Gill, Benton, Lunde-Earth and Environmental - NHCS
advertisement
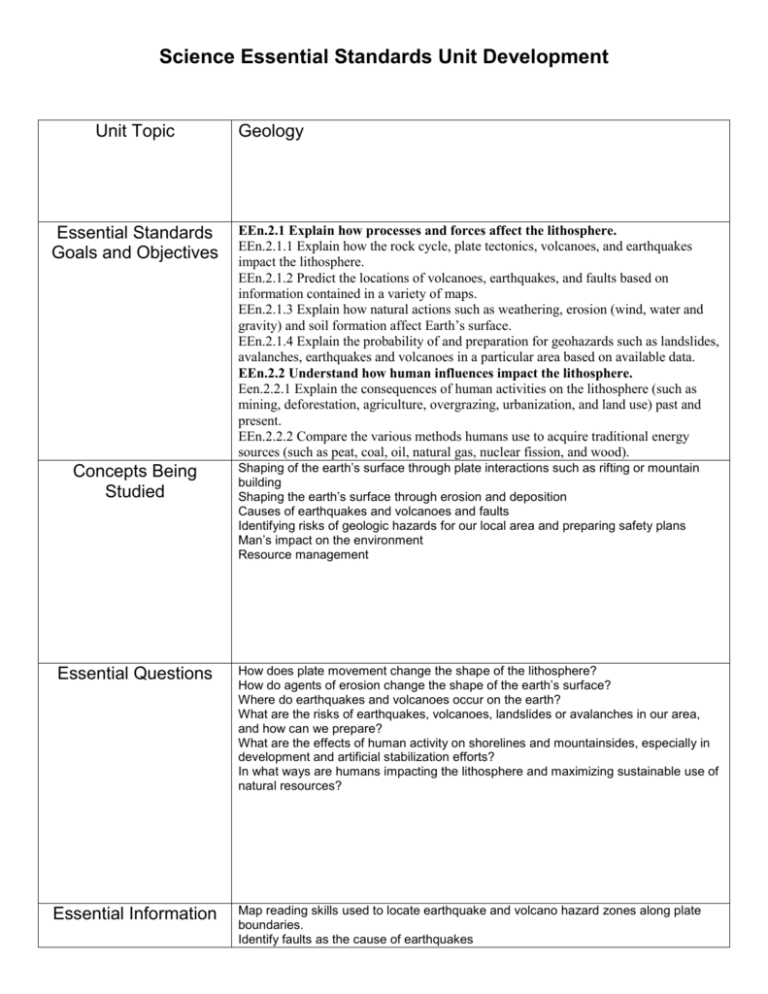
Science Essential Standards Unit Development Unit Topic Essential Standards Goals and Objectives Concepts Being Studied Essential Questions Essential Information Geology EEn.2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the lithosphere. EEn.2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the lithosphere. EEn.2.1.2 Predict the locations of volcanoes, earthquakes, and faults based on information contained in a variety of maps. EEn.2.1.3 Explain how natural actions such as weathering, erosion (wind, water and gravity) and soil formation affect Earth’s surface. EEn.2.1.4 Explain the probability of and preparation for geohazards such as landslides, avalanches, earthquakes and volcanoes in a particular area based on available data. EEn.2.2 Understand how human influences impact the lithosphere. Een.2.2.1 Explain the consequences of human activities on the lithosphere (such as mining, deforestation, agriculture, overgrazing, urbanization, and land use) past and present. EEn.2.2.2 Compare the various methods humans use to acquire traditional energy sources (such as peat, coal, oil, natural gas, nuclear fission, and wood). Shaping of the earth’s surface through plate interactions such as rifting or mountain building Shaping the earth’s surface through erosion and deposition Causes of earthquakes and volcanoes and faults Identifying risks of geologic hazards for our local area and preparing safety plans Man’s impact on the environment Resource management How does plate movement change the shape of the lithosphere? How do agents of erosion change the shape of the earth’s surface? Where do earthquakes and volcanoes occur on the earth? What are the risks of earthquakes, volcanoes, landslides or avalanches in our area, and how can we prepare? What are the effects of human activity on shorelines and mountainsides, especially in development and artificial stabilization efforts? In what ways are humans impacting the lithosphere and maximizing sustainable use of natural resources? Map reading skills used to locate earthquake and volcano hazard zones along plate boundaries. Identify faults as the cause of earthquakes Identify the subduction zones and hot spots as the cause of volcanoes Describe the possible interactions at plate boundaries Define deposition and erosion and identify the results of each. Identify the consequences of various types of land use such as urbanization, deforestation, and agriculture Identify detrimental human impacts on the lithosphere. List ways to maximize sustainable use of natural resources Explore alternative energy technologies in order to get a more complete picture of possible sources of energy for human use. Essay Questions Imagine that you are magma inside a volcano. Describe a possible journey that would carry you through becoming an igneous rock, then a sedimentary rock, and finally a metamorphic rock. Describe the process of subduction. What landforms result? Compare and contrast wind and water as agents of erosion. Compare and contrast Mauna Loa volcano with Mt. St. Helens. Compare the type of volcanic structure that is formed and the type of eruption. Compare the differences between living in Pompeii and experiencing the 79AD eruption of Mt. Vesuvius with living in modern times and experiencing the eruption of Mt. Pinatubo in 1991. List and describe the pros and cons of renewable vs. nonrenewable energy resources. How are deforestation, overgrazing, and urbanization harmful to Earth? Project Ideas Students will develop Power Point presentations on assigned volcanoes Students will do a webquest on plate tectonics Students will build card stock buildings in order to analyze what kinds of structures are safest during an earthquake Students will choose a geologic hazard that is of concern in their area, and develop posters or presentations to educate people about the hazard and safety precautions. They could alternatively put together the appropriate disaster supplies, and donate them to a charity. Technology Power point presentations on volcanoes Webquest on plate tectonics Virtual Earthquake—online simulation that allows students to identify the epicenter of an earthquake and to determine its magnitude Turning Point clickers used for assessment Probeware and accelerometers to determine the strength of s-waves (evaluate the cardstock buildings) Labs, Experiments, Activities, etc. Resources Assessment Comparing the viscosity of substances to model lava types Building models of faults Building models of the seafloor to demonstrate mid-ocean ridges and trenches Using slinkies to demonstrate earthquake waves Cookie mining lab Mapping earthquake and volcanoes on a world map Candy bar plate tectonics Computer lab Data projector Work sheets/copies Maps Candy bars Slinkies Cardstock Text book Probeware and accelerometers Turning Point clickers Turning Point Student Response System Quick Writes Exit cards Lab Reports Essay questions Unit tests Exam