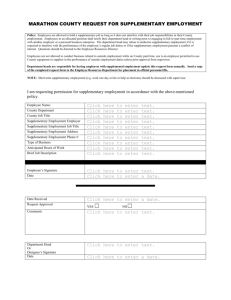
There were no differences in gender, age, education, IQ or 2

Supplementary materials
Effective connectivity of AKT1-mediated dopaminergic working memory networks and pharmacogenetics of antidopaminergic treatment
Hao Yang Tan*, Anthony G Chen*, Bhaskar Kolachana*, Jose A Apud*, Venkatta S
Mattay*, Joseph H Callicott*, Qiang Chen* + , Daniel R Weinberger* +
*Clinical Brain Disorders Branch, Genes Cognition and Psychosis Program, Division of
Intramural Research Programs, National Institute of Mental Health, Bethesda, Maryland
20892, USA.
+
Lieber Institute for Brain Development, Johns Hopkins Medical Center,
855 Wolfe Street, Baltimore, Maryland 21205 Correspondence should be addressed to
H.Y.T. (haoyangtan@gmail.com) or D.R.W. (drweinberger@libd.org)
1
Supplementary materials
Supplementary Table S1: Demographic characteristics of subjects fMRI study on working memory
(n=46 healthy controls)
Pharmacogenetic study
(n=111 schizophrenia patients)
Age, yrs
Gender, % male
Education, yrs
WAIS IQ
AKT1 G-allele frequency
AKT1 A-allele frequency
DRD2 G-allele frequency
DRD2 T-allele frequency
COMT Val-allele frequency
COMT Met-allele frequency
Age of illness onset, yrs
PANSS Positive score
PANSS Negative score
PANSS General score
Antipsychotic dose, CPZ-eq
Mean
32.0
56.5
16.7
110.3
0.74
0.26
0.87
0.13
0.51
0.49
-
-
-
-
-
SD
9.57
-
2.23
9.68
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Mean
36.7
75.5
14.1
95.7
0.76
0.24
0.87
0.13
-
-
23.0
12.3
19.0
23.9
495
SD
9.7
-
2.3
11.5
-
-
-
-
-
-
5.9
4.9
8.5
7.4
361
Premorbid IQ (WRAT) - - 104 10.4
CPZ-eq: Chlorpromazine-equivalent dose; WRAT: Wide Range Achievement Test – Reading;
PANSS: Positive and Negative Symptom Scale
2
Supplementary materials
Supplementary Table S2: Behavioral performance during working memory maintenance and manipulation in fMRI according to genotype (n=46 healthy controls).
Maintenance Manipulation
Accuracy ( AKT GG/ A)
Reaction time, sec ( AKT GG/ A)
Accuracy (DRD2 GG/GT)
Reaction time, sec (DRD2 GG/GT)
Accuracy ( COMT VV/M)
Reaction time, sec ( COMT VV/M)
Mean
0.974/ 0.955
1.183/ 1.174
0.956/ 0.967
SD
0.053/ 0.057
0.202/ 0.202
0.961/ 0.949 0.055/ 0.100
1.156/ 1.186 0.183/ 0.252
0.066/ 0.051
1.187/ 1.180 0.244/ 0.183
Mean
0.943/ 0.955
1.325/ 1.330
0.948/ 0.916
1.307/ 1.300
0.930/ 0.958
1.328/ 1.330
AKT GG: AKT1 rs1130233 G-homozygotes; A: AKT1 rs1130233 A-allele carriers; DRD2 GG:
DRD2 rs 1076560 G-homozygotes, GT: heterozygotes (no TT homozygotes); COMT VV: COMT -
Val158 homozygotes, M: COMT -Met allele carriers.
Behavioral performance differences across genotype groups were all p>0.25.
SD
0.072/ 0.056
0.252/ 0.236
0.063/ 0.161
0.221/ 0.304
0.078/ 0.057
0.302/ 0.214
3
Supplementary materials
Manipulation events in working memory
DLPFC Parietal Cortex Thalamus/ Striatum
Maintenance events in working memory
DLPFC Parietal Cortex Thalamus
Supplementary Figure S1: BOLD activation in the WM maintenance and manipulation events.
Subjects robustly increased BOLD activity in the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, parietal cortex and subcortical brain regions (thalamus and striatum in manipulation, and thalamus in maintenance). Images were thresholded at p<0.05 corrected for false discovery rate. Color bars represent t-scores.
4
Supplementary materials
Supplementary Figure S2: Working memory manipulation task performance and IQ in the imaging data.
Reaction time in the WM manipulation task was correlated with IQ (r=-0.345, p=0.007).
In similar data available on file, WM manipulation accuracy was correlated with IQ
(r=0.368, p=0.004).
5