Chromosomal Abnormalities Worksheet
advertisement

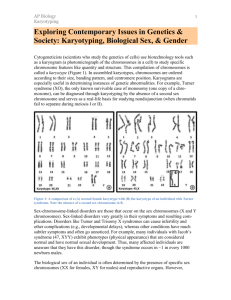
Name ______________________________________ Date ____________ Period _____ HONORS BIOLOGY Chromosomal Abnormalities Directions: Use your class notes and/or textbook to answer the following questions about chromosomal abnormalities. 1. Chromosomes that are paired together because they are similar in size, shape, and the genes they carry are called ________________________. a. analogous chromosomes b. univalent chromosomes c. homologous chromosomes d. tetrads 2. A picture of chromosomes arranged by size and centromere location that can reveal abnormalities is called a __________________. a. karyocature b. karyotype c. chromotype d. chromomere 3. Out of what kind of material(s) are chromosomes made? a. protein only b. DNA only c. scientists do not know yet d. DNA and protein 4. Based on the following karyotype, what can you conclude about this person? a. b. c. d. They are a normal female. They are a normal male. They have Edward’s Syndrome They have Down’s Syndrome 5. A person with Cri-du-Chat Syndrome is a. missing chromosome # 5 b. has trisomy 18 c. missing part of chromosome # 5 d. has trisomy 21 1 6. Another name for trisomy 13 is a. Patau Syndrome b. Down’s Syndrome c. Edward’s Syndrome d. Klinefelter’s Syndrome 7. Klinefelter’s Syndrome is caused by the presence of a. an extra Y-chromosome (XYY) b. an extra X-chromosome (XXY) c. a missing X-chromosome ( _X) d. a third 21st chromosome 8. The odds of a 20-year-old woman having a child with Down’s Syndrome is ________________. a. 1 out of 50 b. 1 out of 1500 c. 1 out of 350 d. none of the above 9. The odds of a 43-year-old-woman having a child with Down’s Syndrome is ________________. a. 1 out of 50 b. 1 out of 1500 c. 1 out of 350 d. none of the above 10. Non-sex chromosomes are called ________________________. a. autosomes b. autochromes c. chromomeres d. chromotypes 11. An accident of meiosis or mitosis, in which both members of a pair of homologous chromosomes or both sister chromatids fail to move apart properly is called ______________________. a. autosomal disjunction c. nondisjunction b. disjunction d. none of the above 12. How many chromosomes do normal human beings have? a. 22 pairs of chromosomes b. 23 chromosomes c. 46 pairs of chromosomes d. 23 pairs of chromosomes USE THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION TO ANSWER THE NEXT TWO QUESTIONS. In humans, unusual numbers of sex chromosomes sometimes occur, such as XO = female, usually sterile; XXX = female, low fertility rate; XXY = male, tall and sexually underdeveloped; XX = female, normal; and XY = male, normal. 13. What phenomenon is responsible for the unusual chromosome numbers? a. nondisjunction c. tetrad formation b. anaphase d. crossing over 2 14. What kind of logical conclusion can be drawn from studies of these disorders of chromosome number? a. The two X chromosomes are necessary to produce females. b. The number of X chromosomes determines the sex of the child. c. The Y chromosome does not carry genetic information. d. The presence of a Y chromosome determines sex in humans. 15. What sex chromosomes would you expect to find in someone with Jacob’s syndrome? a. XYY d. X b. Trisomy-21 e. XXX c. XXY 16. Amniocentesis was performed on a woman. The withdrawn fluid underwent biochemical analysis and the fetal cells were cultured. A karyotype was done. The child was discovered to have an extra #21 chromosome. What is the diagnosis? a. Down Syndrome d. Triplo-X Syndrome b. Turner’s Syndrome e. Klinefelter’s Syndrome c. Jacob’s Syndrome 17. Down Syndrome occurs more frequently in gametes produced by parents nearing middle age. A 40-year old woman who discovers she is pregnant and is worried about the possibility of her baby having Down Syndrome should request a. A special diet during pregnancy. b. Training for the care of a Down syndrome child. c. Examination by amniocentesis. d. Karyotypes for herself and her husband. 18. A normal human male would be expected to have how many Barr bodies in his cells? a. 0 c. 2 b. 1 d. 3 19. A normal human female would be expected to have how many Barr bodies in his cells? a. 0 c. 2 b. 1 d. 3 3 Match the following karyotypes with the appropriate disorder. 20. a. Down’s Syndrome b. Edward’s Syndrome c. Cri-du-Chat d. Klinefelter’s Syndrome e. Jacob’s Syndrome f. Patau Syndrome 21. g. Turner’s Syndrome h. Normal female i. Normal male 22. 23. 24. 25. 4