Types of Chemical Reactions
advertisement

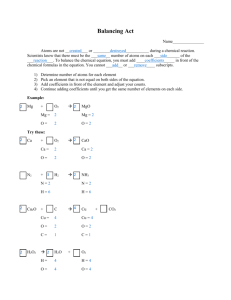
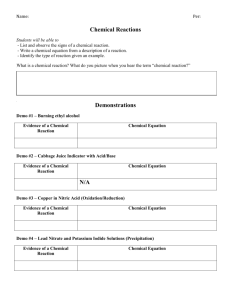
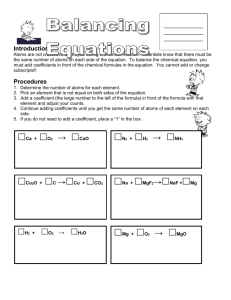
Oct 2013 Chapter 9 is where you will find most of this information There are MANY types of Chemical reactions; we will start with a few Reactants Products (Read as reactants react to form Products) Some reactions take in energy and are “endothermic” Some reactions give off energy and are “exothermic” KNOW THE SEVEN DIATOMIC ELEMENTS!!!!!!! ( I2, Br2, Cl2, F2, O2, N2, H2) Sometimes we use special symbols to indicate the phase of the reactants. The ones you need to know are: (s) (l) (g) (aq) for solid (precipitate) for liquid for a gas (bubbles) for aqueous solutions (chemicals dissolved in water) If a symbol for an element is placed above or below the reaction arrow it indicated that that element is a catalyst. A catalyst doesn’t get used up or produced in the reaction but by having that element present the rate of the reaction is increased. There are two fundamental laws of nature we hope you are familiar with - Matter cannot be created or destroyed (just moved around) o This law has been replaced with: - Energy cannot be created or destroyed (but will flow from areas of higher energy to lower energy) In chemistry it is easier to think of the first statement We will also be studying the naming of chemical compounds some of the basic are: *- Metals and metals form alloys *- A metal and a non-metal form an ionic compound (aka a formula unit or salt) *- A non-metal and a non-metal form a covalent molecule Types of Chemical Reactions Now that you know something about elements and compounds, lets see how they can react to for different stuff! Just like with Lego’s (the snap together building blocks) you can put them together, take them apart or swap them around. 1. A DECOMPOSITION reaction starts with one reactant and ends up with two or more products. Which of the following reactions are decomposition reactions? Circle the letters. a) b) c) d) e) 2. NaCl Na + Cl2 Na + Cl2 NaCl H2O H2 + O2 NaOH + HCl HOH + NaCl H2 + O2 H2O A SYNTHESIS reaction starts with two reactants and ends up with one product. Which of the following reactions are synthesis reactions? Circle the letters. a) b) c) d) e) 3. NaCl Na + Cl2 Na + Cl2 NaCl H2O H2 + O2 NaOH + HCl HOH + NaCl K +Cl2 KCl A SINGLE REPLACEMENT reaction starts with two reactants and ends up with two products. The uncombined element takes the place of the combined element in the compound. Which of the following reactions are single replacement reactions? Circle the letters. a) b) c) d) e) 4. NaCl Na + Cl2 NaOH + HCl HOH + NaCl K + AgCl2 Ag + KCl Na + HCl H2 + NaCl H2O H2 + O2 A DOUBLE REPLACEMENT reaction starts with two reactants and ends up with two products. In this case both reactants are compounds and both products are compounds. Which of the following reactions are double replacement reactions? Circle the letters a) b) c) d) e) NaOH + HCl HOH + NaCl Na + HCl H2 + NaCl K + AgCl2 Ag + KCl KOH + HNO3 KNO3 + HOH Ca + S CaS 5. A COMBUSTION reaction is when the reactants are oxygen and a hydro carbon and 6. the products are water and carbon dioxide. A NEUTRALIZATION reaction is a special type of double replacement reaction that will be covered in detail later on. By now something should be bothering you about many of the Chemical Equations listed above. Many of them ARE NOT BALANCED. Please follow the teacher examples of how to balance equations. Identifying and Balancing Chemical Equations Name: _________________________________ period: ____ Balance these equations (even if the value is one put it in the blank) and identify the type of reaction. (Synthesis, Decomposition, Single Replacement, Double Replacement or Combustion) Type of reaction 1. __HgO __Hg + __O2 2. __ NaCl + __ AgNO3 3. __ Cl2 + __ Ca ____________ __NaNO3 + __AgCl __ CaCl2 ____________ ____________ 4. __ C2H6 + __ O2 __CO2 + __H2O ____________ 5. __ H2O + __ Fe __ Fe2O3 + __ H2 ____________ 6. __ Al2S3 + __Ca(OH)2 __ Al(OH)3 + __ CaS ____________ 7. __ S8 + __ Fe __ FeS ____________ 8. __ N2 + __ H2 __ NH3 ____________ __ KCl + __ O2 ____________ 9. __ KClO3 10. __ Al2(SO4)3 + __Ca(OH)2 __ Al(OH)3 + __ CaSO4 ____________ Chapter 9 in the Glencoe book we will be skipping the net ionic equation stuff for now) Chapter 11 book problems: 1, 2, 3, 4, 11, 12, 14, 15, 18, 24, 28, 41, 49, 51, 54 Student notes on demo’s Take notes on what you see happening to help you remember, is the reaction exothermic or endothermic, how can you know that a chemical reaction has taken place? Single Replacement Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) Cu (s) + FeSO4(aq) Double Replacement 2KI (aq) + Pb(NO3)2 (aq) 2KNO3 (aq) + PbI2 (s) Synthesis Zn (s) + I (s) [H2O] ZnI2 + I2 (g) (IN ‘DA HOOD, reaction takes place in the exhaust hood) web example: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xT9V7Y1iKYc (the water does not undergo a chemical change ( it might undergo a physical change to water vapor )but acts as a catylist to speed up the reaction) Decomposition (sugar decomposition catalyzed by very concentrated acid) Web example: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DOb_BRydnCs C12H22O11 + [H2SO4] 12C (s) + 11H2O + HEAT 2H2O2 (aq) [KI] O2 (g) + 2H2O (l) (Potassium Iodide does not undergo a change but acts as a catylist to speed up the reaction) Types of Chemical Reactions with answers Now that you know something about elements and compounds, lets see how they can react to for different stuff! Just like with Lego’s (the snap together building blocks) you can put them together, take them apart or swap them around. 1. A DECOMPOSITION reaction starts with one reactant and ends up with two or more products. Which of the following reactions are decomposition reactions? Circle the letters. a) b) c) d) e) 2. NaCl Na + Cl2 Na + Cl2 NaCl H2O H2 + O2 NaOH + HCl HOH + NaCl H2 + O2 H2O A SYNTHESIS reaction starts with two reactants and ends up with one product. Which of the following reactions are synthesis reactions? Circle the letters. a) b) c) d) e) 3. NaCl Na + Cl2 Na + Cl2 NaCl H2O H2 + O2 NaOH + HCl HOH + NaCl K +Cl2 KCl A SINGLE REPLACEMENT reaction starts with two reactants and ends up with two products. The uncombined element takes the place of the combined element in the compound. Which of the following reactions are single replacement reactions? Circle the letters. a) b) c) d) e) 4. NaCl Na + Cl2 NaOH + HCl HOH + NaCl K + AgCl2 Ag + KCl Na + HCl H2 + NaCl H2O H2 + O2 A DOUBLE REPLACEMENT reaction starts with two reactants and ends up with two products. In this case both reactants are compounds and both products are compounds. Which of the following reactions are double replacement reactions? Circle the letters. a) b) c) d) e) NaOH + HCl HOH + NaCl Na + HCl H2 + NaCl K + AgCl2 Ag + KCl KOH + HNO3 KNO3 + HOH Ca + S CaS 5. A COMBUSTION reaction is when the reactants are oxygen and a hydro carbon and 6. the products are water and carbon dioxide. A NEUTRALIZATION reaction is a special type of double replacement reaction that will be covered in detail later on. By now something should be bothering you about many of the Chemical Equations listed above. Many of them ARE NOT BALANCED. Please follow the teacher examples of how to balance equations. Identifying and Balancing Chemical Equations Name: _______ANSWERS_________ period: ____ Balance these equations (even if the value is one put it in the blank) and identify the type of reaction. (Synthesis, Decomposition, Single Replacement, Double Replacement or Combustion) Type of reaction 1. _2_HgO + _2_Hg + _1_O2 2. _1_ NaCl + _1_ AgNO3 3. _1_ Cl2 + _1_ Ca __Decomposition_ _1_NaNO3 + _1_AgCl _1_ CaCl2 4. _2_ C2H6 + _7_ O2 _4_CO2 + _6_H2O 5. _3_ H2O + _2_ Fe _1_ Fe2O3 + _3_ H2 6. 1 Al2(SO4)3 + 3 Ca(OH)2 _Double Replace_ ___Synthesis___ __combustion___ _single replacement_ 2 Al(OH)3 + 3 CaSO4 _Double Replace_ 7. _1_ S8 + _8_ Fe _8_ FeS ___ Synthesis __ 8. _1_ N2 + _3_ H2 _2_ NH3 __ Synthesis __ 9. _2_ KClO3 _2_ KCl + _3_ O2 10. 1 Al2(SO4)3 + 3 Ca(OH)2 __Decomposition_ 2 Al(OH)3 + 3 CaSO4 __Double Replace_ Chapter 11 book problems: 1, 2, 3, 4, 11, 12, 14, 15, 18, 24, 28, 41, 49, 51, 54 Book problem answers: 1) Solid sodium metal and liquid water react to form a solution of sodium hydroxide and bubbles of hydrogen gas. 2) S(s) + O2(g) SO2 (g) but you might not know this 3) a) 2 AgNO3 + H2S Ag2S + 2 HNO3 b) 3 Zn(OH)2 + 2 H3PO4 Zn3(PO4)2 + 6 H2O 4) a) b) H2 + S H2S FeCl3 + Ca(OH)2 Fe(OH)3 + CaCl2 11) a) b) Fe(s) + Cl2(g) FeCl3(s) Al2(CO3)3(s) Al2O3(s) + CO2(g) 12) a) 2 SO2 + O2 2 SO3 b) Fe2O3 + 3 H2 2 Fe + 3 H2O c) 4 P + 5 O2 P4O10 d) 2 Al + N2 2 AlN 14) 3 Mg(s) + N2(g) Mg3N2 15) Complete and balance this decomposition reaction: 2 HI H2 + I2 ; remember diatomic elements (I Br Cl F O N H) 18) Write the products of these double-replacement reactions. Then Balance each equation. a) 3 NaOH(aq) + Fe(NO3)3(aq) Fe(OH)3(s) + 3 NaNO3 b) 3 Ba(NO3)2(aq) + 2 H3PO4(aq) Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6 HNO3(aq) 24) 28) Classify and balance each: a) 2 C3H6 + 9 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H20 b) 2 Al(OH)3 Al2O3 + 3 H2O c) Li + O2 Li2O d) Zn + 2 AgNO3 2 Ag + Zn(NO3)2 Write the balanced net ionic equation for this reaction. (as written) Ca2+(aq) + OH-(aq) + H+(aq) + PO4-3(aq) Ca2+ + PO43-(aq) + H2O(l) You just don’t write the stuff that is on both sides: so… Ca2+(aq) + OH-(aq) + H+(aq) + PO4-3(aq) Ca2+ + PO43-(aq) + H2O(l) Or simplified it is: 41) combustion decomposition synthesis single replacement OH-(aq) + H+(aq) H2O(l) Balance each : a) a bb team: C + 2 F + 2 G CF2G2 b) a tricycle: F + 3 W + S + 2 P FW3SP2 49) reactions Write a balanced equation for each of the following double replacement a) H2C2O4(aq) + KOH(aq) K2C2O4 + 2 HOH b) CdBr2(aq) + Na2S(aq) CdS(s) + 2 NaBr(aq) 51) Write a balanced equation for the complete combustion of each compound a) C4H8 + 6 O2 4 CO2 +4 H2O b) C3H6O + 4 O2 3 CO2 + 3 H2O ; (the reactant also has oxygen) 54) Write a net ionic equation for each of the following reactions. a) 2 HCl(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) CaCl2 + 2 HOH as ions it is written as: 2 H+ + 2Cl- + Ca2+ + 2(OH)- Ca2+ + 2Cl- + 2H2O ; water’s a molecule not an ionic compound Cross out the ions that are on both sides gives us: 2 H+ + 2Cl- + Ca2+ + 2(OH)- Ca2+ + 2Cl- + 2H2O Or 2 H+ + 2(OH)- 2H2O ( the net ionic equation) b) AgNO3(aq) + AlCl3(aq) silver chloride is a precipitate so… 3 AgNO3(aq) + AlCl3(aq) 3 AgCl(s) + 1 Al(NO3)3(aq) as ions it is: 3 Ag+ + 3 (NO3)-(aq) + Al3+ + 3Cl-(aq) 3 AgCl(s) + 1 Al3+ + 3(NO3)-(aq) Cross out the same ones to get net ionic: 3 Ag+ + 3 (NO3)-(aq) + Al3+ + 3Cl-(aq) 3 AgCl(s) + 1 Al3+ + 3(NO3)-(aq) Or simply: 3 Ag+ + 3Cl-(aq) 3 AgCl(s) (the net ionic equation)