Mitosis and Meiosis
advertisement

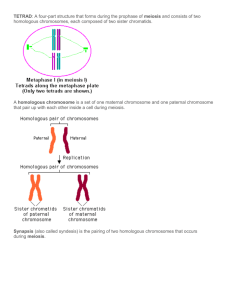
Mitosis and Meiosis Diploid (2n): 2 sets of homologous chromosomes Haploid (1n): 1 single set of homologous chromosomes. This cell has 2 pairs of chromosomes; 1 long, 1 short. There are two sets of 2 similar (homologous) chromosomes. Ploidy = diploid, 2n # of chromosomes = 4 # of chromatids = 4 This cell has 2 pairs of duplicated homologous chromosomes; 1 long, 1 short. Ploidy = diploid, 2n # of chromosomes = 4 # of chromatids = 8 This cell has 2 chromosomes; 1 long, 1 short. There is only 1 copy of each chromosome, so it is haploid. Ploidy = haploid, 1n # of chromosomes = 2 # of chromatids = 2 This cell has 2 duplicated chromosomes; 1 long, 1 short. There is only 1 copy of each chromosome, so it is haploid. Ploidy = haploid, 1n # of chromosomes = 2 # of chromatids = 4 This is a diploid cell in metaphase and anaphase of mitosis. In the metaphase cell, there are 4 chromosomes (8 chromatids) total and two sets of homologous chromosomes that are duplicated. In the anaphase cell, there are 8 chromosomes. The resulting daughter cells will also be diploid and genetically identical to the mother cell. This is a haploid cell in metaphase and anaphase of mitosis. There are 2 chromosomes (4 chromatids); 1 big chromosome, 1 small chromosome in the metaphase cell. In the anaphase cell, there are 4 chromosomes present. The resulting daughter cells would be halploid and genetically identical to the mother cell. There are two divisions in meiosis. The cell entering meiosis is diploid. In meiosis homologous chromosomes pair (allows crossing over of genetic material), but homologous do not pair in mitosis. Another difference is that after the first meiotic division, the cells do not reenter interphase and DNA is not replicated. In metaphase 1 of meiosis, bivalents orient at the metaphase plate and homologous are paired. Each chromosome of a homologous pair attaches to fibers from opposite poles. The sister chromatids attach to fibers from the same pole. In anaphase 1, the centromere does not divide and homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles. This is the separation of homologous chromsomes. These are the products of the first meiotic division. Only 1 of each chromosome (long and short) is present, therefore the daughter cells produced from the first meiotic division are haploid. In between meiosis 1 and 2, the DNA does not replicate and the starting cells are haploid. In metaphase 2, the chromosomes align at the metaphase plate and sister chromatids attach to spindle fibers from opposite poles. In anaphase 2, the centromeres divide and chromatids move to opposite poles. This is the separation of sister chromatids. The daughter cells produced are also haploid, having only 1 of each chromosome (long and short).