File - DRD2 and the Impulsivity Link
advertisement

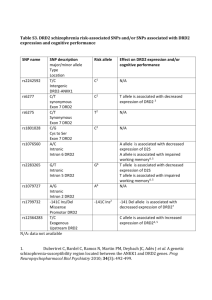
DRD2 and the Impulsivity Link By: Shu Hui Lye How is impulsivity defined? hAps://boardgame>me.files.wordpress.com/2012/04/table_flip.jpg ‘Rapid, unplanned reac>ons towards internal and external s>muli’ Impulsivity is a symptom in various psychiatric disorders Addic8on ADHD Schizophrenia hAp://sta>c.psychguides.com/wp-­‐content/uploads/schizophrenia2-­‐215x300.jpg hAp://img2.>meinc.net/health/images/gallery/condi>on-­‐centers/causes-­‐of-­‐adhd-­‐400x400.jpg DRD2 codes for a dopamine receptor DRD2 belongs to the GPCR superfamily hAp://sta>c1.squarespace.com/sta>c/52ec8c1ae4b047ccc14d6f29/t/54e0b408e4b0419b74cc5102/1424012297546/striatum.png De Mei, C., Ramos, M., Iitaka, C., & Borrelli, E. (2009). Ge]ng specialized: presynap>c and postsynap>c dopamine D2 receptors. Current opinion in pharmacology, 9(1), 53-­‐58. DRD2 is highly expressed in the striatum DRD2 is well-­‐conserved across vertebrates % iden>ty Humans 7 tm_1 443aa Chimpanzees 7 tm_1 443aa 100% Rhesus Macaque 7 tm_1 443aa 99% Horse 7 tm_1 443aa 98% House Mouse 7 tm_1 Blind Cave Fish 7 tm_1 444aa 452aa 95% 69% What does GO tell us about DRD2? Biological Processes Cell membrane Molecular Func8on GPCR signalling, dopamine regula>on Postsynap>c density Associa>ve learning Cellular Component Dopamine ac>vity via G protein coupling DRD2 is associated with impulsivity Polymorphisms associated with drug addic>on and smoking Comings, D. E., et al. (1996), Najafabadi, M. S., et al. (2005) Low DRD2 levels in obese subjects Volkow, N. D., et al. (2008) High drug self-­‐administra>on in DRD2 KO/KD animals Dalley, J. W., et al. (2007) Knowledge gap: Why are there conflic8ng studies on associa>ons? hAp://bipolarcaregivers.org/wp-­‐content/uploads/2010/07/Computer-­‐conflict-­‐arrows.jpg May be due to complex regulatory mechanisms of DRD2 DRD2 isoforms have different func>ons. D2L (Long) 443aa Acts at postsynap>c sites D2S (Short) 414aa Acts at presynap>c sites Possible antagonis8c func8ons! A third isoform has also been reported. D2L (Long) 443aa Acts at postsynap>c sites D2S (Short) 414aa Acts at presynap>c sites D2Longer 445aa ??? D2Longer has two extra amino acids D2L D2Longer D2S Extra amino acids may affect ligand binding Hypothesis Regula8on of DRD2 expression is cri>cal for impulse control and responsiveness to an>psycho>c drug treatment Hypothesis Regula8on of DRD2 expression is cri>cal for impulse control and responsiveness to an>psycho>c drug treatment Isoforms Polymorphisms A A T C G C C C A G T A A A T C G G C C A G T A Aim 1: To study the prevalence and expression levels of D2Longer Long isoform Short isoform Longer isoform RNA-­‐Seq: Quan>fy transcript abundance in different brain regions Obtain samples (post-­‐ mortem brains) Propor8on of DRD2 transcripts D2L Control Substance abuse Psychiatric illness D2S D2Longer Example: DRD2 expression in striatum mRNA expression level D2L D2S D2Longer Control Substance abuse Psych. illness Aim 2: Study proteins interac>ons in D2S and D2Longer AP-­‐MS with TAP tagging Compare to STRING Proteins interac>ng with D2L are involved in signal transduc8on Cor8sol regula8on Binds drugs Dopamine regula8on G-­‐Protein Signaling Somatotropin regula8on Hypothesis: Some proteins do not interact with D2S and D2Longer Aim 3: Study the rela>onship between gene polymorphisms and DRD2 protein affinity to specific compounds Genotype individuals with different DRD2 gene polymorphisms Use CRISPR to create cell lines expressing polymorphisms Test protein affinity to drugs What drugs act on DRD2? Ropinirole Haloperidol LSD Some Future Direc8ons Elucidate func>on and cellular localiza>on of D2Longer KO/KD experiments More associa>on studies? Long-­‐term goal Develop therapies to offset impulse control dysregula>on that is characteris>c of psychiatric illnesses References Comings, D. E., et al. (1996). The dopamine D2 receptor (DRD2) gene: a gene>c risk factor in smoking. Pharmacogene7cs and Genomics, 6(1), 73-­‐79. Dalley, J. W., et al. (2007). Nucleus accumbens D2/3 receptors predict trait impulsivity and cocaine reinforcement. science, 315(5816), 1267-­‐1270. Dal Toso, Sommer, Ewert, Herbe, et. al. 1989. The dopamine D2 receptor: two molecular forms generated by alterna>ve splicing. The EMBO Journal. Vol. 8 no. 13 pp. 4025-­‐4034. Najafabadi, M. S., et al. (2005). Associa>on between the DRD2 A1 allele and opium addic>on in the Iranian popula>on. American Journal of Medical Gene7cs Part B: Neuropsychiatric Gene7cs, 134(1), 39-­‐41 Usiello, A., Baik, J.-­‐H., Rouge-­‐Pont, F., Pice], R., Dierich, A., LeMeur, M., Piazza, P. V., Borrelli, E. Dis>nct func>ons of the two isoforms of dopamine D2 receptors. Nature 408: 199-­‐203, 2000 Volkow, N. D., et al. (2008). Low dopamine striatal D2 receptors are associated with prefrontal metabolism in obese subjects: possible contribu>ng factors. Neuroimage, 42(4), 1537-­‐1543