stereoselectivity. O Me LDA (kinetic), THF -78°C; then TBSCl OMe O Model to Explain Stereoselectivity: Me OMe O Me LDA (kinetic), THF -78°C; then TBSCl OMe O Me LDA (kinetic), THF/HMPA -78°C; then TBSCl LDA (kinetic), THF/HMPA -78°C; then TBSCl OMe Model to Explain Stereoselectivity: 8) (a) Please propose a synthesis of 1 using 1,3-propane diol and propionic acid as the only sources of carbon in the product. You may use any other reagents required, including those that contain carbon. O OH O OH H3C + OH HO H H O Me 1 single enantiomer Synthesis: (b) Please provide a rationale for the stereoselective steps in your synthesis. Stereochemical Rationale: