Scavenger Hunt
advertisement

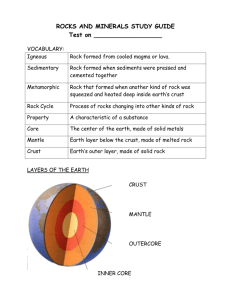
A6 McDonald Nardella 6 Thematic Scavenger Hunt Earth Science – Grade 4 The properties of rocks and minerals reflect the processes that formed them. As a basis for understanding this concept: 4.a, 4.b 1. How are igneous rocks formed? They are formed by the crystallization and solidification of molten magma. Magma forms when rock is heated to high temperatures (between 625 and 1200° Celsius) beneath the Earth's surface. Website: http://www.physicalgeography.net/fundamentals/10e.html 2. Name two ways that heat moves from the Earth's core towards the solid outer crust. A. By convection. Convection involves the transfer of heat energy by means of vertical mass motions through a medium B. By conduction. Conduction consists of energy transfer directly from atom to atom and represents the flow of energy along a temperature gradient Website: http://www.physicalgeography.net/fundamentals/10e.html 3. How is Metamorphic Rock Formed? Metamorphic rocks are rocks that have "morphed" into another kind of rock. These rocks were once igneous or sedimentary rocks. How do sedimentary and igneous rocks change? The rocks are under tons and tons of pressure, which fosters heat build up, and this causes them to change. If you exam metamorphic rock samples closely, you'll discover how flattened some of the grains in the rock are. Website:http://www.cdli.ca/CITE/rocks_metamorphic.htm 4. Metamorphic rocks are separated into two groups by texture. What are these two groups named? A. Foliated (having layers or banding) and Nonfoliated (not layered). Examples of foliated: Slate is heavy, often dark colored and smooth when it breaks in sheets. It does not contain visible minerals, but with a microscope, you would see that all its minerals are lined up. The properties of slate make it ideal to use on the top of pool tables, shingles on roofs, walking stones, and the original blackboards, which teachers write on. Phyllite resembles slate but has a somewhat coarser texture. The flat surfaces have a lustrous sheen due to mica and chlorite. However, it is not as hard or flat as slate, and not used in construction like slate. A6 McDonald Nardella 6 Gneiss is coarsely foliated in bands. The bands can be straight, pancake-like, or wavy. The bands differ in composition and are coarse grained making them easy to identify. Many of the light-colored bands are composed of either quartz or feldspar. The dark bands belong to the augite/hornblende groups. Schist is finely foliated forming thin parallel bands. The individual minerals are visible but are usually platy or rod-like. Some minerals are larger within the foliated minerals, and these can include garnet, pyroxene or feldspars. Schist looks like it is composed of "glitter Examples of nonfoliated: Hornfels are nonfoliated rocks composed of equal sized minerals in a random orientation. It is usually formed in low pressure, high temperature, during contact metamorphism. Quartzite is usually nonfoliated and composed of recrystallized quartz. Sandstone and chert are the common parent rock. Marble is composed of either calcite or dolomite, and usually derived from limestone. The purity of the marble will depend on the purity of the limestone. Serpentinite is nonfoliated, and composed mainly of the mineral serpentine. Serpentinite also occurs as a fibrous variety, especially found near fault zones. Website: http://msnucleus.org/membership/html/jh/earth/metamorphic/index.html 5. From what type of metamorphic rock did Michelangelo carve his most famous statues, such as “la Pieta” and “David”? A. Marble – Cabrera marble Website: http://msnucleus.org/membership/html/jh/earth/metamorphic/index.html 6. How are sedimentary rocks formed? Sedimentary Rocks are formed in layers as the result of moderate pressure on accumulated sediments. Website: http://www.rocksandminerals.com/rockcycle.htm A6 McDonald Nardella 6 7. What is the difference between rocks and minerals? Minerals are homogeneous, naturally occurring, inorganic solids. Each mineral has a definite chemical composition and a characteristic crystalline structure. A mineral may be a single element such as copper (Cu) or gold (Au), or it may be a compound made up of a number of elements. About 2,500 different minerals have been described Rocks are made up of one or more minerals. Website: http://www.rocksandminerals.com/rockcycle.htm 8. Name four of the six main kinds of sedimentary rocks and explain why they are categorized as they are. The 6 main kinds of sedimentary rocks are categorized depending on the appearance of the rock. Conglomerate rock has rounded rocks (pebbles, boulders) cemented together in a matrix Sandstone is a soft stone that is made when sand grains cement together. Sometimes the sandstone is deposited in layers of different colored sand. Shale is clay that has been hardened and turned into rock. It often breaks apart in large flat sections Limestone is a rock that contains many fossils and is made of calcium carbonate &/or microscopic shells. Gypsum, common salt or Epsom salt is found where sea water precipitates the salt as the water evaporates Porphory rock is when jagged bits of rock are cemented together in a matrix. Website: http://www.rocksforkids.com/RFK/howrocks.html 9. Which mineral can be used in pencil leads? Graphite website: http://geology.about.com/gi/dynamic/offsite.htm?site=http://www.uni%2 Dwuerzburg.de/mineralogie/links.html 10. What is the name of the scale that measures the hardness of Minerals? Mohs Hardness scale - A measurement that was devised by Austrian scientist Fredrick Mohs to determine the hardness of a mineral. website: http://www.minerals.net/glossary/terms/m/mohs.htm A6 McDonald Nardella 6 11. What does it mean if a mineral is isometric? Any mineral that falls under the following specifications belongs to the isometric crystal system: Three axes, all of them are equal in length and lie at 90° from the other. website: http://www.minerals.net/glossary/terms/i/isometri.htm 12. To be classified as a "true" mineral, what must be occur in a substance? To be classified as a "true" mineral, a substance must be a solid and have a crystal structure. It must also be an inorganic, naturally-occurring, homogeneous substance with a defined chemical composition. website: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mineral 13. The hope diamond is what color(s) & what causes it to be that color(s)? It is classified as a type IIb diamond, which are semi-conductive and usually phosphoresce. The Hope diamond phosphoresces a strong red color, which will last for several seconds after exposure to short wave ultra-violet light. The diamond's blue coloration is attributed to trace amounts of boron in the stone. website: http://www.minerals.si.edu/hope.htm 14. What is the single most common mineral in the earths crust? QUARTZ is undoubtedly the single most common mineral in the Earth's crust, ranging from perhaps 12% of continental crust to as much as 50% of oceanic crust as indicated by the composition of spreading-ridge volcanic lavas. Some estimates place quartz at 21% of the Earth's total lithosphere. website: http://mineral.galleries.com/minerals/by-name.htm 15. What is Thermoluminescence? Name an example of a mineral that is thermoluminescent? Thermoluminescence is a property of some minerals to glow when they are heated. The minerals contain chemical bonds that emit light when thermal energy (heat) is applied to them. It is well know that steel becomes luminescent when it has been heated and is being worked. Some minerals glow when they are subjected to temperatures of between 50 and 475 degrees C. Activator elements must be present in these minerals just like in UV fluorescence. In some minerals, they will glow only once during heating and then never glow again. This is because the excited electrons were trapped in a higher state during crystallization and only when heated were they allowed to lower their energy state by emitting the photons of light. Minerals that have been known to show this unusual property are: APATITE, CALCITE, some FELDSPARS, FLUORITE and LEPIDOLITE. Website;http://mineral.galleries.com/minerals/property/pleochro.htm#phos