Supplementary
advertisement

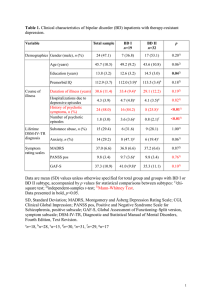
Supplementary Figure 1. Stereoscopic versions of stimuli. Each row is composed of a pair of stereo images: R (the right-eye image) and L (the left-eye image). These two images are arranged as triplets LRL with R in the middle and L on both sides of R. Two ways of fusing the stereo pairs to obtain the true 3-D configurations are shown by the two-headed arrow symbols: either (i) Depth, illusions, schizophrenia 2 “cross-fuse” the middle R and rightmost image L or (ii) “uncross-fuse” the leftmost L and middle image R (by diverging the eyes). Under these viewing conditions, the two top rows will yield a concave mask, and the third row will yield a convex mask. Finally, the bottom two rows will yield a 3-D scene with a locally concave region in the middle of the object, around the small green fixation mark. Depth, illusions, schizophrenia 3 TOP VIEW SIDE VIEW FRONT VIEW Supplementary Figure 2. Orthographic projections of scenes. Top, front and side orthographic projections of the concave scenes (“reverse perspectives”). The dotted lines correspond different views of the stimulus and are for illustration only. Depth, illusions, schizophrenia 4 Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients Variable Age (years) Chlorpromazine equiv. (mg/day) Days since last acute PH admission (Log10) Education, father (years) Education, mother (years) Education, self (years) Ethnicity (% Caucasian) FSIQ (Shipley) Gender (% male) Handedness (% right) Neuroleptics: typical/atypical/both PANSS,positive PANSS, negative PANSS, general PANSS, total Supplementary Table S1 Outpatient (N=10) Mean SD Extended (N=10) Mean SD Acute (N=10) Mean SD 51.1 8.1 46.0 15.0 42.7 16.2 F(3,51)=.8, p=.481 400 210 437 213 495 213 F(2,27)=.5, p=.607 3.1 0.2 2.4 0.4 1.3 0.4 F(2,27)=63.3, p=10-10 13.1 3.5 13.2 2.9 10.7 6.3 F(3,48)=.9, p=.450 12.2 3.1 11.9 3.0 10.1 6.0 F(3,49)=.6, p=.622 12.8 2.0 13.6 1.6 13.2 2.4 F(3,51)=.3, p=.845 80.0 NA 80.0 NA 20.0 NA Χ2 = 20.1, p = 0.065 88.6 60.0 70.0 12.5 NA NA 90.0 70.0 90.0 10.9 NA NA 86.7 80.0 80.0 16.2 NA NA F(3,48)=.1, p=.935 Χ2 = 3.6, p = 0.31 Χ2 = 3.2, p = .363 1/8/1 11.8 14.2 24.7 50.7 NA 3.5 3.7 5.6 9.7 1/9/0 14.9 16.0 28.5 59.4 NA 5.0 5.1 7.1 15.5 2/8/0 17.3 21.6 36.3 75.2 Group Comparison NA 4.1 4.6 7.3 14.1 F(2,27)=4.3, p=.025 F(2,27)=7.4, p=.003 F(2,27)=7.7, p=.002 F(2,27)=8.7, p=.001